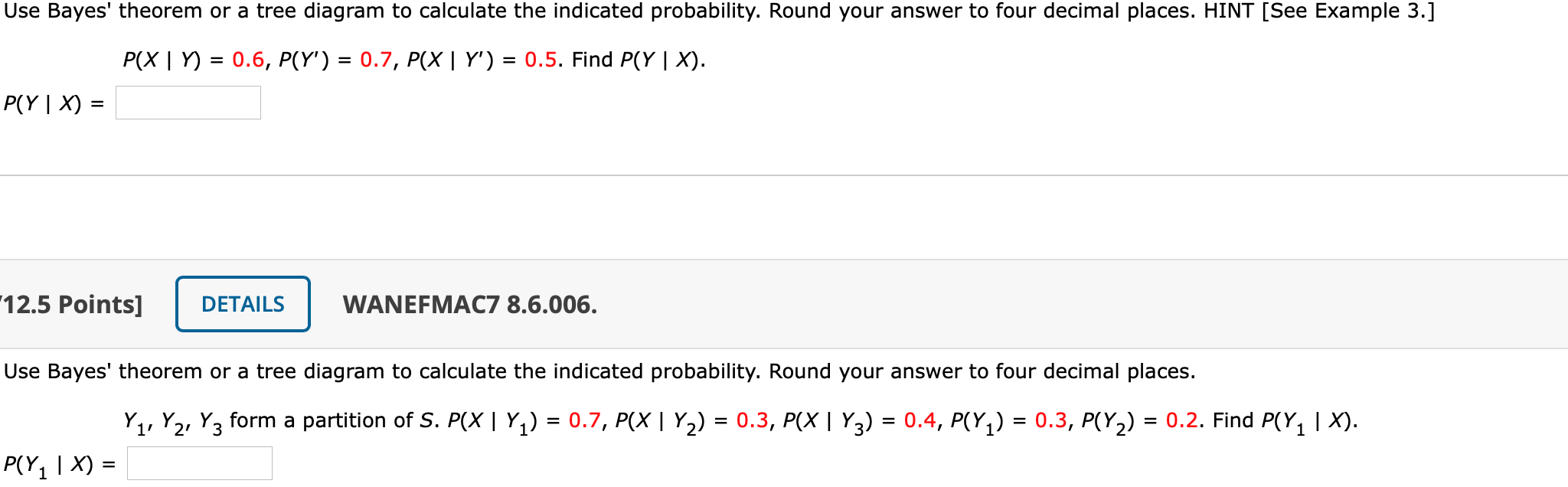
37 bayes theorem tree diagram
Bayes’ Theorem We can draw a tree diagram representing the information we are given. If we choose a touch screen at random from those produced in the factory, we let MA be the event that it came from Machine A and let MB be the event that it came from Machine B. We let D denote the event that the In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem (alternatively Bayes' law or Bayes' rule; recently Bayes–Price theorem: 44, 45, 46 and 67 ), named after Thomas Bayes, describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if the risk of developing health problems is known to increase with age, Bayes' theorem allows ...
Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem. Conditional probability using two-way tables. ... Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted.
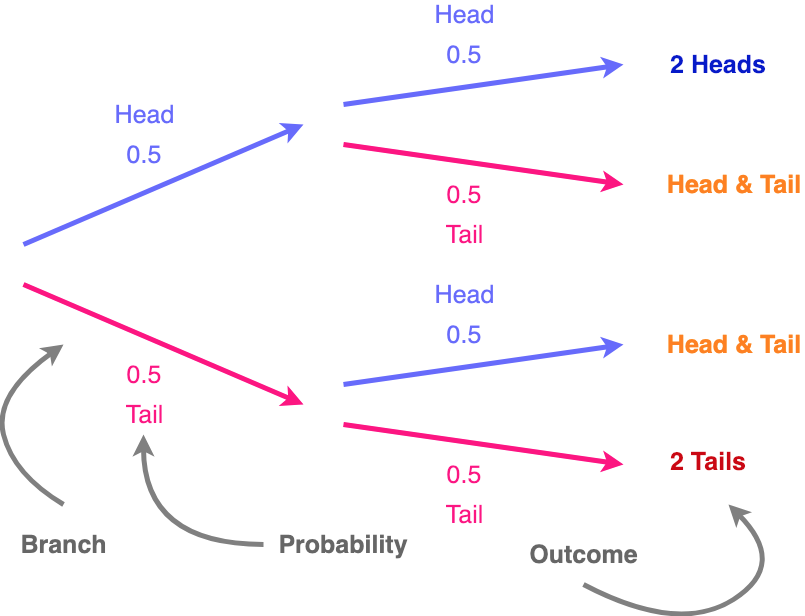
Bayes theorem tree diagram
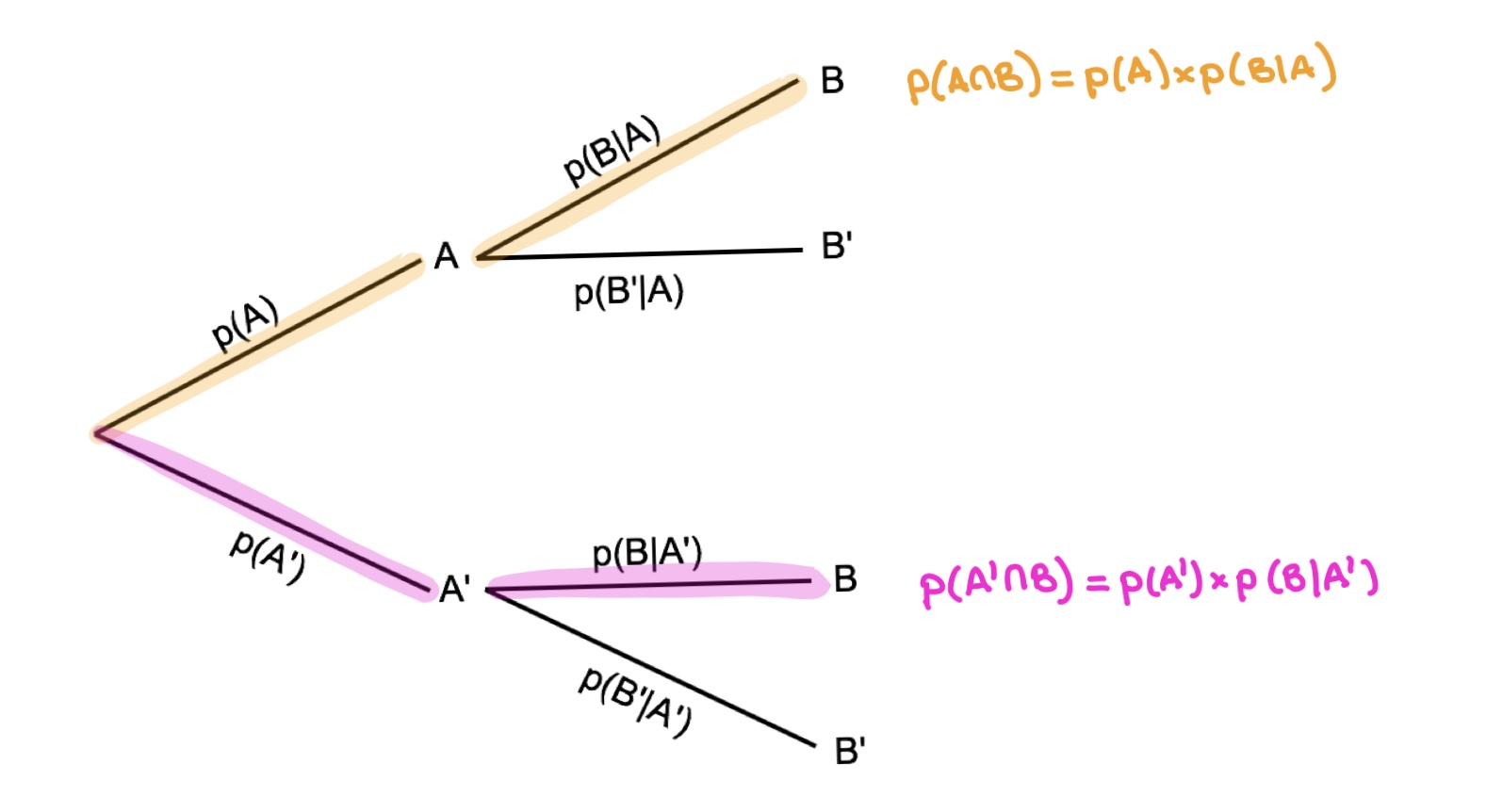
