34 b2+ molecular orbital diagram
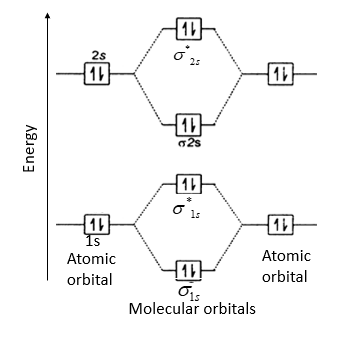
The molecular orbital corresponding to the sum of the two H 1s orbitals is called a σ1s combination (pronounced "sigma one ess") (part (a) and part Figure 5.3.1 Molecular Orbitals for the H2 Molecule (a) This diagram shows the formation of a bonding σ1s molecular orbital for H2 as the sum of the... The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p Experiments have shown that O2 and F2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but B2, C2, and N2 are best...
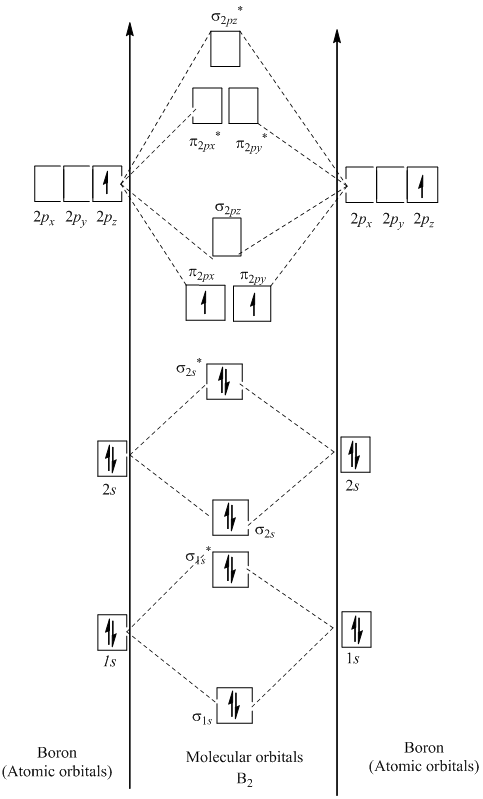
B2+ molecular orbital diagram
• Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and... Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the... Jan 27, 2022 · What is the molecular orbital configuration of C2? Looking at the appropriate MO diagram, we see that the π orbitals are lower in energy than the σp orbital. The valence electron configuration for C2 is (σ2s)2(σ∗2s)2(π2py,π2pz)4 ( σ 2 s ) 2 ( σ 2 s ∗ ) 2 ( π 2 p y , π 2 p z ) 4 .
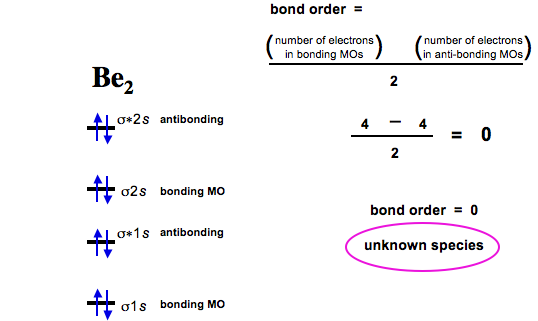
B2+ molecular orbital diagram. - Molecular orbital are formed by addition and subtraction of AO's. Æ Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO). • Energy level diagram represents this interaction. - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular orbital. Aug 11, 2018 · Molecular Orbital Diagram Be2. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and ... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. 1. Draw a molecular orbital diagram and determine the bond order expected for the molecule B2. For full credit on MO diagrams (b) Write the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in BC and in BC1-. (c) Which of the molecular orbitals in BC do not have a planar node along the.
Mar 13, 2019 · Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory helps us to explain and understand certain Part B – Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams & Bond Order . + and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic ... I’ve been tasked with drawing rhe MO diagram for Sulfure Oxide and I’m not sure about the energies of the relatove orbitals. Since Oxygen is more electronegative I expect the 2s and 2p orbitals to have much lower energy than the 3s and 3p orbitals sulfur has. But the energy difference would be really high then. So I’m not sure what 2 orbitals combine to form the sigma 3s or sigma* 3s orbital. The difference in energy kevels confuses me as every example I’ve done has the same orbitals (2s,2p’s) c... There are two different explanations, which lead to the same conclusion, available. The more common one involves the formation of hybrid orbitals, which then form the molecular orbitals. This results in a triplet ground state. The finished valence molecular orbital diagram is pictured below. The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. For example, homonuclear diatomic molecules of second row elements like Li2, Be2, B2 , C2, N2 , the σ 2pz MOs is higher in energy than π 2px and π 2py MOs.
Molecular Orbital Theory- To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Have you ever thought about how sigma and pi bonds are formed? What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic behaviour? Jan 15, 2022 · A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory ... 29 Sept 2017 — Fluorine molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of two fluorine atoms, each having nine electrons, thus making 18 electrons.2 answers · 62 votes: O2 and F2 is an execption so their Z shell is down ... Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown for comparison. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels. hey! I have a question: how do i draw a molecular orbital diagram for SO2? i only found examples for diatomic diagrams and im not sure how to do it if i have more then two atoms in the molecule.
This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.
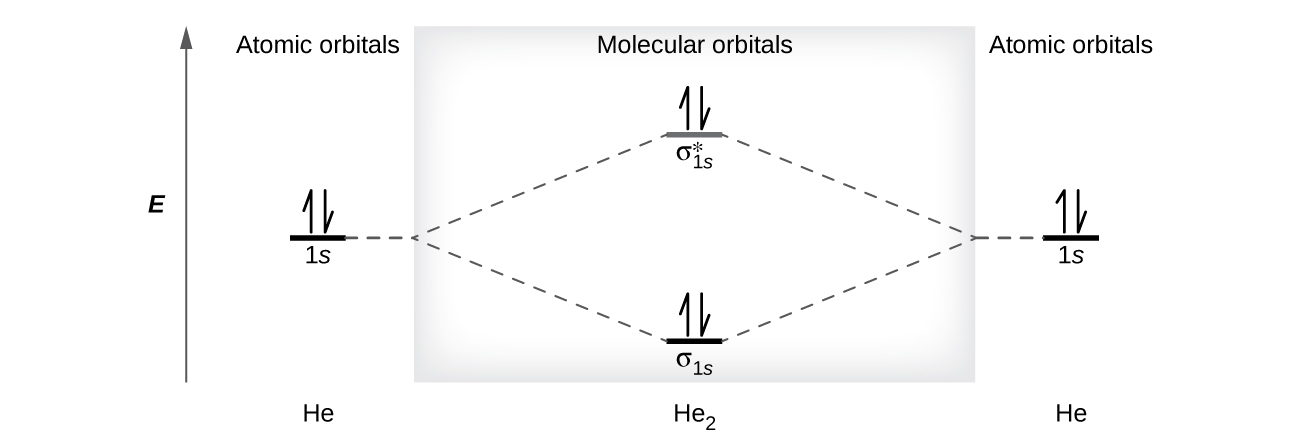
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. The solid lines represent the relative energies of the indicated atomic and molecular orbitals. (a) The diagram for H2, He2, Li2, Be2, B2, C2, and N2...
In molecular orbital (MO) approach - overlap orbitals for the whole molecule -bonding is therefore DELOCALISED. We will look first at DIATOMIC MOLECULES and only later move on to POLYATOMIC MOLECULES. Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic.
Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons Energy. This problem has been solved! See the answerSee the answer.
I've been getting the hang of creating MO diagrams and I understand the very basics. My problem is in the 2p orbital's bonding section where sometimes the pi 2p section is lower energy than the sigma 2p section (i.e MO diagram for B2 diatomic molecule). I understand that the lower energy must be filled in first and so my question is, how do I know if the pi 2p is lower energy than sigma 2p?
https://i.imgur.com/GgRlFtK.jpg (Not homework) I am trying to improve by using past papers. Can someone explain how to solve these 3 questions?
9. (10 points) i) Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram of B2. Label the symmetry of all molecular orbitals. ii) Use the diagram to determine the multiplicity of B2 (singlet, doublet or triplet) in its ground electronic state. iii) Sketch the shape (s) of the highest occupied molecular orbital (s) of B2 and indicate their relative ...
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the B2 (boron) molecule. The bond order of the boron molecule is also calculated and...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Sep 14, 2018 · N22+ B22+ B B2 CeV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of the lowest energy molecular orbital with respect to the 3s orbital of sulfur. This lowest energy orbital is .
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one The covalent bond between the two B atoms is a single bond and the corresponding MOT calculations show agreement with this
Molecular Orbital Diagrams (H2 and He2) One of the strengths of molecular orbital theory is its ability to describe the energy of both occupied and unoccupied molecular orbitals for a molecule. A molecular orbital diagram shows both the energy of the atomic orbitals (from the atoms that are...
the valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. Which of the following options correctly interpret this diagram? - B2- has a shorter - the MO diagram shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each MO - The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict...
I need to construct the molecular orbital diagram for the hypothetical species Li4, which has the following geometrical arrangement: https://preview.redd.it/npsjre5pch571.png?width=197&format=png&auto=webp&s=c2a7948c2efa04a975bee1db722838fae7482456 The first step is to identify the point symmetry group. In this particular case, we consider that there is only one axis of rotation of order four (actually, other symmetry elements can be observed, but this is a previous consi...
Jan 28, 2022 · Molecular orbital diagram for n2. No2 Valence Electrons - 9 images - solved question 9 of 13 determine the number of valence e, ppt chemical bonding powerpoint presentation free, Shouldn’t you count the valence electrons for Be (which is 2) and subtract 1 because of the + sign?
Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in Molecular Orbital Theory - BH3. The BH3 molecule exists in the gas phase, but dimerizes to B2H6...
Hi! I am a physicist student preparing a solid state physics exam and we discussed molecular orbitals, (sigma, pi) bonding, hybridization, etc... way more than I would like. Since it is the first time I see it some books would be appreciated!
I’m a little confused on the connection between a molecules molecular orbital diagram and it’s individual atomic hybridization. Can anyone help me? Thank you
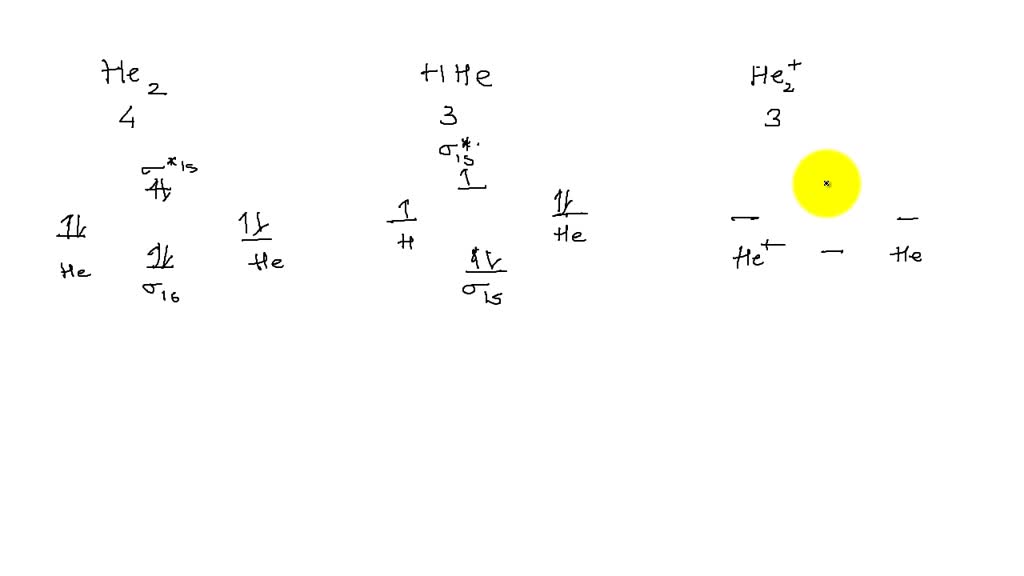
sketch the molecular orbital diagram of each of the following diatomic species and place them in order of increasing bond order b22 b2 b22 22438
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The MOs for the valence orbitals of the second period are shown in Figure 8.37. Looking at Ne2 molecular orbitals, we see that the order is consistent with the generic diagram...
What happens to the molecular orbital diagram when a metal-ligand complex is oxidized? Oxidation removes an electron, e.g. you go from d8 metal to d7 metal. As consequence the antibonding orbital has an unpaired electron making the complex less stable (weaker M-L bond, since less pi-backdonation), but how does it change the gap between the metal MO and LUMO of ligand, as well as the gap between the metal MO and HOMO of the ligand?
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ- bonding in tetrahedral complexes can be shown as Two metal-orbital sets of a1g symmetry, one set of b1g symmetry and one set on e u symmetry participate in σ-bonding while the doubly degenerate e g and singly degenerate b2g sets...
The Molecular Orbital Theory is a chemical bonding theory developed at the turn of the twentieth century by F. R. Hund and R. S. Mulliken to explain the structure and properties of various molecules. The valence-bond theory failed to adequately explain how certain molecules, such as...
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.
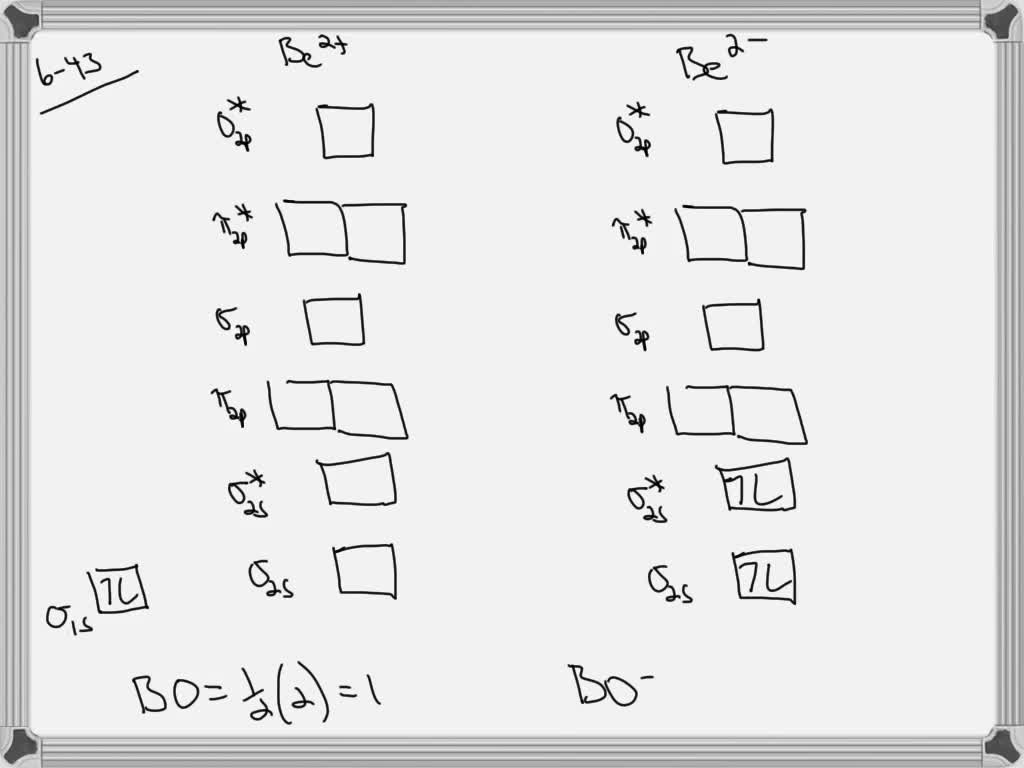
draw an mo energy diagram and predict the bond order of be2 and be2 do you expect these molecules to
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In such interactions are so weak, we will not include them in other molecular orbital. energy level diagrams. Additional labels describe the orbitals.
Hi I am a PhD candidate and I need help making a frontier molecular orbital visualization diagram for the molecule pentacene. I only need 4 molecular orbital visualizations and they are HOMO, LUMO, HOMO-1, and LUMO +1. I am currently using chemissian with the imput from IQMOl but I am having difficulties getting a visual MO composition output. Can anyone help me?
I didn't take Chem 2070 (used AP credit), so I know essentially nothing about molecular orbitals. However, Professor Fors said we would see molecular orbitals quite a bit in 3580 and I already don't understand the first lecture (HOMO and LUMO who?). How in-depth with molecular orbitals does the class go, and is understanding MOs actually important for the exams or is it more just background information to help explain reactions, but you don't really need to know it?
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Shouldn’t you count the valence electrons for Be (which is 2) and subtract 1 because of the + sign? For O2, N2, NO, F2, etc, you count the number of valence electrons instead of the atomic number. Why is it that for Be, though, you look at the atomic number instead of the number of valence electrons it has? I apologize if this is a stupid question, but I appreciate any clarification on this
Jan 27, 2022 · What is the molecular orbital configuration of C2? Looking at the appropriate MO diagram, we see that the π orbitals are lower in energy than the σp orbital. The valence electron configuration for C2 is (σ2s)2(σ∗2s)2(π2py,π2pz)4 ( σ 2 s ) 2 ( σ 2 s ∗ ) 2 ( π 2 p y , π 2 p z ) 4 .
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the...
• Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and...






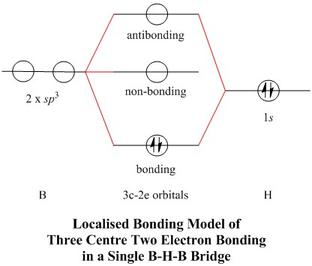


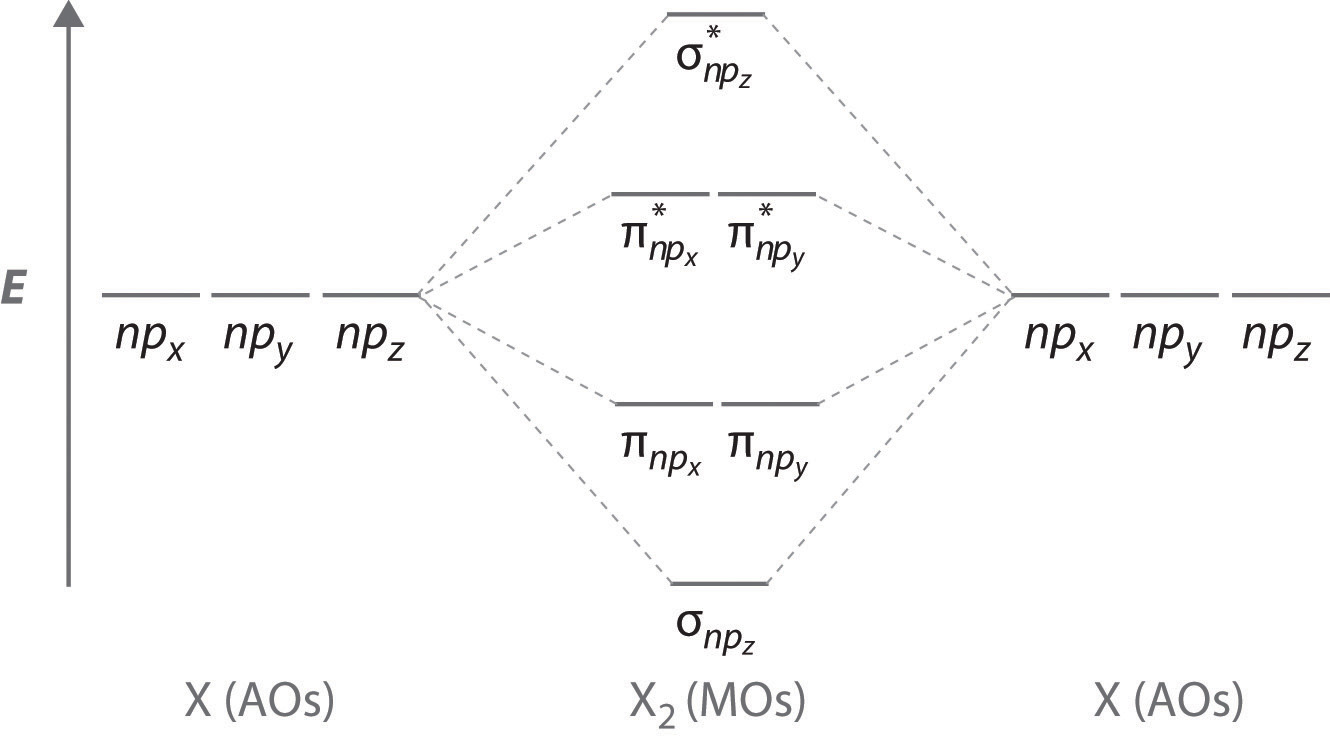

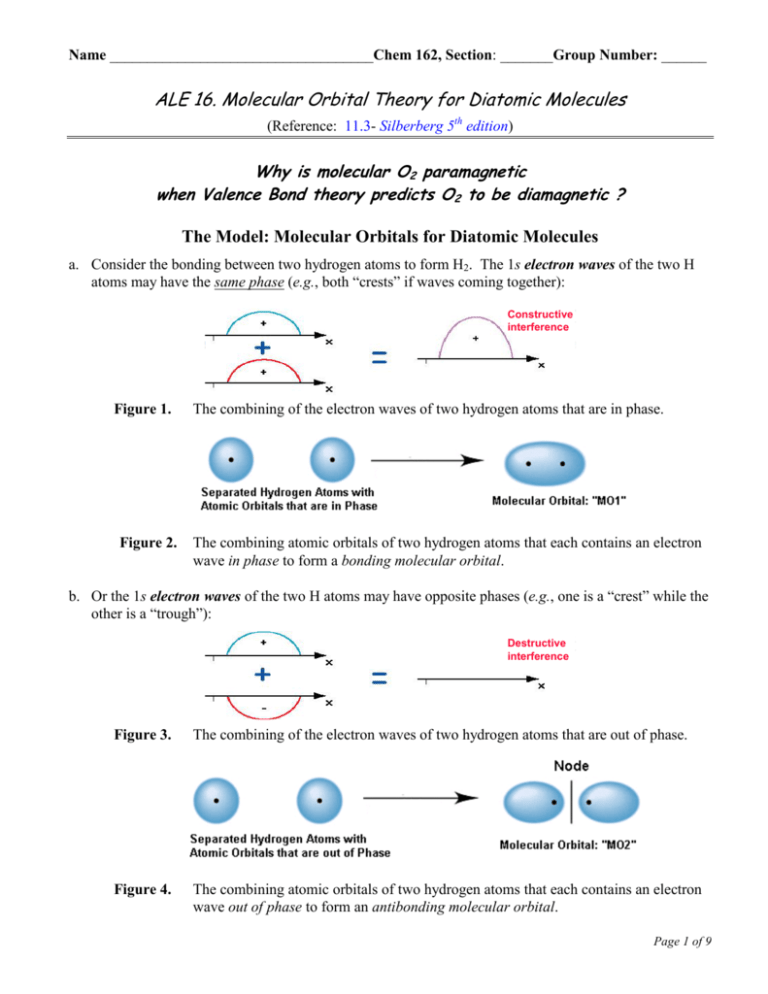

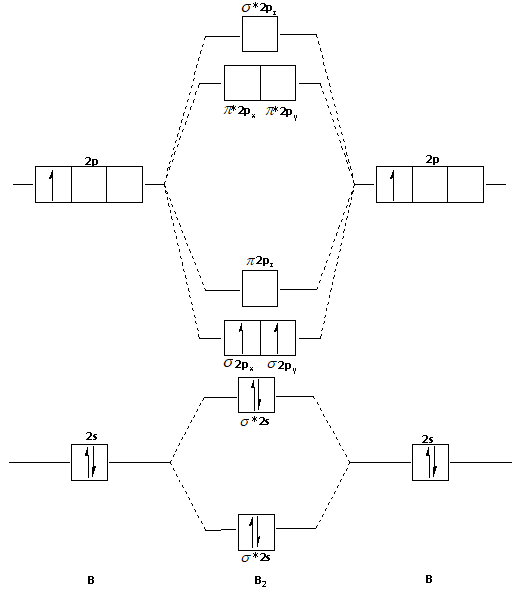
![Solved] Using Figures 9.35 and 9.43 as guides, draw the ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.question.images/image/images11/876-(557)-1.png)
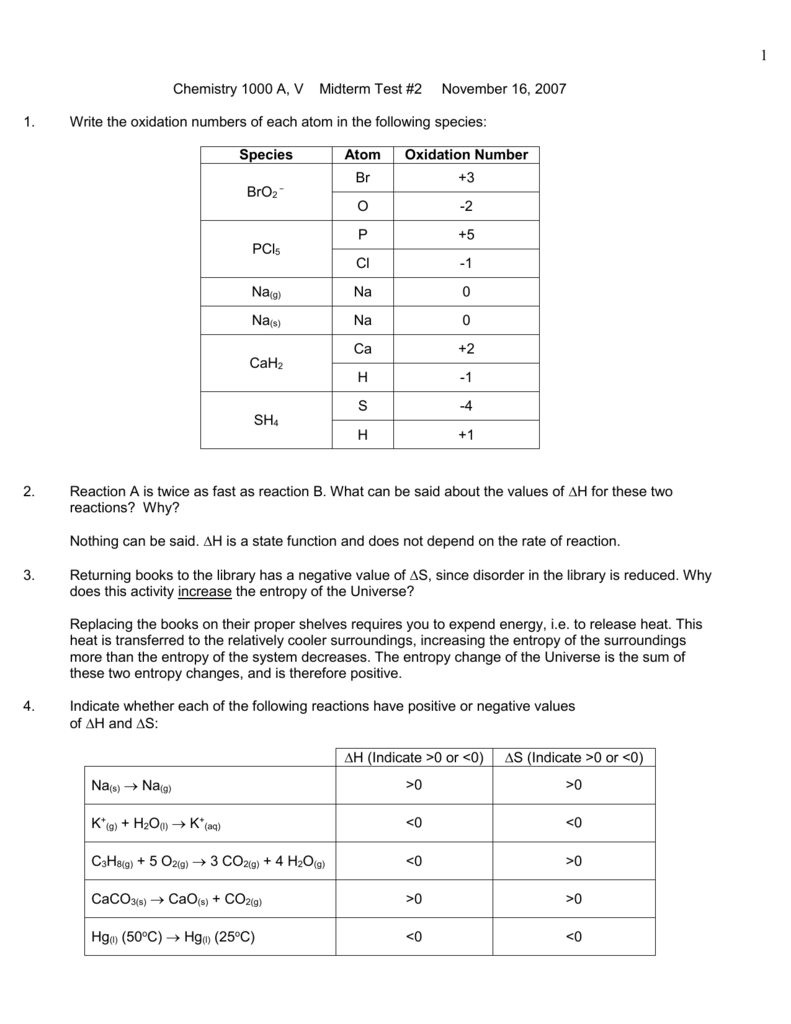




0 Response to "34 b2+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment