39 mo diagram for hf
6. Use the MO diagram to predict where the electron density in the HF bond lies, closer to the H atom or closer to the F atom? Explain. 7. Now draw the Lewis structure for HF. 8. Using the Lewis structure you drew in Q7 and the MO diagram above, how do the 2 models for bonding (Valence bond theory and MO theory) compare for the HF molecule? Wiha‘s vast collection of screwdrivers offers the variety and sizes for all tool connoisseur alike. From Precision sets to Insulated sets, there’s a driver for your job.…
The highest occupied molecular orbital (or HOMO) is the σ *2s MO. Bond order is defined as the number of electrons in bonding MOs minus the number of electrons ...3 answers · 33 votes: The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation ...

Mo diagram for hf
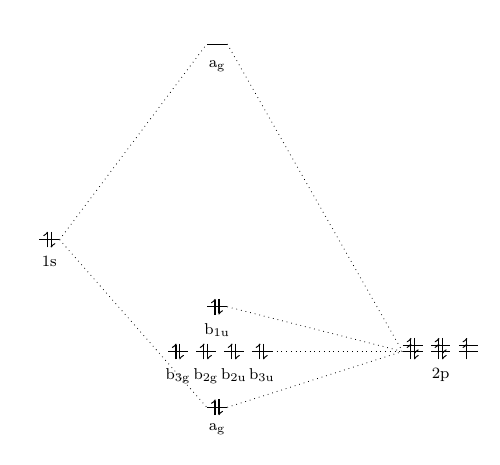
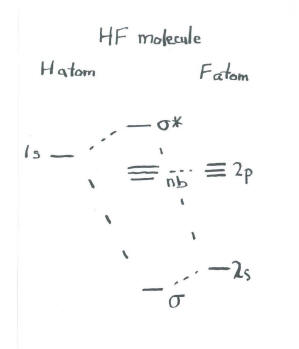
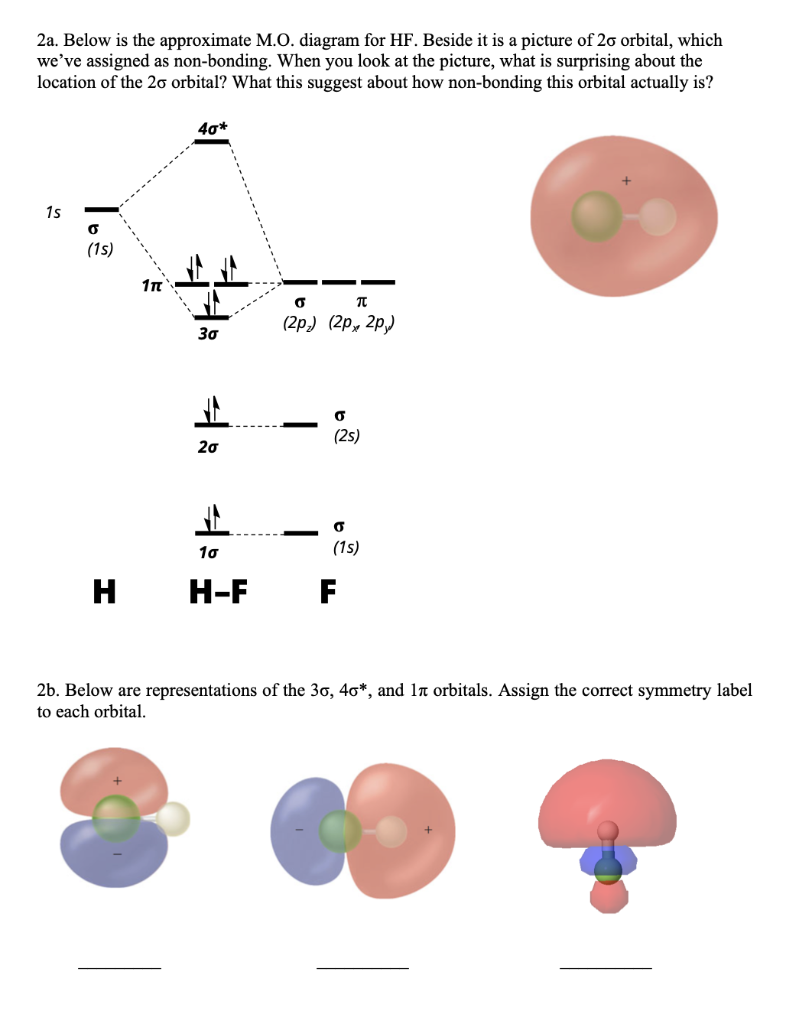
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih. We shall consider the molecular orbitals in LiH, CH and HF to illustrate how molecular orbital theory describes the bonding in heteronuclear molecules, and to. and 2p orbitals, but that is not how sodium chloride is made. Sodium atoms are Construct an MO diagram for LiH and suggest what type of bond it might have. Molecular orbital diagram for the hf molecule interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma bonding and a sigma antibonding molecular orbital as shown below. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of hf molecule will not be symmetrical. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Mo diagram for hf. Jul 19, 2021 · The third major category of elements arises when the distinguishing electron occupies an f subshell. The first example occurs in the case of the lanthanoids (elements having atomic numbers between 57 and 71).The lanthanoids have the general electron configuration [Kr]4d 10 4f i 5s 2 5p 6 5d 0 or 1 6s 2. where i is a number between 0 and 14. Thus in the building-up process for the lanthanoids ... Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... Nov 06, 2021 · 1971 Chevelle Wiring Diagram free download - Automotive Wiring Diagram ECM Wiring Diagram Electrical Wiring Diagram and many more programs. Decoding Chevrolet VIN, trim tags, cowl tags, engine, engine block casting numbers, 1971 Chevelle Fisher Body Number Plate (a. 5 new Mustang Tag Decoder results have been found in the last 90 days, which ...
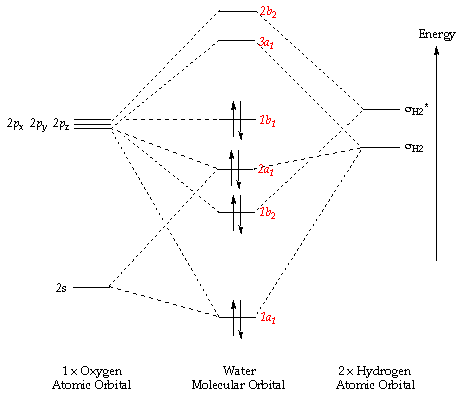
Drawn below is an incomplete molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the molecule HF. a. b. c. d. (3 pts.) Label the atomic orbitals.3 pages 1 answerIt is a diatomic molecule that contains two different atoms in which one is more electronegative. And the one which is more electronegative will have lower ... molecular orbital diagram as a non-bonding molecular orbital. 7. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. sp Hybrid Orbitals in BeH2 1. The Lewis structure shows that the beryllium in BeH 2 makes 2 bonds and has no lone pairs. It is a linear molecule. Chemistry 104 ... Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
35 Molecular Orbital Diagram For Hf Worksheet Cloud. Savvy Chemist Chemical Bonding 3 Bond Hybridisation. Filemo Diagram Co2svg Wikipedia. Molecular Orbital Diagrams 101 Diagrams. Concentrations Of Dissolved Methane Ch4 Nmol L 1 In. Methane Molecular Orbitals Methane Ch4 Molecular. corresponding diagram for HF. How will the diagrams differ? Characterize the HOMO and LUMO as antibonding, bonding, or nonbonding. The diagrams differ in the relative energies of the AOs involved and in that there are nonbonding valence electrons on the OH radical, whereas there are none on HF. The HOMO is the 1π, which is a nonbonding MO. The ... The next molecule in the series HF, H2O and H3N, is H4C (methane) - which was discussed earlier - and unlike the other three molecules has no non-bonding ... In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a separate signal called the modulation signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images ...
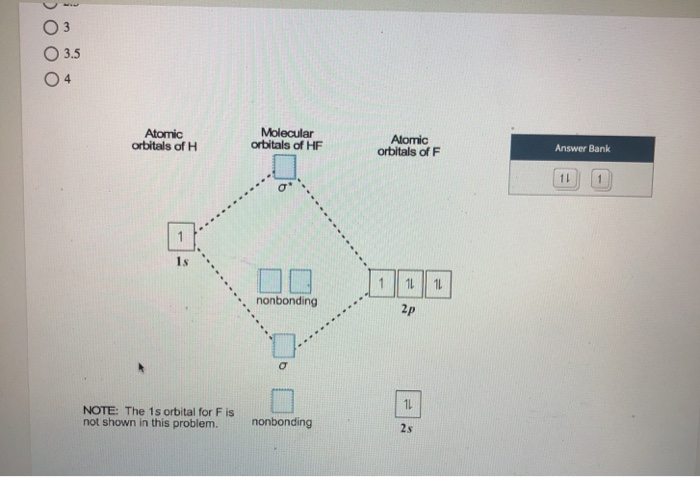
The MO diagram for the HF molecule below will include only valence electrons of Hand F. Indicate on the diagram below atomic orbitals of the Hand Fatoms as well as the bonding antibonding and nonbonding orbitals of the HF molecule (i.e. s.p., and where necessary). Add electrons to the diagram Note: While we have not taught you about non bonding ...
The qualitative molecular orbital diagram, as depicted in Fig. 2, also shows the two-center three-electron (2c-3e) σ half-bonding character of HF − (X 2 Σ + ) ...
MOLECULAR ORBITAL APPROACH Basis of VB approach: overlap orbitals in each bond separately. Each bond is LOCALISED between two atoms. In molecular orbital (MO) approach - overlap orbitals for the whole molecule - bonding is therefore DELOCALISED. We will look first at DIATOMIC MOLECULES and only later move on to POLYATOMIC MOLECULES.
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface-CO ...
Answer (1 of 3): The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. As has been already explained ,only a pz orbital is able to combi...
Answer (1 of 2): Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and therefore they cannot mix and form bond. The 3p electrons of Cl have comparable energy with the ...
ZrO2 is Fluorite structured and crystallizes in the cubic Fm-3m space group. The structure is three-dimensional. Zr4+ is bonded in a body-centered cubic geometry to eight equivalent O2- atoms. All Zr–O bond lengths are 2.23 Å. O2- is bonded to four equivalent Zr4+ atoms to form a mixture of edge and corner-sharing OZr4 tetrahedra.
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule.This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one-electron ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Bonding Orbitals In Methane Sp3 Hybrids . Draw the MO diagram for HBr including energy levels each orbitals shape each orbitals character meaning what atomic orbitals contribute to each MO. Hbr mo diagram. Hydrogen bromide HBr is a colorless gas. Molecular Orbital Theory which is used to sketch the ...
Motion graph practice
Yt hf jnftn resume by alarm write a c program illustrating variable scope. Best admission essay writer for hire for mba, cover letter for resume biotechnology make a thesis statement for an expository essay name my Graffiti write write Graffiti my name how to write an iambic pentameter, essay of freedom fighters of india gullivers travel ...
HfO2 is Baddeleyite structured and crystallizes in the monoclinic P2_1/c space group. The structure is three-dimensional. Hf4+ is bonded to seven O2- atoms to form a mixture of distorted corner and edge-sharing HfO7 pentagonal bipyramids. There are a spread of Hf–O bond distances ranging from 2.05–2.26 Å. There are two inequivalent O2- sites.
For atoms from different periods, use the valence atomic orbitals to construct MO's e.g. for HF K F (2s F) 2 (σ b) 2 (π 2p nb) 4 1s 2P x,y,z σ b σ * H F HF 2s 2s F π 2p x,y MO diagram for HF SCF-LCAO-MO Simplest MO treatment, one atomic orbital from each atom: e.g. Ψ = C(1S A + 1S B ) LCAO-MO can include many more AO's.
mo of hfg an advanced molecular orbital diagram of hf for the inorganic or physical chemistry student. Hf Molecular Orbital Diagram - Quantum‐mechanical Condensed Matter Simulations With Crystal Wires. molecular orbital diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in ...
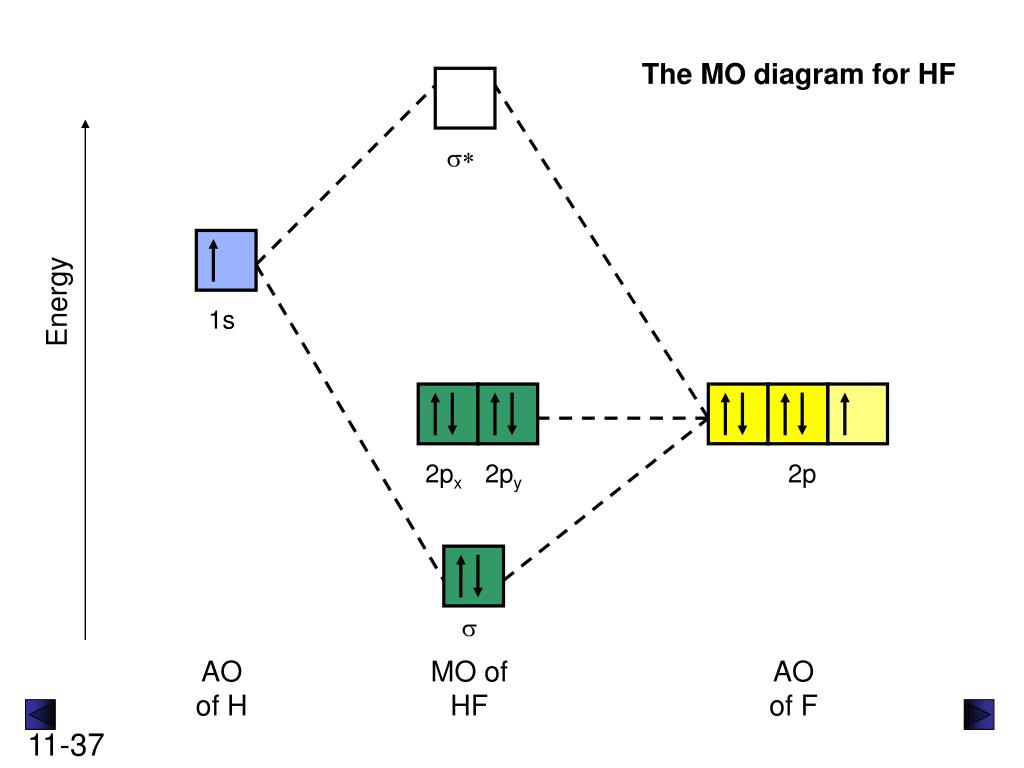
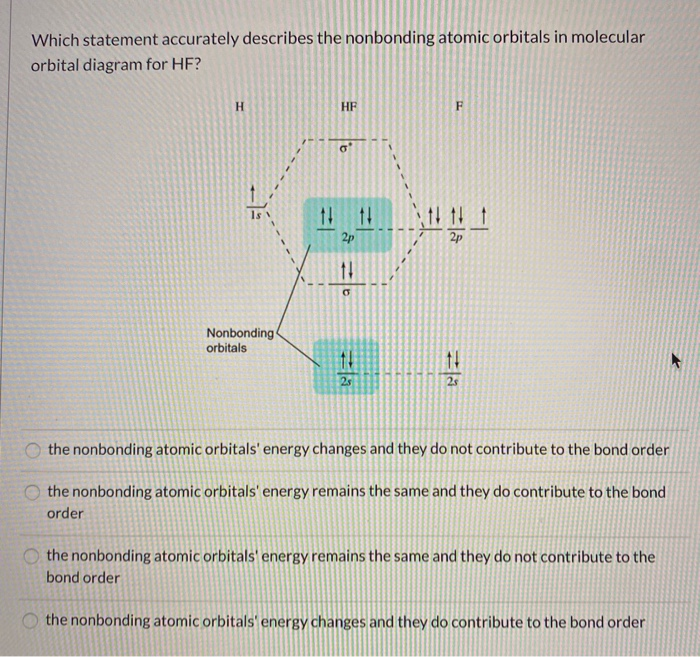
The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
is the valence molecular orbital energy level diagram for HF. You will need to add the electrons again. Use these two diagrams to explain why HBr is a stronger Lewis acid than HF. [4 marks] A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor, so it will accept electrons into its LUMO. The LUMO of HBr is lower in energy than the LUMO of HF, so electrons ...
Since 1s of H and 2px of F will overlap axially ,then the m.o. formed will be sigma bonding and sigma*. Both these electrons will be filled in sigma s-px molecular orbital. Rest atomic orbitals of F will not form any m.o.and will maintain their atomic character. HF = K , (2s2) , (2py2) , (2pz2) , sigma 2px 2 ,sigma spx 2 , sigma* spx0.
An advanced molecular orbital diagram of HF for the inorganic or physical chemistry student.
diagram by adding electrons to the appropriate energy levels. (2 pts.) Determine the bond order for HF. BO = (2 - 0)/2 = 1 H F 2s 2px2py2pz 1s!*! HF e. (2 pts.) Determine the effect that removing an electron would have on the strength of the HF bond. No effect because a nonbonding electron is removed. BO = (2 - 0)/2 = 1 f. (2 pts.)
In this screencast, Andrew Burrows walks you through how to construct the MO energy level diagram of HF. http://ukcatalogue.oup.com/product/9780199691852.do#...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves).
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
MO Theory • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection.
The HF electron configuration reflects that the other electrons remain in three lone pairs and that the bond order is one. While MOs for homonuclear diatomic molecules contain equal contributions from each interacting atomic orbital, MOs for heteronuclear diatomics contain different atomic orbital contributions.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Molecular orbital diagram for the hf molecule interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma bonding and a sigma antibonding molecular orbital as shown below. The molecular orbitals formed in the case of hf molecule will not be symmetrical.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih. We shall consider the molecular orbitals in LiH, CH and HF to illustrate how molecular orbital theory describes the bonding in heteronuclear molecules, and to. and 2p orbitals, but that is not how sodium chloride is made. Sodium atoms are Construct an MO diagram for LiH and suggest what type of bond it might have.






















0 Response to "39 mo diagram for hf"
Post a Comment