Bayes’ Theorem Bayes’ Theorem, named after the English mathematician Thomas Bayes (1702–1761), is an important formula that provides an alternative way of computing conditional probabilities. Before the formula is given, take another look at a simple tree diagram involving two events and as shown in Figure C.14. FIGURE C.14 Bayes' Theorem is based off just those 4 numbers! Let us do some totals: And calculate some probabilities: the probability of being a man is P(Man) = 40100 = 0.4; the probability of wearing pink is P(Pink) = 25100 = 0.25; the probability that a man wears pink is P(Pink|Man) = 540 = 0.125 Bayesian classification is based on Bayes' Theorem. Bayesian classifiers are the statistical classifiers. Bayesian classifiers can predict class membership probabilities such as the probability that a given tuple belongs to a particular class. Baye's Theorem. Bayes' Theorem is named after Thomas Bayes. There are two types of probabilities −
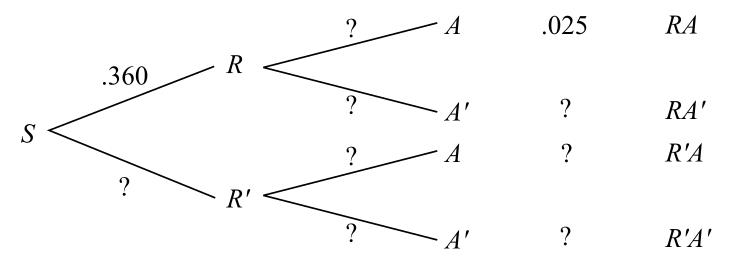
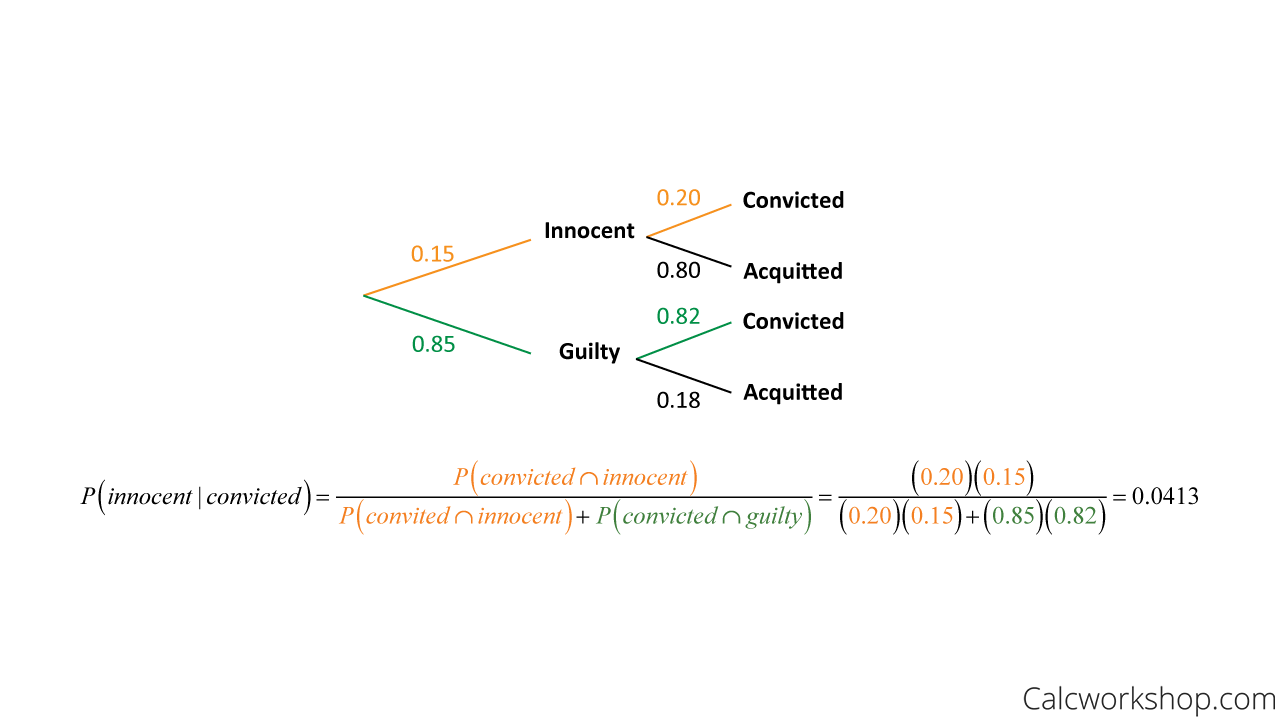
Bayes theorem tree diagram. Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem. This is the currently selected item. Conditional probability using two-way tables. Practice: Calculate conditional probability. Conditional probability and independence. Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent ... Bayes theorem tree diagram. Ask Question Asked 6 months ago. Active 7 days ago. Viewed 153 times 2 $\begingroup$ A bag I contain $4$ white and $6$ black balls while another Bag II contains $4$ white and $3$ black balls. One ball is drawn at random from one of the bags, and it is found to be black. Sep 25, 2020 · Bayes Theorem Tree Diagram. Now, we are ready to answer the question, “supposing a defendant is convicted, find the probability the defendant is innocent.” All this means is that we are being asked to find the probability of innocence, given conviction. So, we will use Bayes’ Rule while working backward along our tree branches, as ... Bayes’ theorem describes the probability of occurrence of an event related to any condition. It is also considered for the case of conditional probability. Bayes theorem is also known as the formula for the probability of “causes”. For example: if we have to calculate the probability of taking a blue ball from the second bag out of three different bags of balls, where each bag contains ...
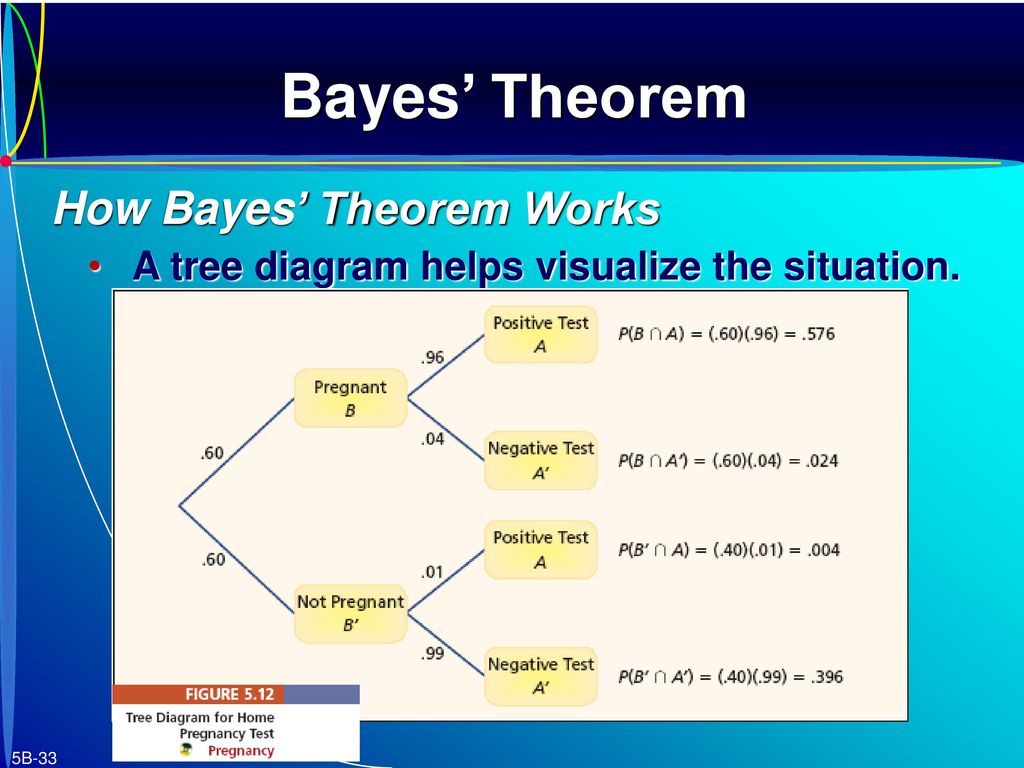
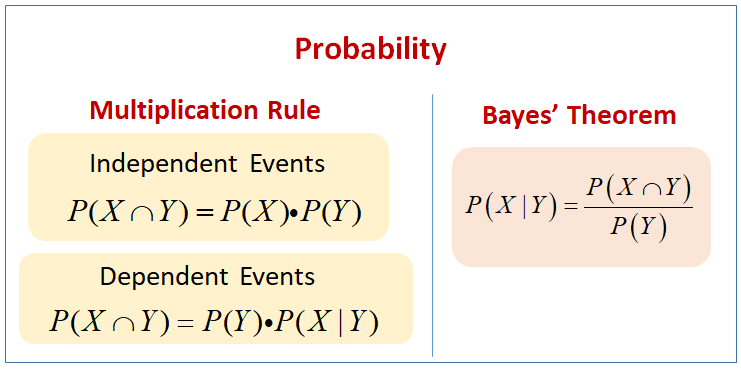
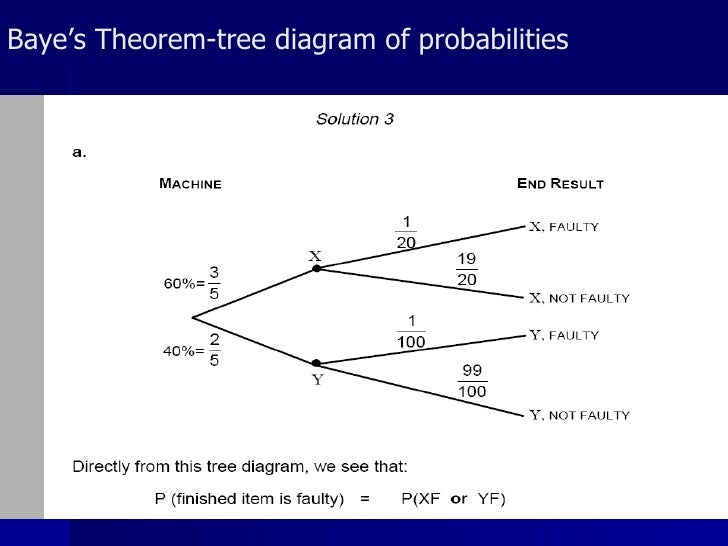
Bayes’ Theorem Bayes' Theorem The Bayes theorem (also known as the Bayes’ rule) is a mathematical formula used to determine the conditional probability of events. Mutually Exclusive Events Mutually Exclusive Events In statistics and probability theory, two events are mutually exclusive if they cannot occur at the same time. Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures!In this video I will calculate a numeric answer to the “tree diagram” method of finding th... Bayes' 5: Bayes Theorem and Tree Diagrams There is another more intuitive way to perform Bayes' Theorem problems without using the formula. That is, using a Tree Diagram. If you look at how a tree diagram is created, these are really conditional probabilities. If we want to determine a conditional probability, the formula is 𝑃( | )= A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the ...
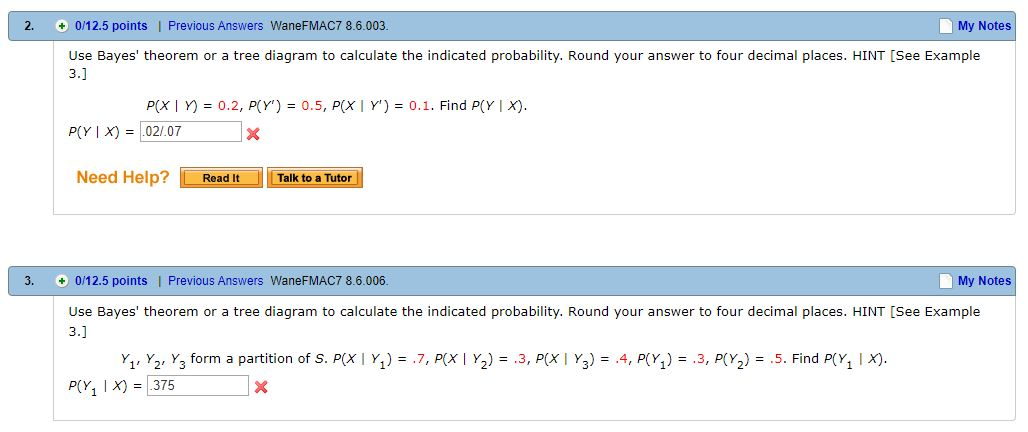
Mar 14, 2017 · The Bayes theorem describes the probability of an event based on the prior knowledge of the conditions that might be related to the event. If we know the conditional probability , we can use the bayes rule to find out the reverse probabilities . The Bayes’ theorem is given by . Bayes’ theorem can be derived from the multiplication law . Bayes’ Theorem can also be written in different forms . Bayes' Theorem Formulas The following video gives an intuitive idea of the Bayes' Theorem formulas: we adjust our perspective (the probability set) given new, relevant information. the tree diagram. Please do so when you try to do them, or when you read the solutions {draw the diagram to try to follow what’s happening. 2. solutions Exercise 1. A doctor is called to see a sick child. The doctor has prior information that 90% of sick children in that neighborhood have the u, while the other 10% are sick with 1 Use of Bayes' Thereom Examples with Detailed Solutions. Example 1 below is designed to explain the use of Bayes' theorem and also to interpret the results given by the theorem. Example 1 One of two boxes contains 4 red balls and 2 green balls and the second box contains 4 green and two red balls. By design, the probabilities of selecting box 1 ...
Conditional Probability, Independence and Bayes’ Theorem. Class 3, 18.05 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom. 1 Learning Goals. 1. Know the definitions of conditional probability and independence of events. 2. Be able to compute conditional probability directly from the definition. 3.
Bayesian classification is based on Bayes' Theorem. Bayesian classifiers are the statistical classifiers. Bayesian classifiers can predict class membership probabilities such as the probability that a given tuple belongs to a particular class. Baye's Theorem. Bayes' Theorem is named after Thomas Bayes. There are two types of probabilities −
Bayes' Theorem is based off just those 4 numbers! Let us do some totals: And calculate some probabilities: the probability of being a man is P(Man) = 40100 = 0.4; the probability of wearing pink is P(Pink) = 25100 = 0.25; the probability that a man wears pink is P(Pink|Man) = 540 = 0.125
Bayes’ Theorem Bayes’ Theorem, named after the English mathematician Thomas Bayes (1702–1761), is an important formula that provides an alternative way of computing conditional probabilities. Before the formula is given, take another look at a simple tree diagram involving two events and as shown in Figure C.14. FIGURE C.14

















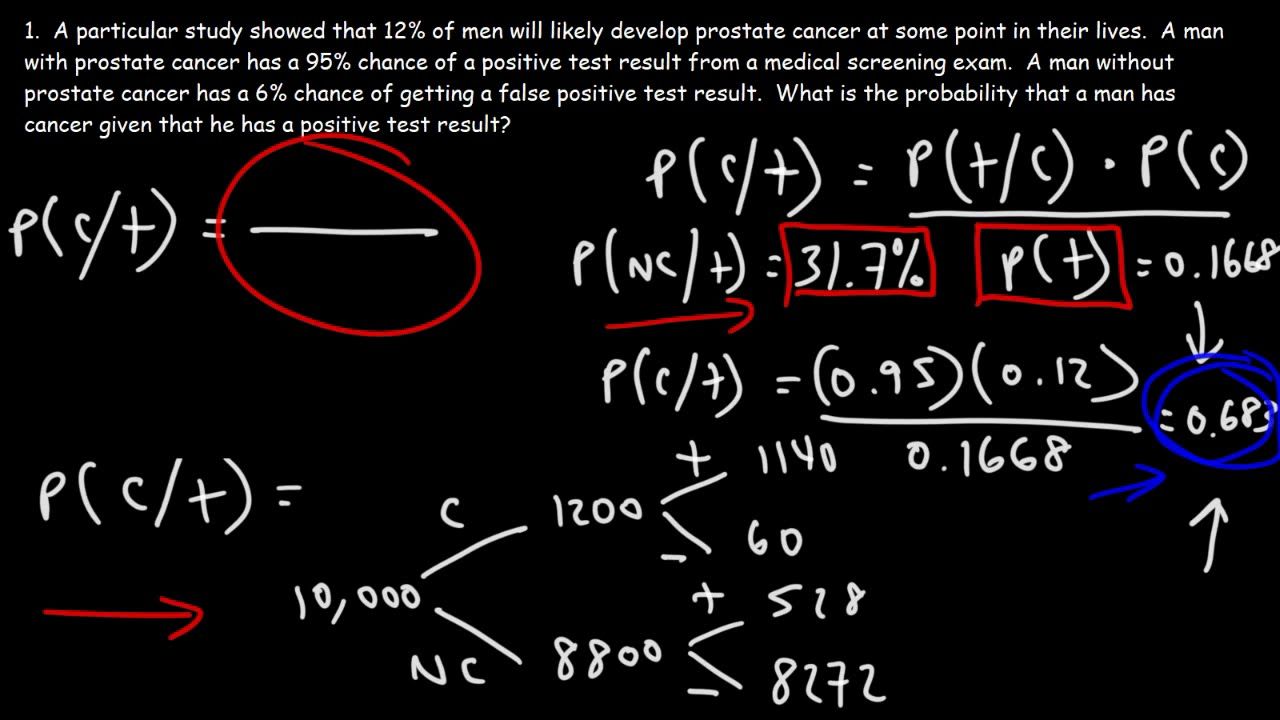
0 Response to "37 bayes theorem tree diagram"
Post a Comment