39 exothermic reaction coordinate diagram
Hey All, I'm new to the forum here and a struggling O-Chem student. I'm taking OChem 1, and although I do enjoy it, I'm still timid about my answers. I'm doing a test review problems, and I was wondering if I could get some help to verify my answers. I'm not hundred percent sure, and any inputs would be greatly appreciated. Anything that isn't clear, too vague, etc. Thank you in advance! :) (**4**). Explain why free radical halogenation produces racemic mixtures of products. -Because the ra... As shown by the top reaction in the following diagram, this cyclobutanol (R 1 = R 2 = CH 3) may then undergo a facile base-catalyzed retroaldol fragmentation to a 1,5-diketone. This sequence thus achieves the attachment of a short alkyl chain to each carbon atom of the double bond. Further base induced reactions, such as epimerization of the initial cis-configuration, and aldol cyclization of ...
Nov 20, 2021 · Exothermic Reaction Coordinate Diagram Exothermic Reaction Illustration - Twinkl Exothermic Vs Exergonic Reactions: Know the difference Exothermic and Endothermic ...
Exothermic reaction coordinate diagram
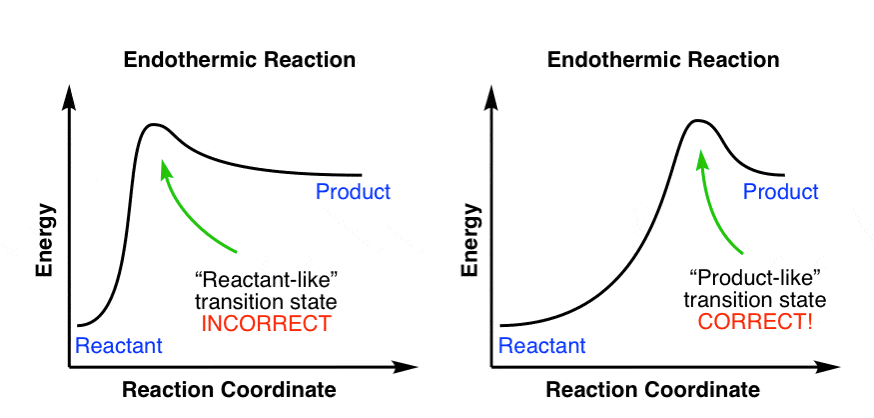
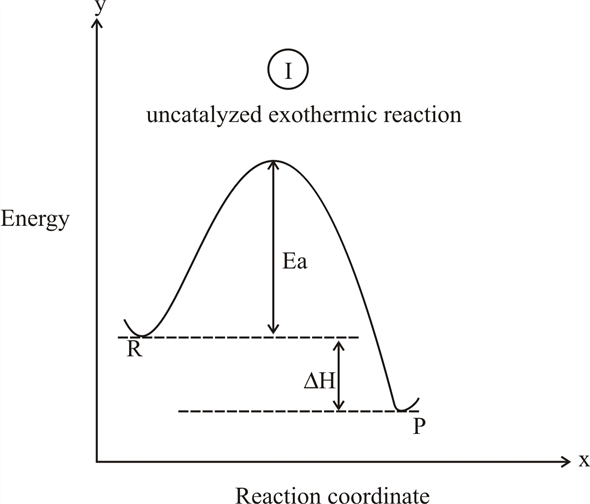
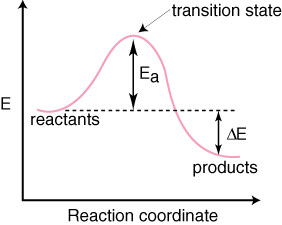
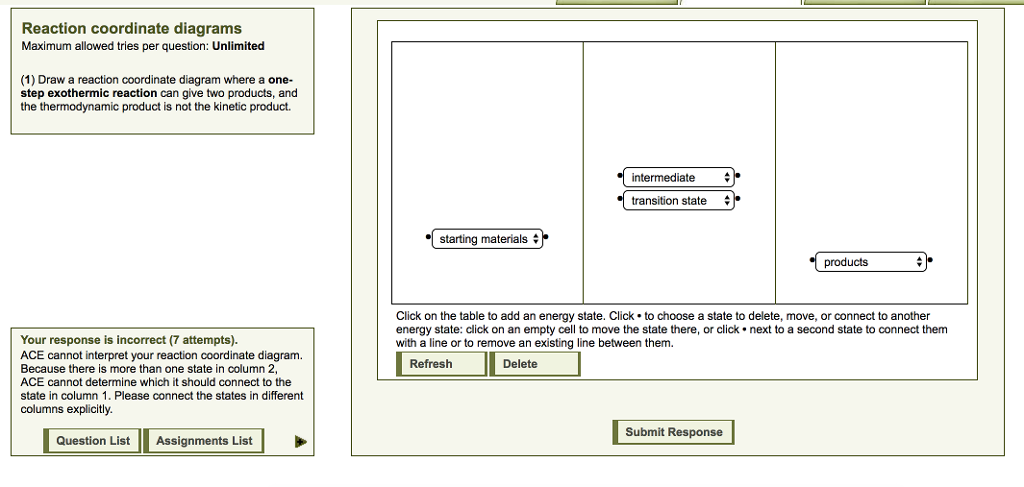
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Let's consider a general reaction where a reactant or set of reactants, A, is transformed into a product or set of products, B. The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction (heat is given off ... Exothermic Reactions : Energy Release! 2 C 8 H 18 + 25 O 2 → 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 O! Burning Gasoline (Octane)" Exothermic Reactions : Energy Release! An Exothermic (Exergonic) Reaction! 2 C 8 H 18 + 25 O 2 → 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 O! ΔGoo = (-)! Burning Gasoline (Octane)" Exothermic Reactions : Energy Release! Δ H! 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 O! (Products are all the same.)!! 2 C 8 H 18 + 25 O 2 → 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants.
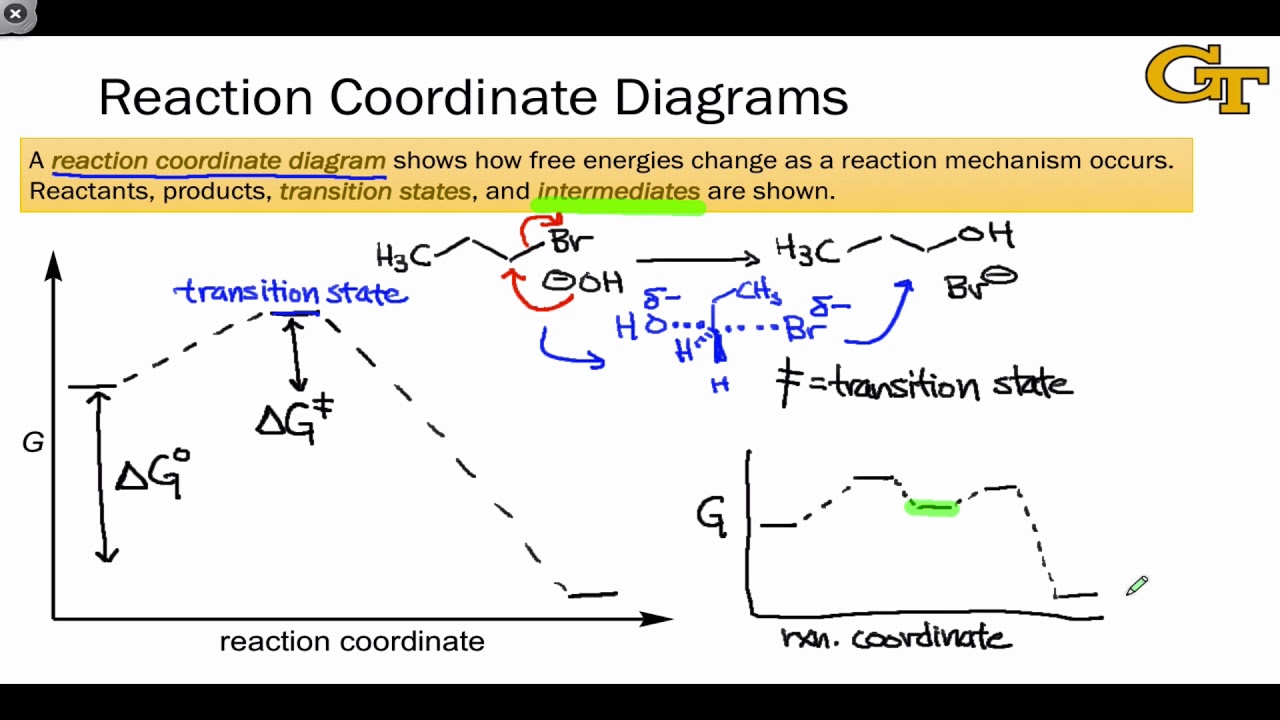
Exothermic reaction coordinate diagram. The energy level diagram for the reaction of hydrogen with chlorine to form hydrogen chloride gas. Exothermic reaction. In an exothermic reaction, the reactants are higher in energy than the products ; The reactants are therefore closer in energy to the transition state; This means that exothermic reactions have a lower activation energy compared to endothermic reactions . The energy level ... For a chemical reaction or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical representation of a single energetic pathway, ... Reaction coordinate Transition state ΔG 1 ‡ ΔG 1 ‡' ΔG –1 ‡' ΔG –1 ‡ ΔG° G A G P Initial state Final state Fig. 4.2 A free energy (G) diagram for a simple reversible exothermic reaction A↔P(solid and broken lines). G A and G P represent the average free energies per mole for the reactant A and the product P, the initial and final states respectively. The standard state ... An enthalpy diagram allows us to easily see details of a chemical reaction. By knowing how to draw and label an enthalpy diagram we can see what the starting energy level is, how much energy is ...
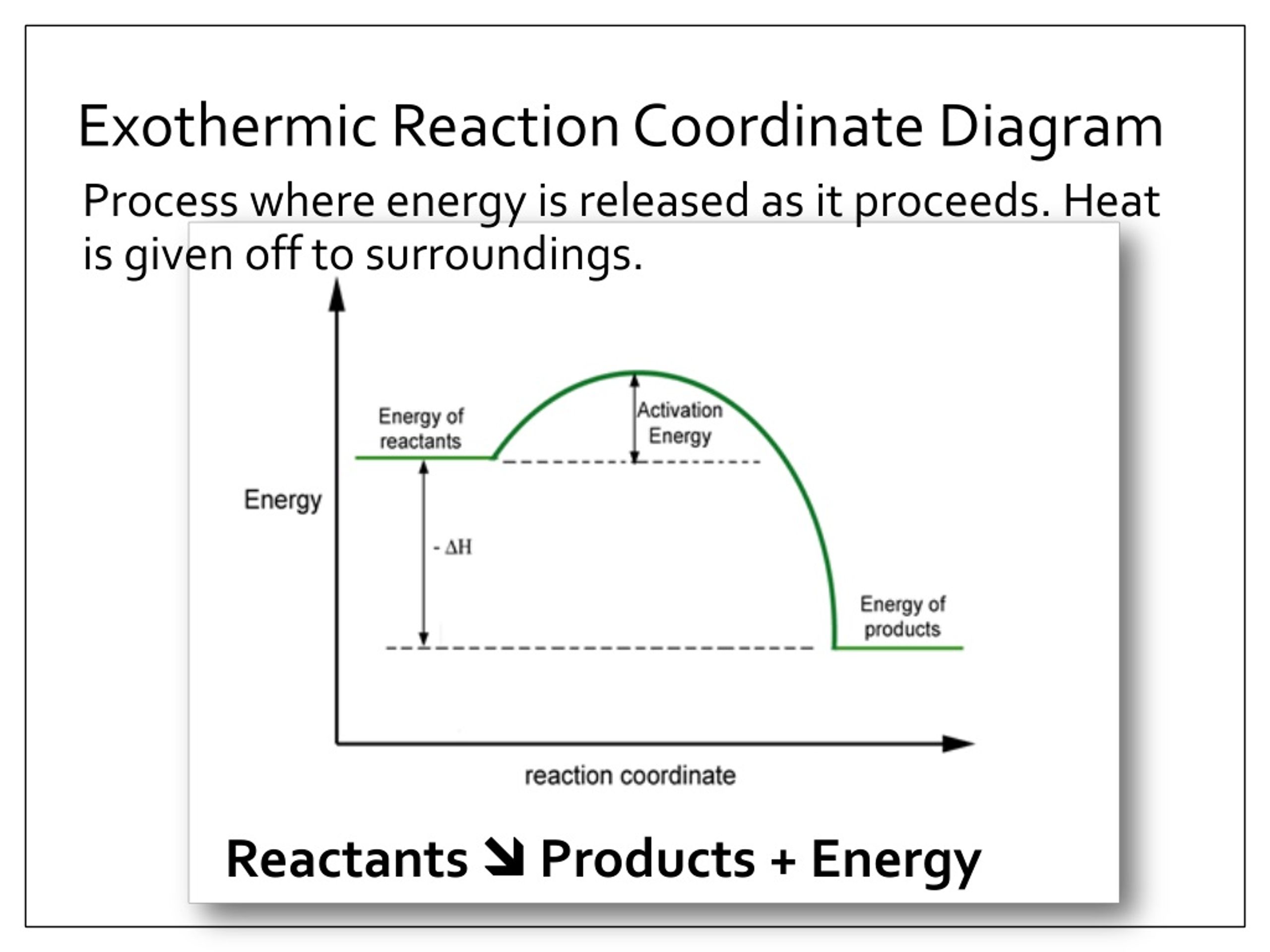
Reaction Enthalpy If ∆Hreaction is negative, energy is given off. –“Exothermic” If ∆Hreaction is positive, energy is absorbed. –“Endothermic” We can NOT predict whether a reaction will occur based only on ∆H! Energy Diagram E n t h a l p y “Reaction Coordinate” Ea … 20.07.2017 · Figure 01: The reaction-coordinate diagram for an exothermic chemical reaction. The above image shows a reaction-coordinate diagram for a particular chemical reaction. In this reaction, the reactants have a high potential energy than the products. Therefore, during the progression of this reaction, excess energy is released to the surrounding. What are Products. Products are substances … Hey All, I'm new to the forum here and a struggling O-Chem student. I'm taking OChem 1, and although I do enjoy it, I'm still timid about my answers. I'm doing a test review problems, and I was wondering if I could get some help to verify my answers. I'm not hundred percent sure, and any inputs would be greatly appreciated. Anything that isn't clear, too vague, etc. Thank you in advance! :) (**4**). Explain why free radical halogenation produces racemic mixtures of products. -Because the ra... Reaction coordinate diagram for an exothermic reaction. 3.7.2.1 First principle–based approaches3.7.2.1.1 Transition State Theory. The power of DFT is well established. However, so far we have mostly concentrated on estimating global energy minima of a compound using this method, which refers to calculations performed at 0 K. However, 0 K is excessively cold for reactions to take place. …
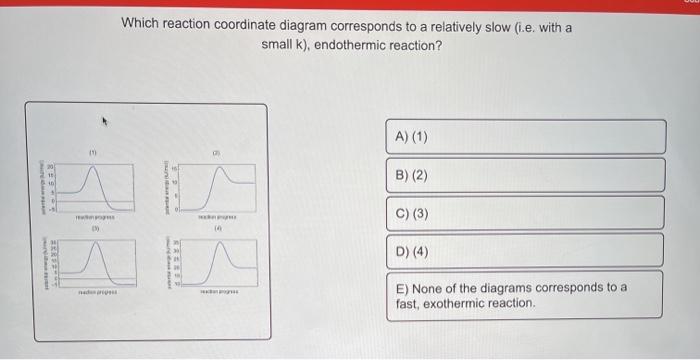
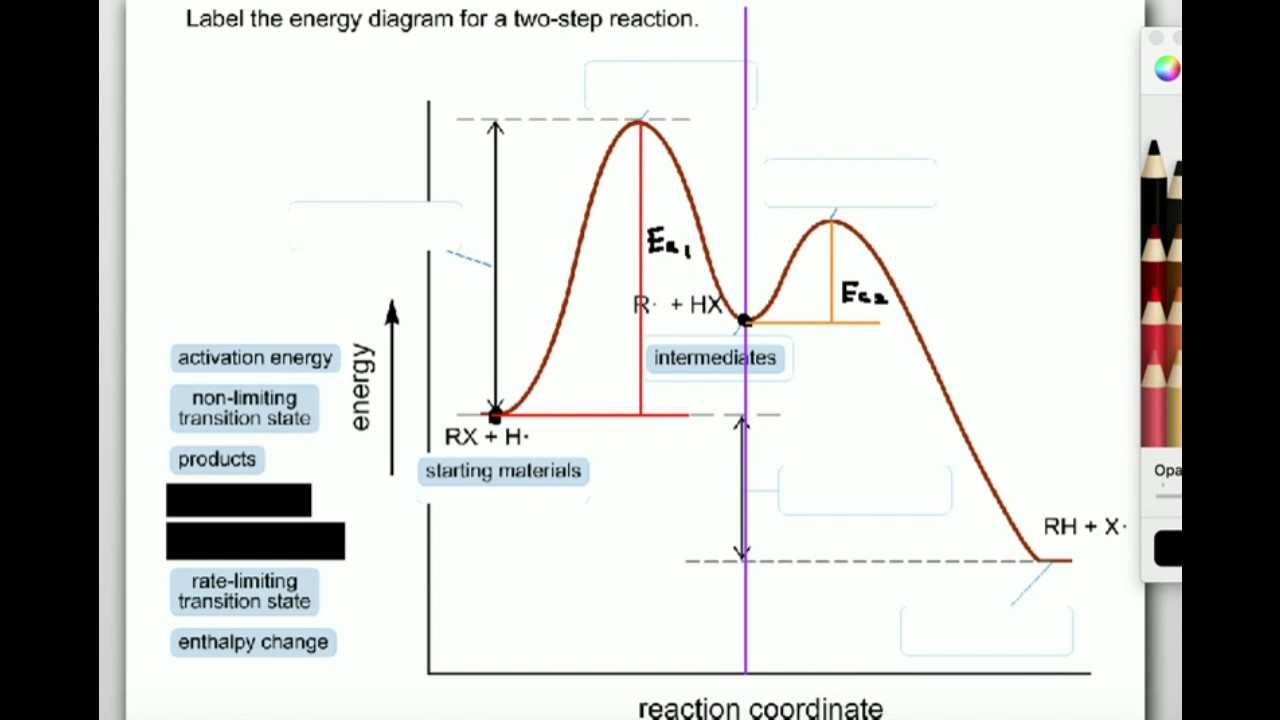
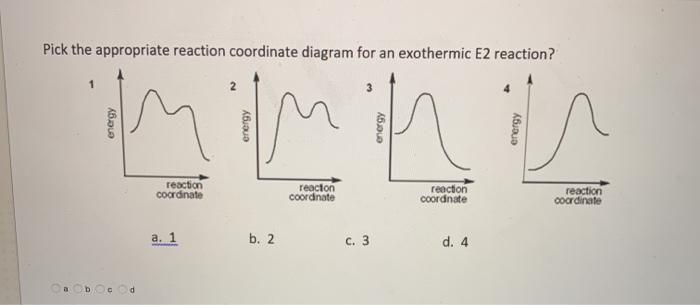
We can draw a coordinate diagram from a mechanism with more than one step, if we know the RATES of each step, and the ENTHALPY of the reaction… The LARGER the E A, the SLOWER the reaction, so the RATE DETERMINING STEP should have the HIGHEST E A. FASTER ’ssteps should have . LOWER E. A, with the . FASTEST. having the . LOWEST. If . EXOTHERMIC, H. reacts > H. prods. If Chemical Reaction: A transformation ... coordinate covalent bonding of a phosphorous Lewis base to a boron Lewis acid creates a complex in which the formal charge of boron is negative and that of phosphorous is positive. In this complex, boron acquires a neon valence shell configuration and phosphorous an argon configuration. If the substituents (R) on these atoms are not large, the complex ... 17 Oct 2019 — 6.7: Reaction Coordinate Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism ... Since exothermic reactions are energetically (thermodynamically) ... Reaction Coordinate. En e rg y reactant A product B transition state (TS‡). -AHo. Exothermic reaction. Early TS‡. The Hammond Postulate ...12 pages
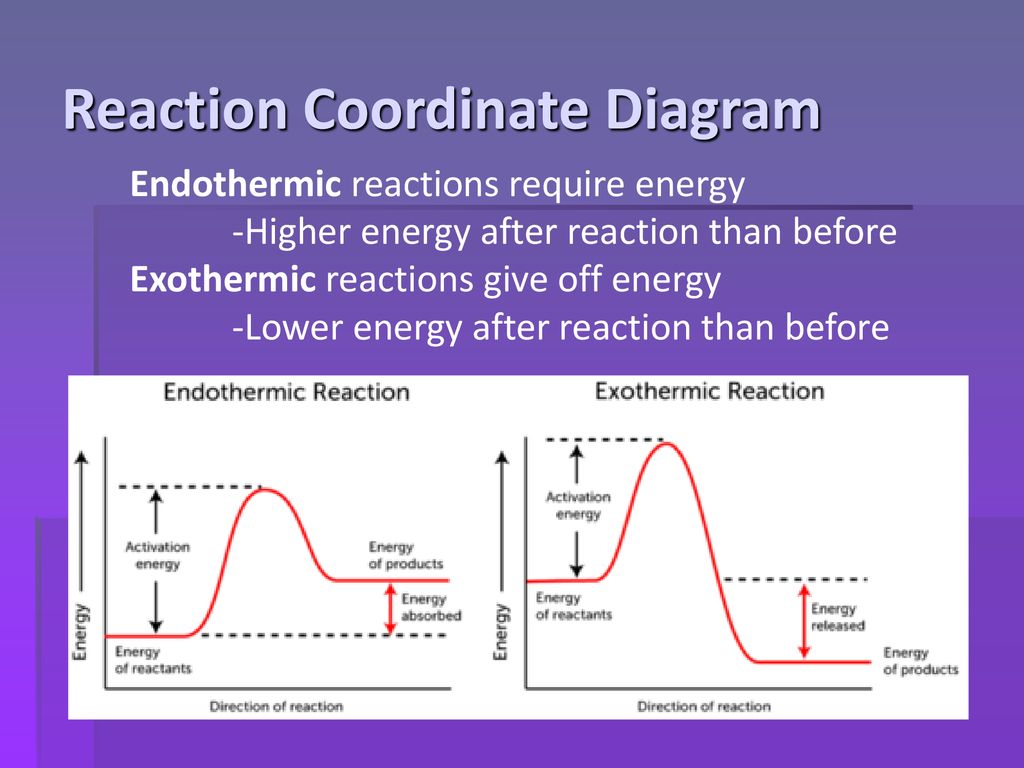
In the case of an endothermic reaction, the reactants are at a lower energy level compared to the products—as shown in the energy diagram below. In other words, ...
Hey All, I'm new to the forum here and a struggling O-Chem student. I'm taking OChem 1, and although I do enjoy it, I'm still timid about my answers. I'm doing a test review problems, and I was wondering if I could get some help to verify my answers. I'm not hundred percent sure, and any inputs would be greatly appreciated. Anything that isn't clear, too vague, etc. Thank you in advance! :) (**4**). Explain why free radical halogenation produces racemic mixtures of products. -Because the ra...
Endothermic Versus Exothermic Reactions ... An endothermic reaction is one where at the end of the reaction, energy is put into the molecule instead of released.

45 The Following Reaction Coordinate Diagramrepresentsenergyproductsreactantsreaction Pathway 1 An Brainly In
I am confused on whether in a reaction coordinate diagram, does the difference between the reactants and products equal deltaH or deltaG I have seen graphs that demonstrate both. If some could explain that would be great!   for reference this khan article states it as deltaH: https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/chemical-processes/thermochemistry/a/endothermic-vs-exothermic-reactions   This khan article states it as deltaG: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biolog...
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time. Reaction rates can vary dramatically. For example, the oxidative rusting of iron under Earth's atmosphere is a slow reaction that can take many ...
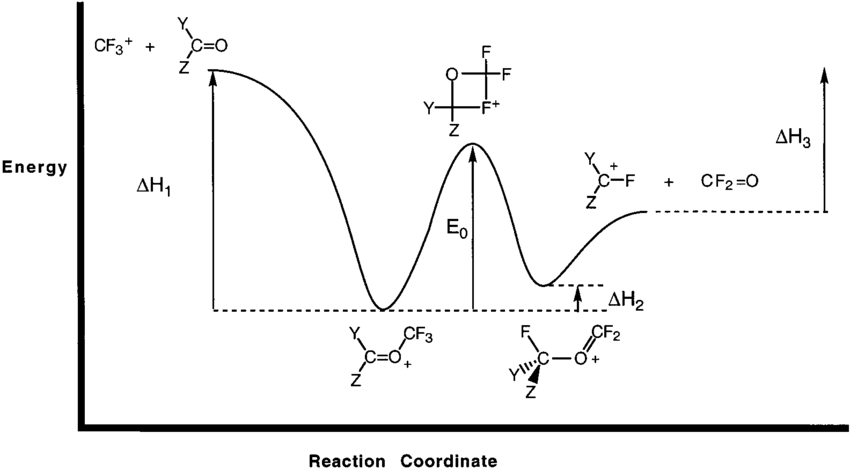
Diagram. The reaction coordinate diagram is represented below: Things to note. ΔH represents the difference between enthalpy of reactants and products. Ea1 and Ea2 represent the activation energy for step 1 and step 2 in the reaction. The step with the highest activation energy is the slowest step reaction. The step with the lowest activation energy is the fastest step in the reaction.
The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants.
Exothermic Reactions : Energy Release! 2 C 8 H 18 + 25 O 2 → 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 O! Burning Gasoline (Octane)" Exothermic Reactions : Energy Release! An Exothermic (Exergonic) Reaction! 2 C 8 H 18 + 25 O 2 → 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 O! ΔGoo = (-)! Burning Gasoline (Octane)" Exothermic Reactions : Energy Release! Δ H! 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 O! (Products are all the same.)!! 2 C 8 H 18 + 25 O 2 → 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Let's consider a general reaction where a reactant or set of reactants, A, is transformed into a product or set of products, B. The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction (heat is given off ...






















0 Response to "39 exothermic reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment