35 hcn molecular orbital diagram
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagram of 3 hydrogens interacting with S vacancy states. (a) Origin of a 1 , a 2 , b 1 , and b 2 states for the C 2v 2 electron, +1 configuration. Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules, atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals.
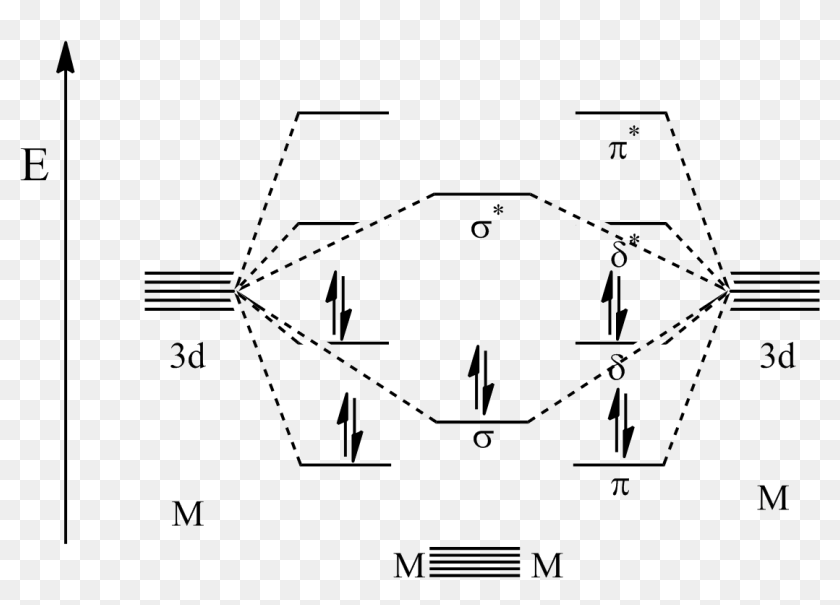
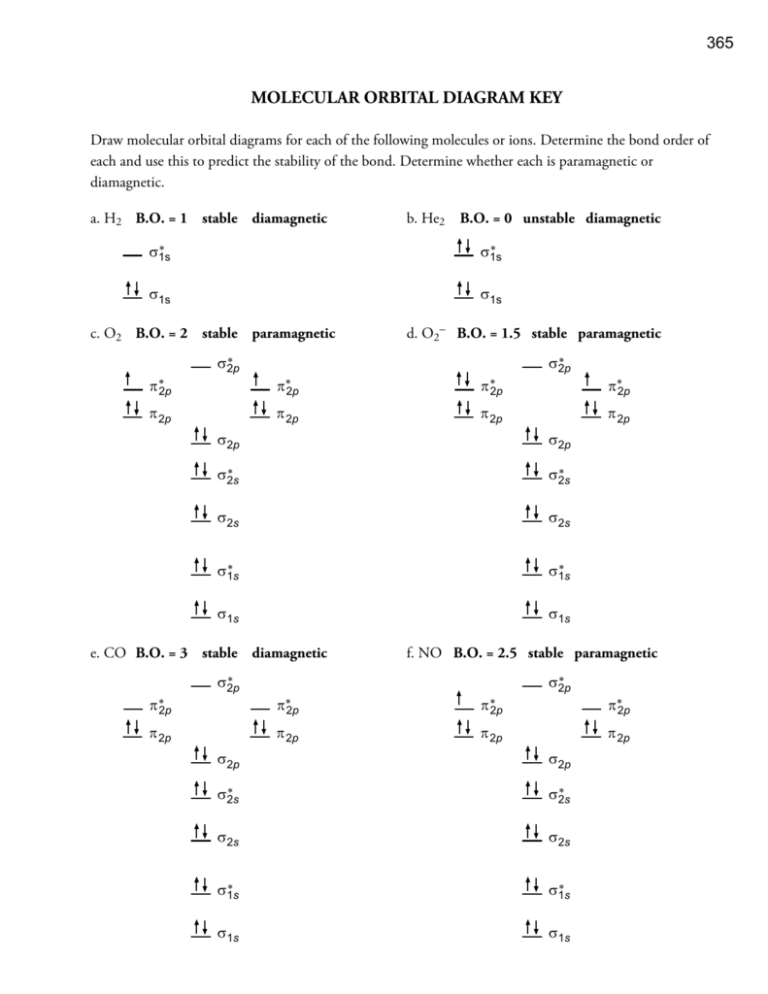
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable.
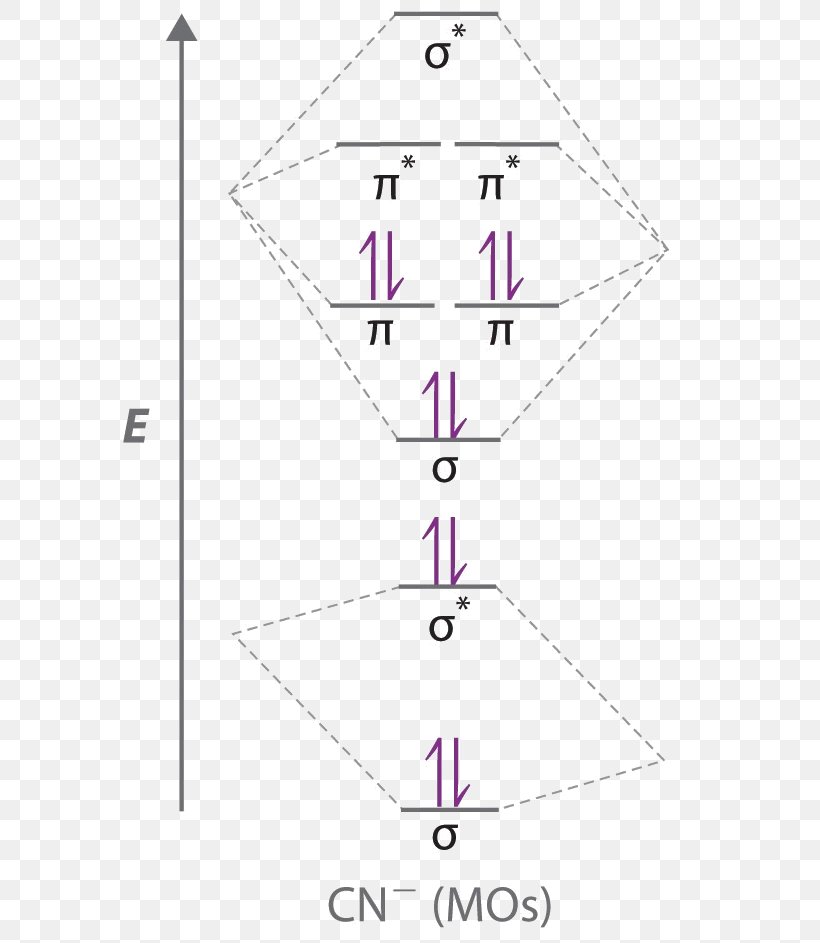
Hcn molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of Li2 & Be2 : Number of electrons in Li2 molecule =6. Other articles where molecular orbital energy-level diagram is discussed: chemical bonding: Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The molecular orbital Figure 8: Molecular orbital energy-level diagrams for (A) beryllium hydride, BeH2, with linear shape, and (B) water, H2O, with bent shape. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
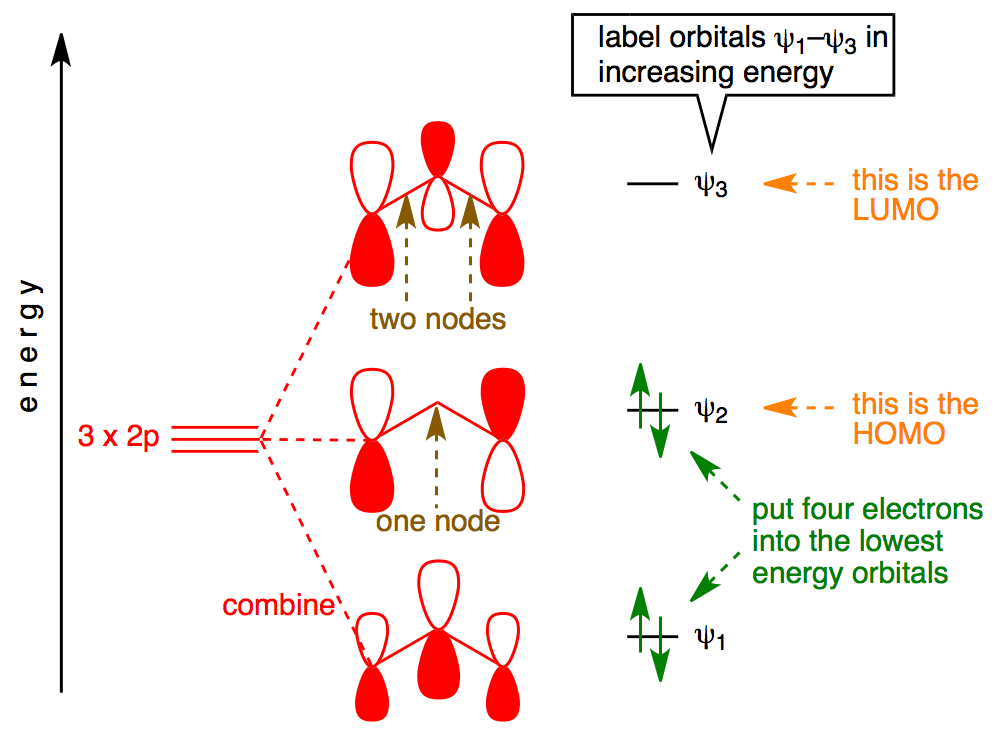
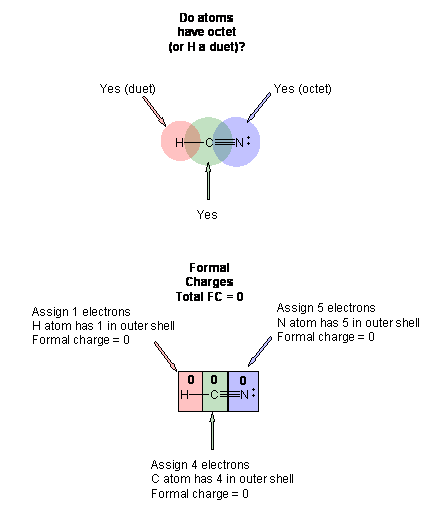
Hcn molecular orbital diagram. HCN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, MO Diagram, and Polarity. The atomic number of Carbon is 6 so 2 electrons are filled in 's' orbital and the rest 4 are in the outer orbital that is why the valence number of electrons in carbon is 4. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. However, with more atoms, computers are required to calculate how the atomic orbitals combine. • Molecular Orbital Theory - How atomic orbitals on different atoms interact - The labelling of the new molecular orbitals. • Energy level diagram represents this interaction - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular orbital - Electrons fill the...
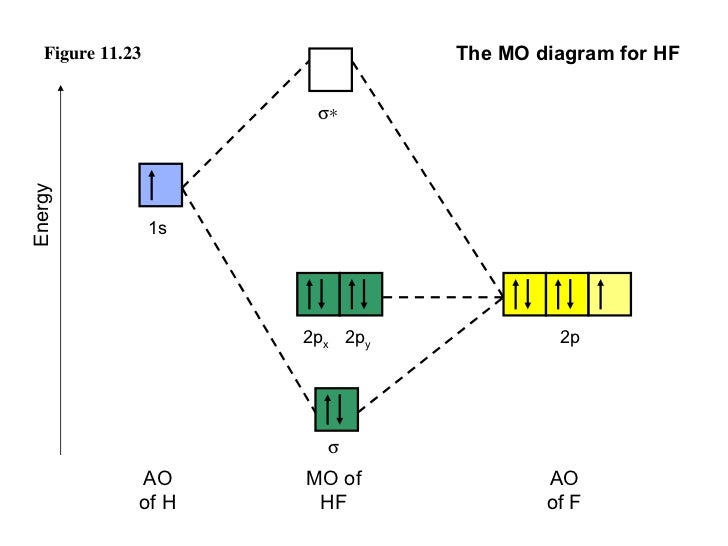
Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon. Molecular orbital energy level diagram of CO molecule can be given as. The electronic of hydrogen and fluorine are 1s¹ and 1s²2s²2p⁵ respectively. In the formation of HF molecule ,only 2p electrons of fluorine atom would combine effectively with the solitary electron of hydrogen atom. Molecular orbital theory is more powerful than valence-bond theory because the orbitals reflect the geometry of the molecule to which they are applied. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms. orbital diagram pictorial representation of the electron configuration showing each orbital as a box and each electron as an arrow. p orbital dumbbell-shaped region of space with high electron density, describes orbitals with l = 1. An electron in this orbital is called a p electron.
element. Accordingly, a molecular orbital diagram such as Figure 9-5 is inappropriate for heteronuclear diatomic molecules. If the two elements are similar (as in NO or CN mole-cules, for example), we can modify the diagram of Figure 9-5 by skewing it slightly. Bonding and antibonding orbitals. Simple molecular orbital diagrams. Dihydrogen and its ion H2+. Dihelium He2. The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that lead... Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw a correlation So here, I basically ask, how do I draw a correlation diagram? Like, how do I know how many electrons to put in the bonding atomic orbital and... A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Molecular Orbital Theory: Detailed information on the molecular orbital theory class 11 and more in this article above. An approach, known as Molecular Orbital Theory, was established primarily by Hund and Mulliken in \(1932 The molecular orbital energy level diagram for lithium is shown below.
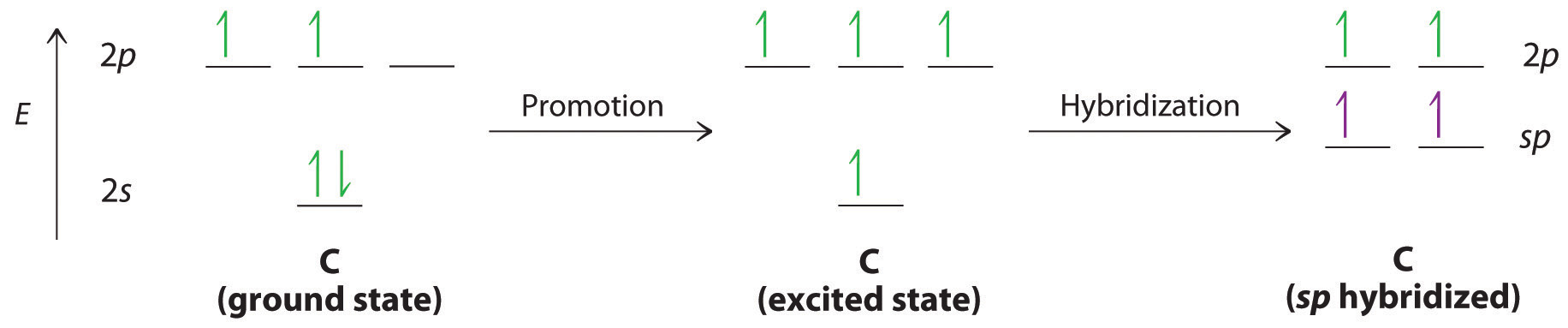
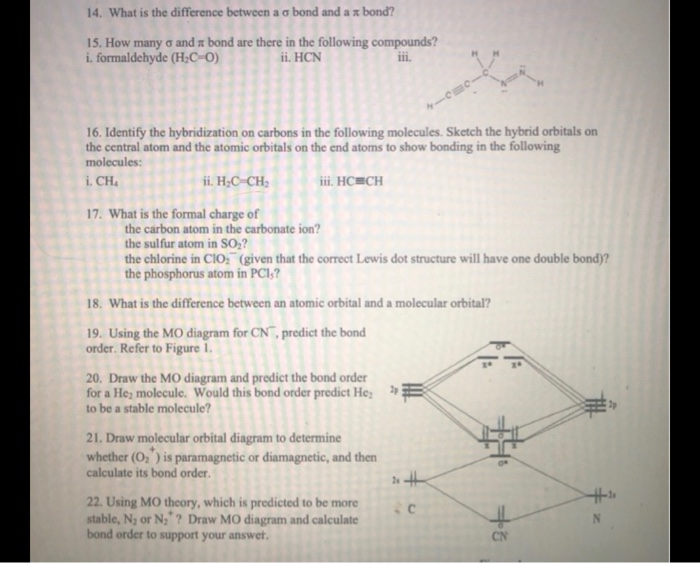
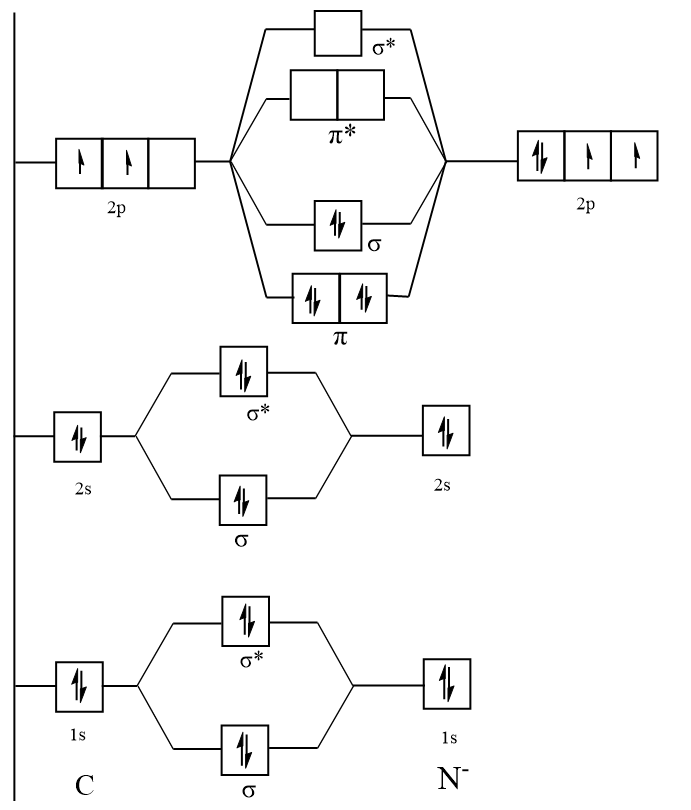
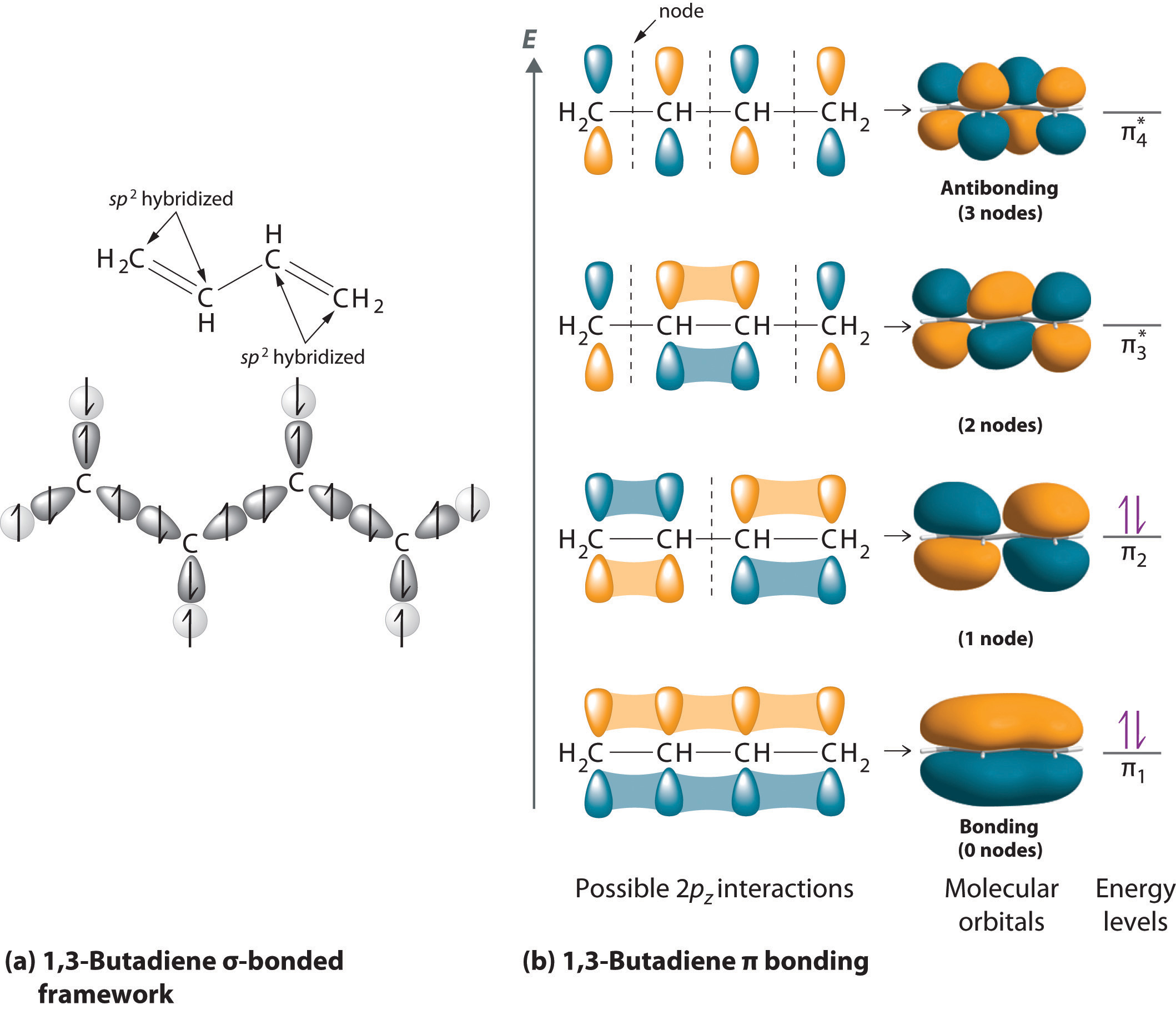
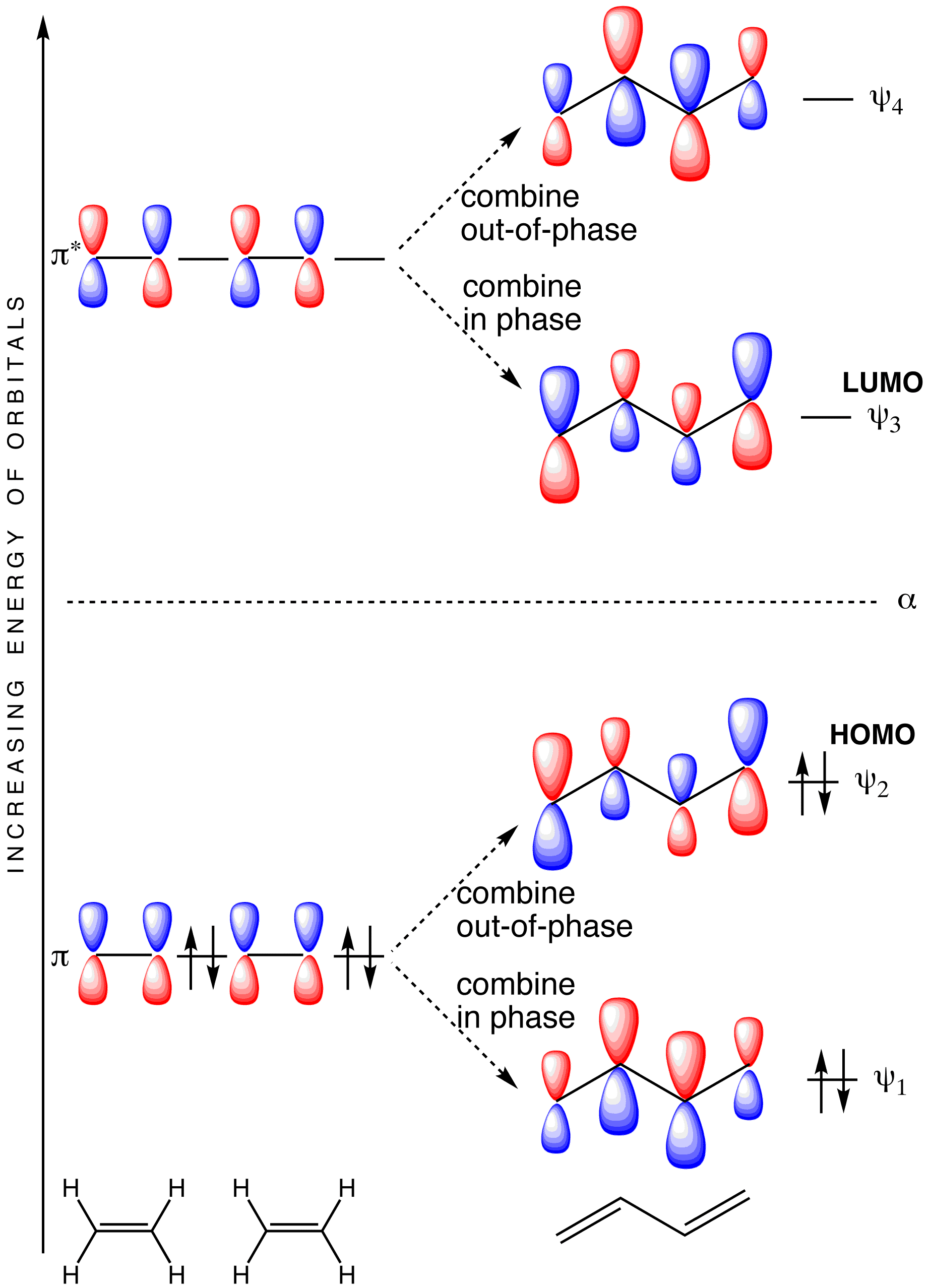
365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. n. HCN hybridization for the C sp hybridization for the N sp There is one C-H sigma bond due to sp-1s overlap.
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown for comparison. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store! Correlation Diagrams - by considering the positions and energies of...
Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. Molecular Orbital Theory - BH3. The BH3 molecule exists in the gas phase, but...
Diatomic molecules are necessarily linear, but a triatomic molecule can be either linear like CO2 and HCN or bent like SO2 and H2O. See other pages where Molecular orbital diagrams triatomic molecules is mentioned: [Pg.104] [Pg.406] [Pg.247] [Pg.87] [Pg.119] [Pg.107] [Pg.16] [Pg.122]...
Figure 9. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. A dihydrogen molecule contains two bonding electrons and no antibonding electrons so we have.
is the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for He 2 + . This ion has a total of three valence electrons. Because the first two electrons completely fill the σ 1 s molecular orbital, the Pauli principle states that the third electron must be in the σ⋆1s.
Molecular Orbital ~ a l c u l aitons. John D. Roberts. c. acetonitrile d. phenanthrene e. graphite f. HCN. IN THE APPLICATION of molecular orbital theory to calculations of chemical binding energies, we shall use s e v e r a l basic principles, some of which w e r e mentioned in Chapter 1 and...
In a molecular orbital diagram, which of the following is listed down the center of the diagram? Select the correct answer below: atomic orbitals atomic or a diatomic molecule, how many molecular orbitals will have an n value of 1? 2 [For a diatomic molecule there will be a σ1s bonding orbital and...
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
Other articles where molecular orbital energy-level diagram is discussed: chemical bonding: Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The molecular orbital Figure 8: Molecular orbital energy-level diagrams for (A) beryllium hydride, BeH2, with linear shape, and (B) water, H2O, with bent shape.
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of Li2 & Be2 : Number of electrons in Li2 molecule =6.






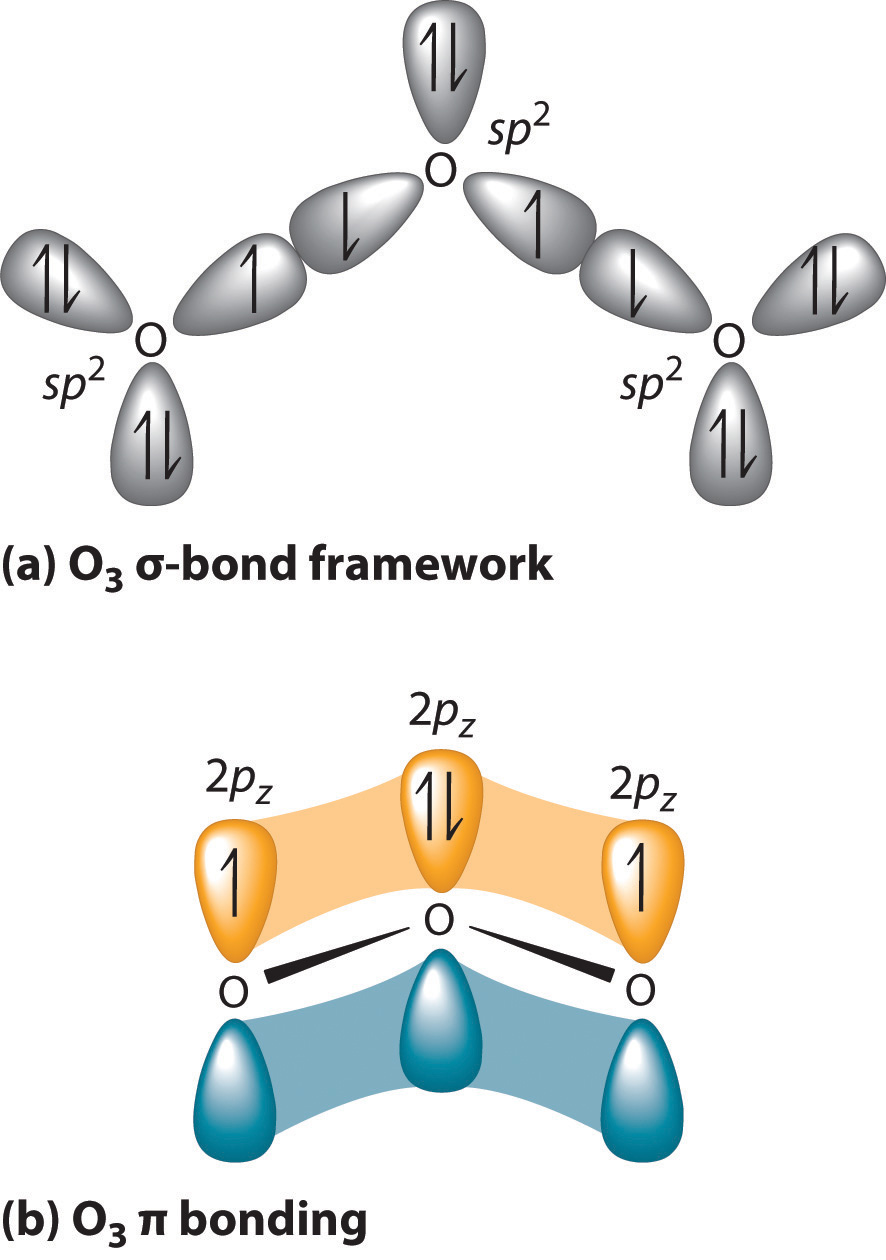

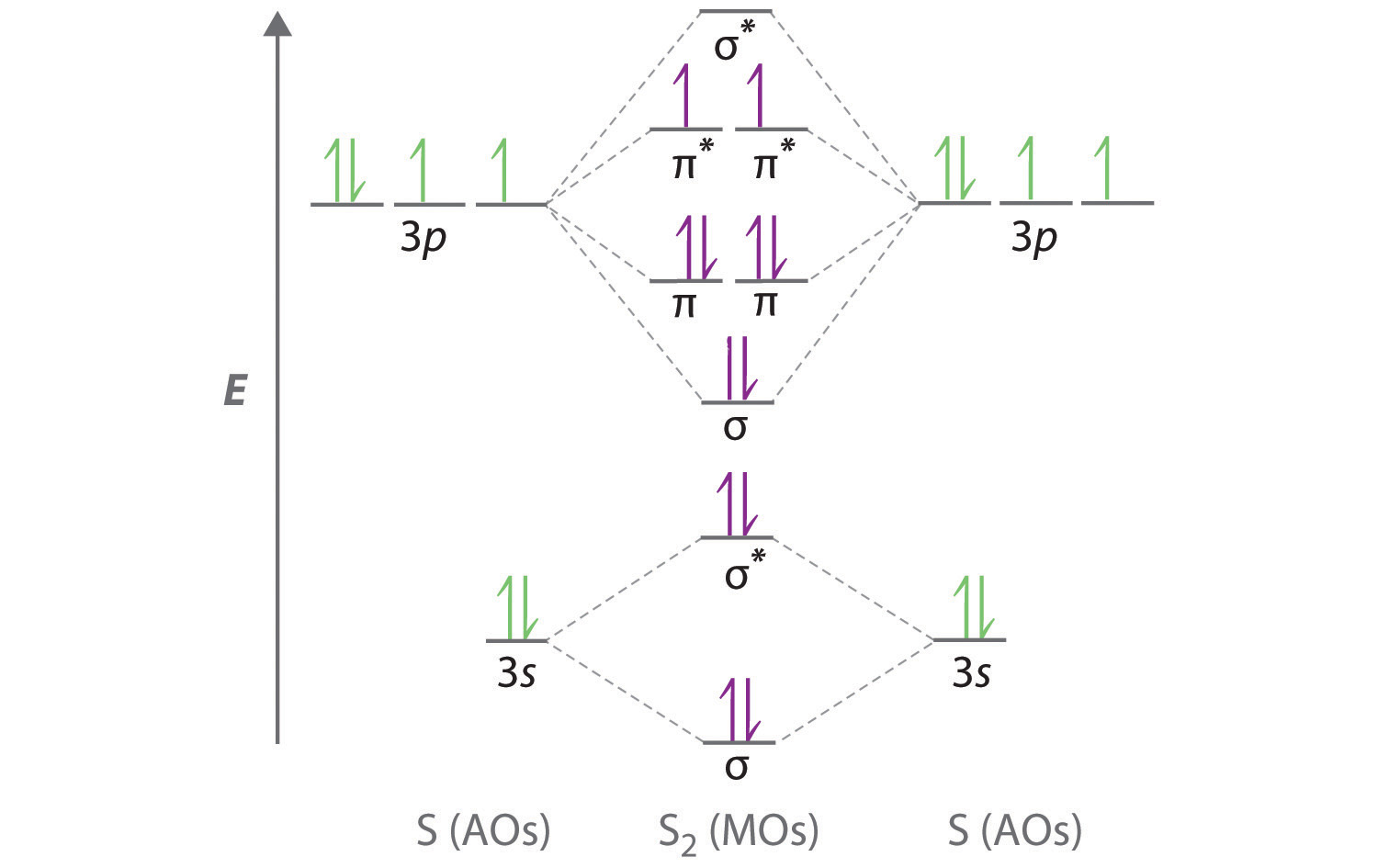









0 Response to "35 hcn molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment