34 construct the molecular orbital diagram for h22– and then identify the bond order.
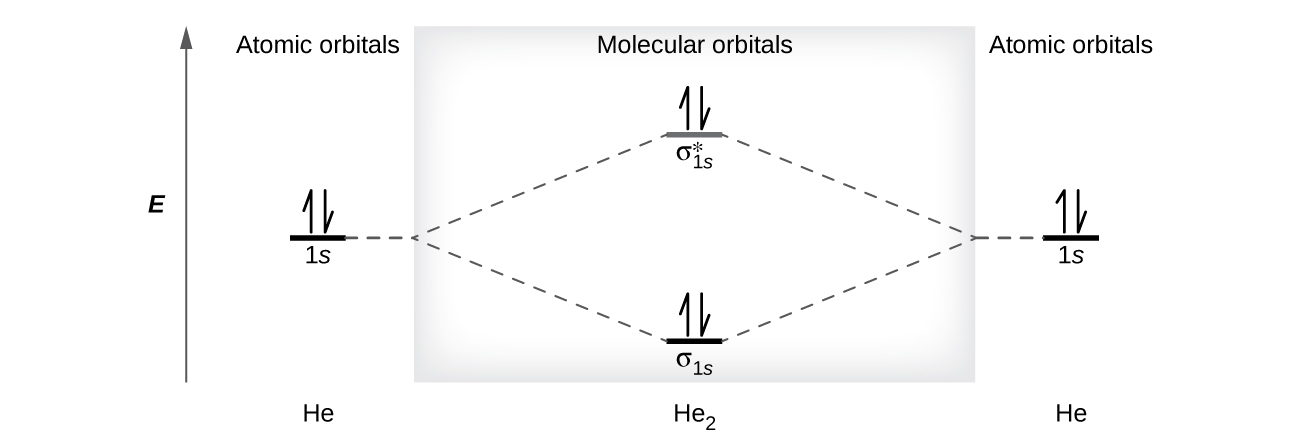
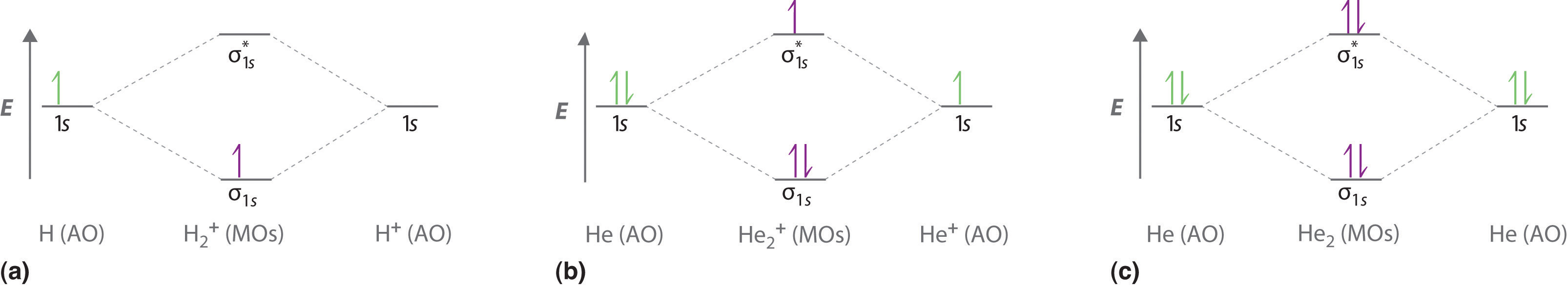
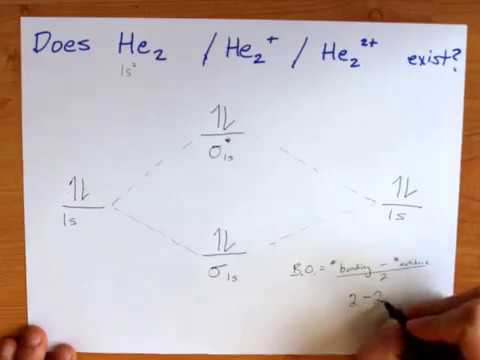
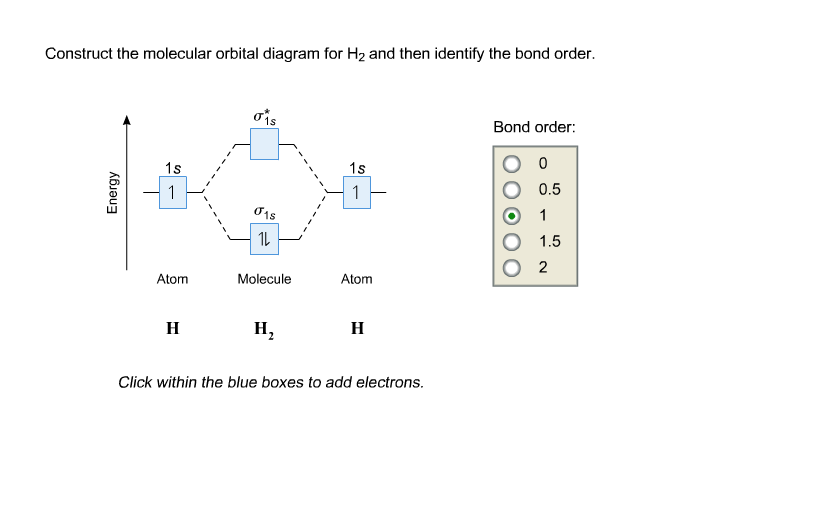
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2. The procedure can be introduced by considering the h2 molecule. Description of the molecular orbitals of the h2 molecule with an introduction to molecular orbital diagrams. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+.
Problem Details. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Bond order: a) 0. b) 0.5. c) 1. d) 1.5. e) 2.

Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h22– and then identify the bond order.
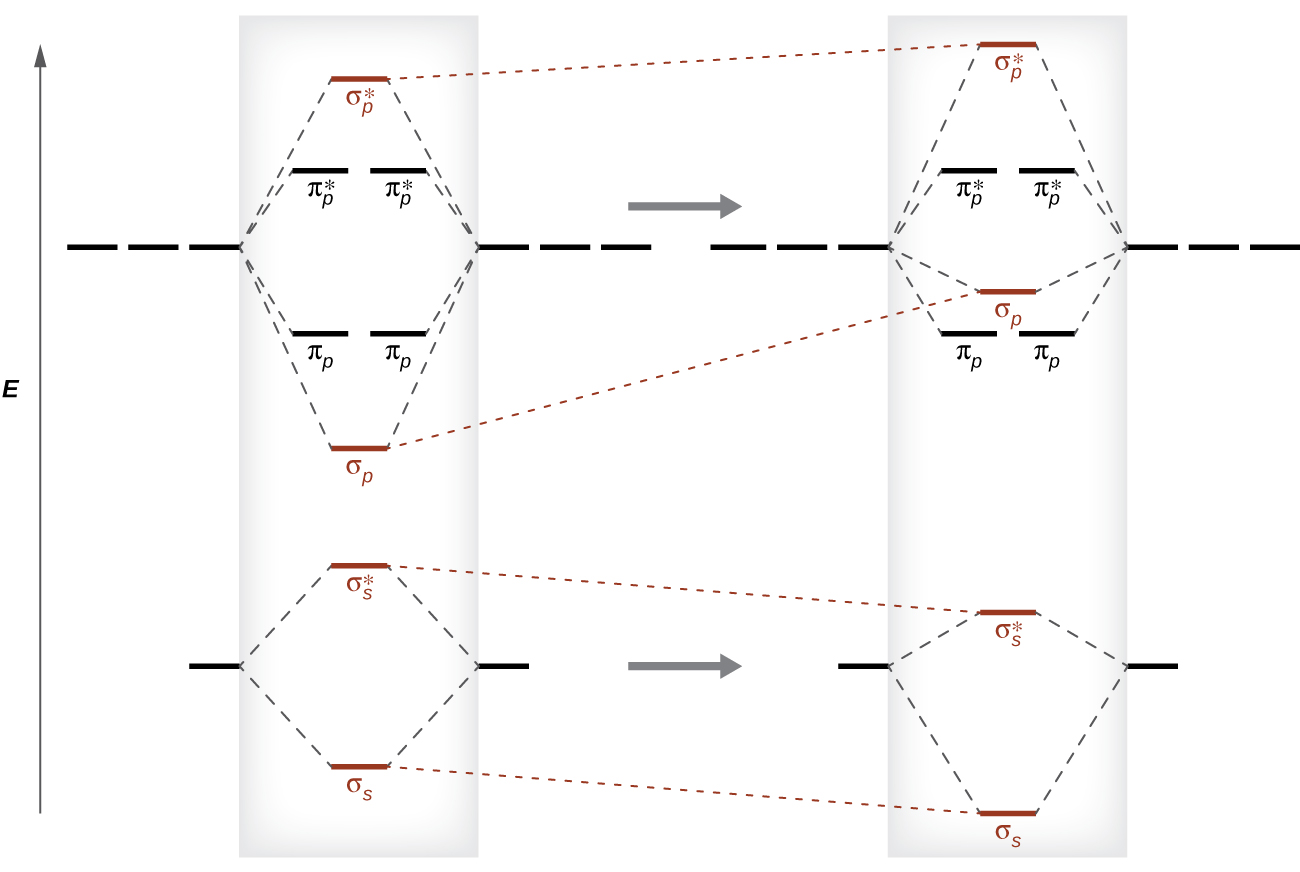
Bond order and the molecular orbital of the diagram is given below. bond order Energy He atom He atom oooo He2 Molecule Atom Atom Explanation Common mistakes Bond order of the given molecule (He) has been calculated by using the bond order formula with the help of molecular orbital diagram. Bond order calculation: B.O=}(B.E - A.B.E) where, B ... Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h22– and then identify the bond order.. This problem has been solved! A.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^2+ and then identify the bond order. B.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. C.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^- and then identify the bond order. D.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^+ and then ... Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. 100% (32 ratings) Bond …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He22+ and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Previous question Next question. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H22+ And Then Identify The Bond Order. Thanks Question: Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H22+ And Then Identify The Bond Order.
Problem Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 + and then identify the bond order. Since both molecular ions have a bond order of 1/2, they are approximately equally stable. Problem: Surprisingly, the hybridization of the starred oxygen in the following molecule is sp 2, not sp 3. Bond order: Cli Show transcribed image text Construct ... Solution for construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2− and then identify the bond order Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. Addition of two orbitals can lead to bonding MO and anti-bonding MO. On this page MO for schematron.org Figure1: MO diagram for H2. The filling of Bond order = 1/2 (#e- in bonding MO - #e- in antibonding MO). A draw the molecular orbital diagram. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. Show transcribed image text construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. C would this ion exist. Molecular orbital energy diagram total of bonding electrons of sigma bonds bond order total.
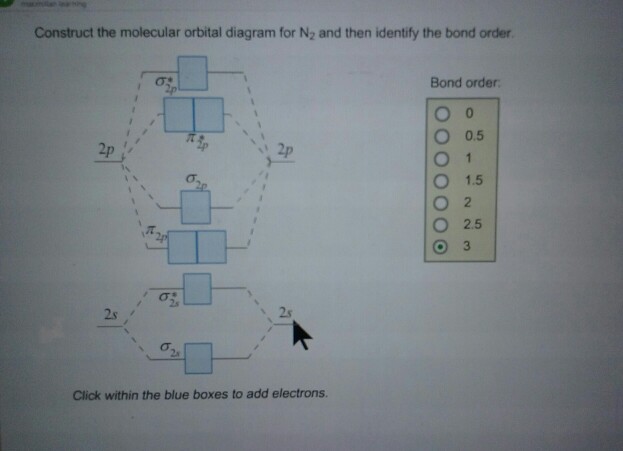
Chemical bonding molecular orbitals of h2 and he2. This problem has been solved. Description of the molecular orbitals of the h2 molecule with an introduction to molecular orbital diagrams. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for n2 and then identify the bond order. Draw the lewis structure of pf 3a how many share. In this example problem, we show how to fill a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule and use molecular bond theory to compare bond order, bond st... Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. You are watching: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. A molecular orbital diagram is used to define chemical bonding in a molecule. This chart is based ~ above the molecular orbital theory.
on Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2 And Then Identify The Bond Order. Addition of two orbitals can lead to bonding MO and anti-bonding MO. On this page MO for schematron.org Figure1: MO diagram for H2. The filling of Bond order = 1/2 (#e- in bonding MO - #e- in antibonding MO). For H2, bond. one electron in bonding orbital; so ...
The molecular orbital diagram for He2+ 2 H e 2 2 + is provided below. The number of electrons in BMO = 2. The number of electrons in ABMO = 0. Bond order = 1 2(2−0) = 1 B o n d o r d e r = 1 2 ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for the HF Molecule. Interaction occurs between the 1s orbital on hydrogen and the 2p orbital in fluorine causing the formation of a sigma-bonding and a sigma-antibonding molecular orbital, as shown below. Figure 1: Molecular orbitals of HF. (CC BY-SA-NC 2.0 UK: England & Wales License; Nick Greeves).
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2- and then identify the bond order - 9826551 jbugluv4604 jbugluv4604 04/26/2018 Chemistry High School Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2- and then identify the bond order 1 See answer jbugluv4604 is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points.
1 ½ e. 2 Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H 2- a What charge would be needed on F 2 to. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1s Atomic Orbitals.
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular…
Jul 23, 2018 · Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules. The lewis structure for h2 is h h predicting a single bond between each hydrogen atom with two electrons in the bond. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2. Discussed in this video are.
So, next one electron will go into 1s shell of anti-bonding orbital. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here.
Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals.
Transcribed image text: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H22 and then identify the bond order. Bond order 1s O 0.5 -따 O 1.5 2 Atom Molecule Atom 2+ Click within the blue boxes to add electrons.
Bond order: Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Show transcribed image text Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. 1s Bond order: 、、 1s 0 O O 2 Atom.
Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. 100% (34 ratings) Transcribed image text: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for N2 and then identify the bond order Bond order 0.5 O 1.5 O 2.5 2s 2s Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Previous question Next question.
Step 1 of 2. The given molecule is which has 4 electrons in it. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule is shown below. Molecular orbital diagram has been drawn for the given molecule. This has totally 4 electrons in it. In molecular orbital diagram, it is clearly shown that the bonding orbital and the antibonding orbitals has two electrons ...
Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H
Bond order and the molecular orbital of the diagram is given below. bond order Energy He atom He atom oooo He2 Molecule Atom Atom Explanation Common mistakes Bond order of the given molecule (He) has been calculated by using the bond order formula with the help of molecular orbital diagram. Bond order calculation: B.O=}(B.E - A.B.E) where, B ...

















0 Response to "34 construct the molecular orbital diagram for h22– and then identify the bond order."
Post a Comment