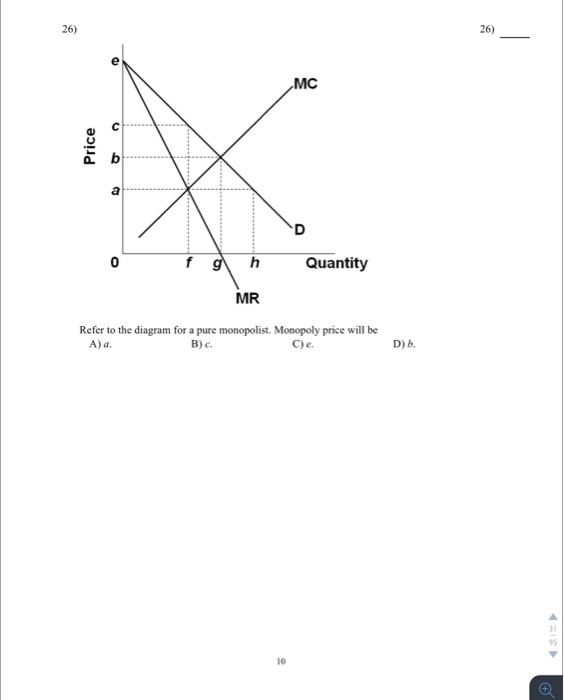
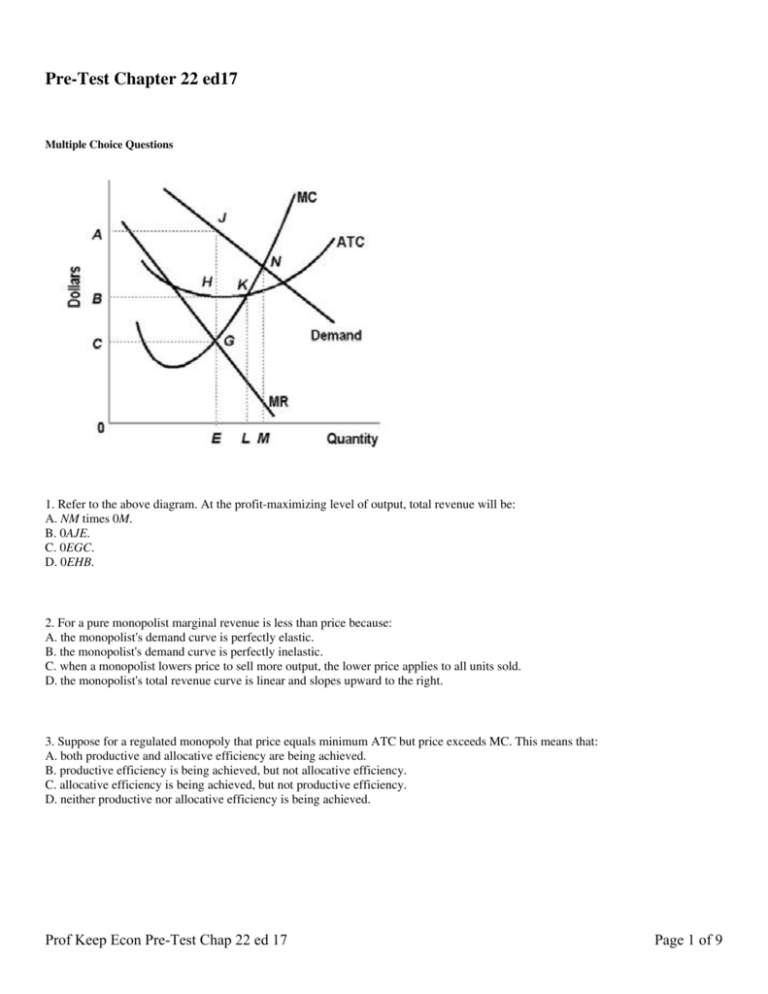
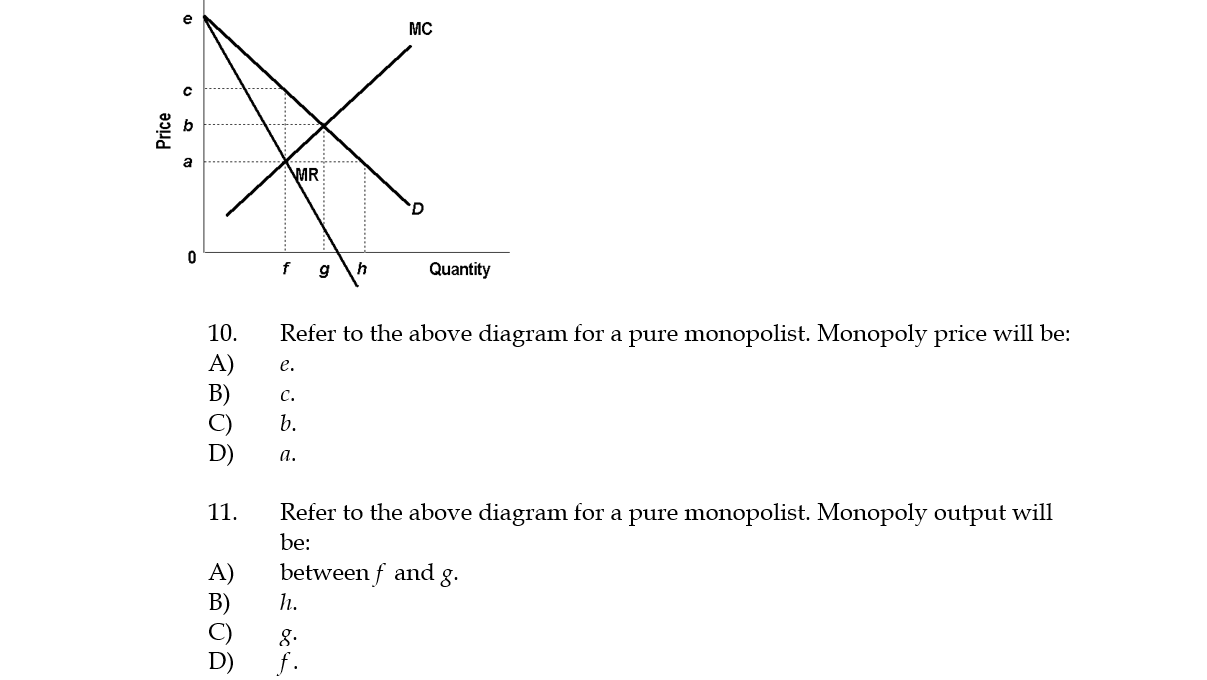
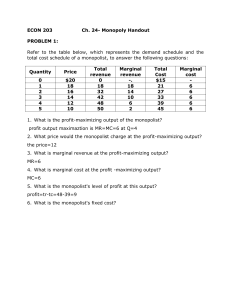
37 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: ... Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 10 units of output at $5 per unit and 11 units at $4.90 per unit. The marginal revenue of the eleventh unit is: A. ... does not apply to pure monopoly because price exceeds marginal revenue. D. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be. f. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit. cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run, a monopolist's economic profits. may be positive or negative depending on market demand and cost conditions.
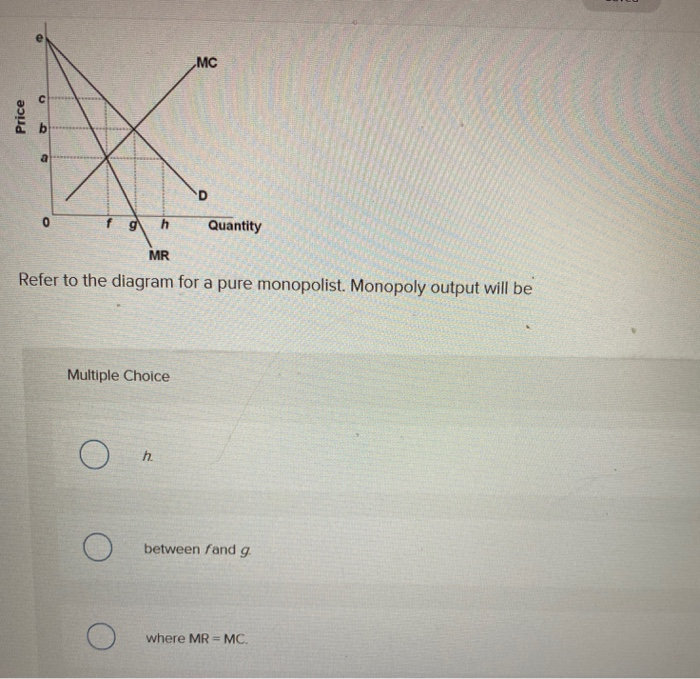
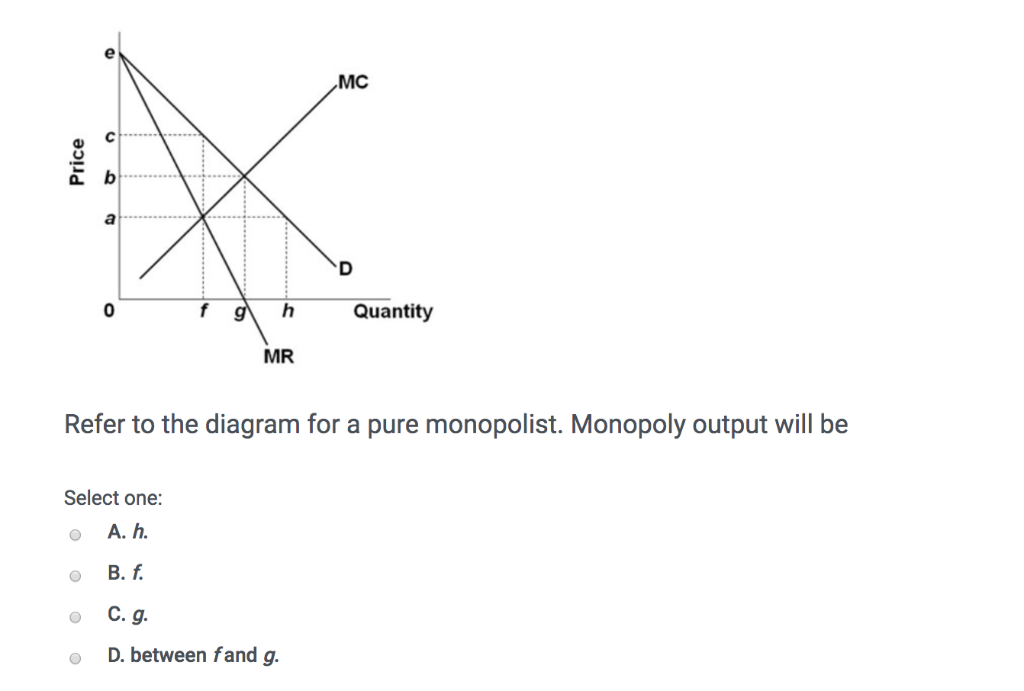
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly output will be A f B g C h D from ECON 101 at James Campbell High School
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:
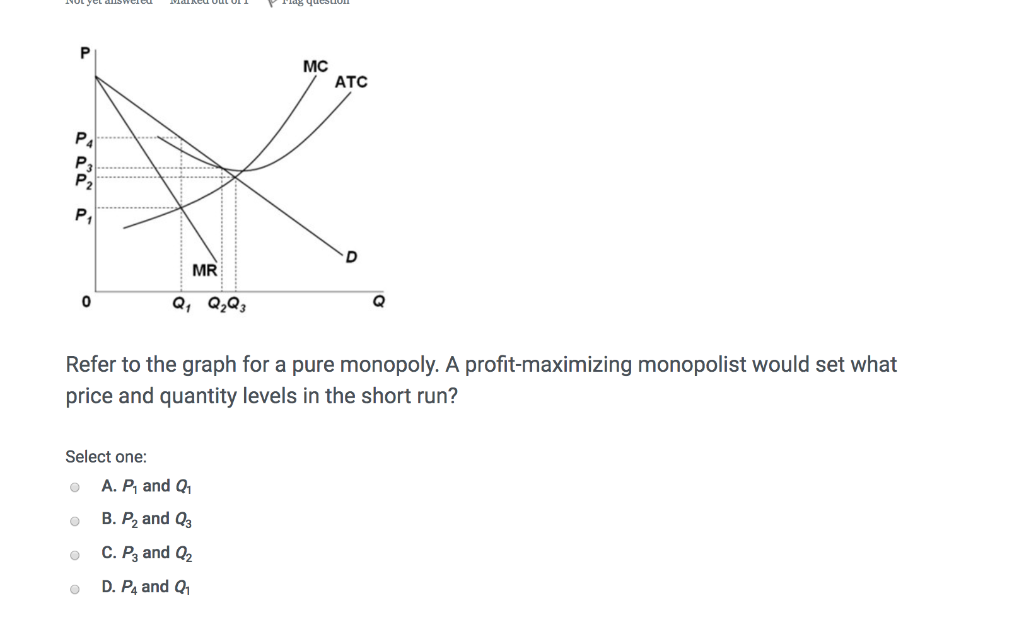
Refer to the diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by. producing Q2 units and charging a price of P2. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be. Nice work! D) f . 32. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: a.cannot be determined from the information given. b.will be ae per unit sold. c.will be bc per unit sold. d.will be ac per unit sold. 33. Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g. 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its profit-maximizing output, price will A) equal MR. B) be less than MR. C)
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:. Board: AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB. A pure monopolist in an industry is a single seller. It is rare for a firm to have a pure monopoly - except when the industry is state-owned and has a legally protected monopoly. Monopoly Price Output and Profit - revision video. Monopoly profit analysis. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: F. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: Cannot be determined from the information given. If the industry depicted in the graph is purely monopolistic, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be: 48. Refer to the above diagram for pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with "fair return" it will set price at Monopoly price will be:c. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will:f . Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit:cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit:may be positive, zero, or negative. Purely competitive firms and pure monopolists are ...
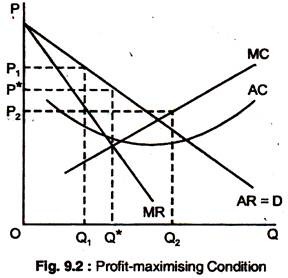
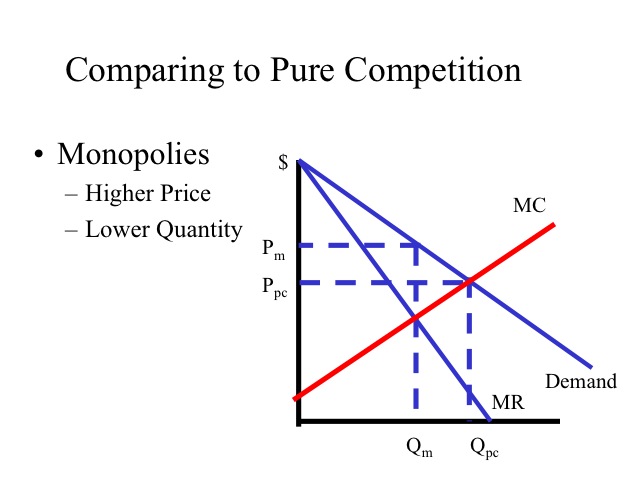
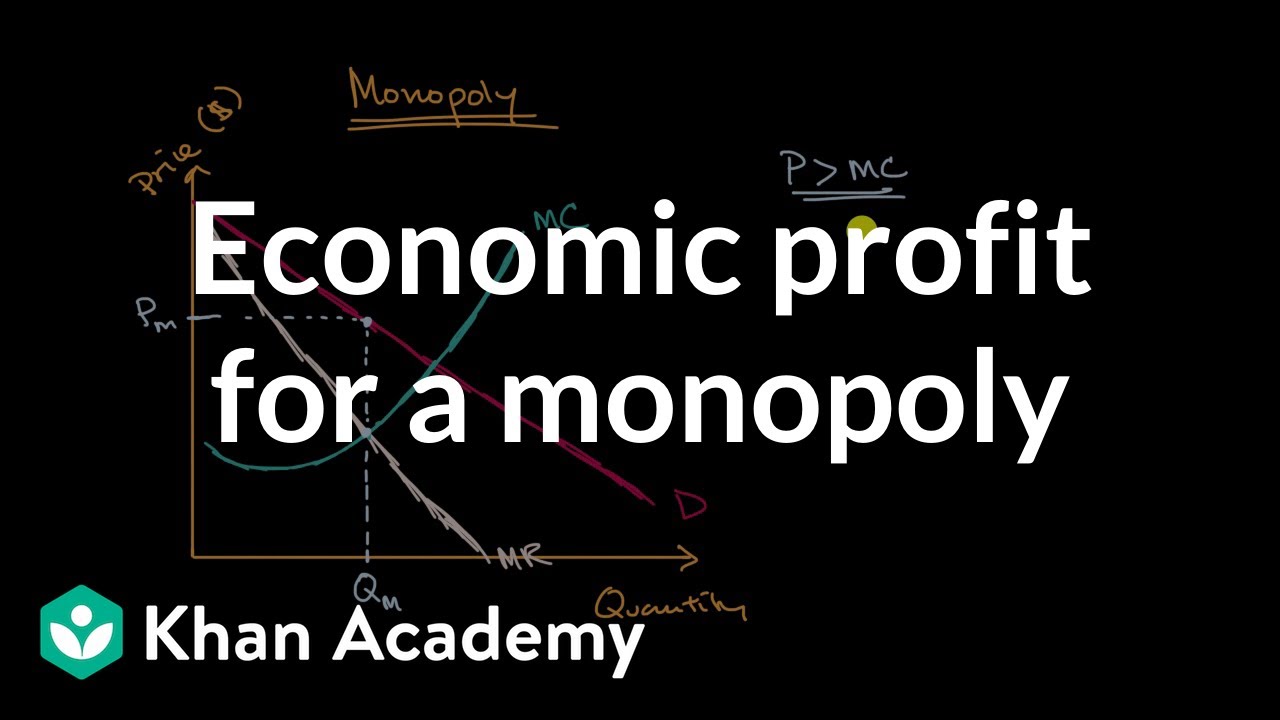
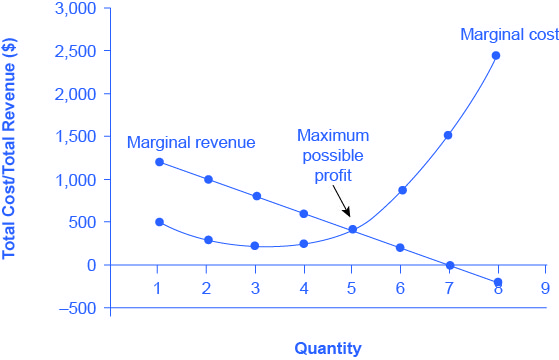
Monopoly Graph. A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC. This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output. Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q. Blue area = Deadweight welfare loss (combined loss of producer and consumer surplus ... Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be; Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, total variable cost is equal to: Refer to the diagram in which qf ... Monopoly output will be: A. between f and g B. h C. g D. f. . . . . 10-5. Chapter 10 - Pure Monopoly 72. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold. 73. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: ... In Exhibit 13-3, if this is an unregulated monopoly firm, the price and output which would maximize profits are: asked Feb 26, 2019 in Economics by joey_kelly.
60. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q production will be unprofitable. True False 61. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for this firm is J. True False 62. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output M total variable ... Refer to the diagram below for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A) a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B) price P3 and producing output Q3. C) price P2 and producing output Q2. D) price P1 and producing output Q1. 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ. B) an economic profit of ACGJ. C) a loss of GH per unit. D) a loss of JH per unit. 10. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: A) e. B) c. C) b. D) a. 11. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3.. B. price P3 and producing output Q3.. C. price P2 and producing output Q2.. D. price P1 and producing output Q1.. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist.
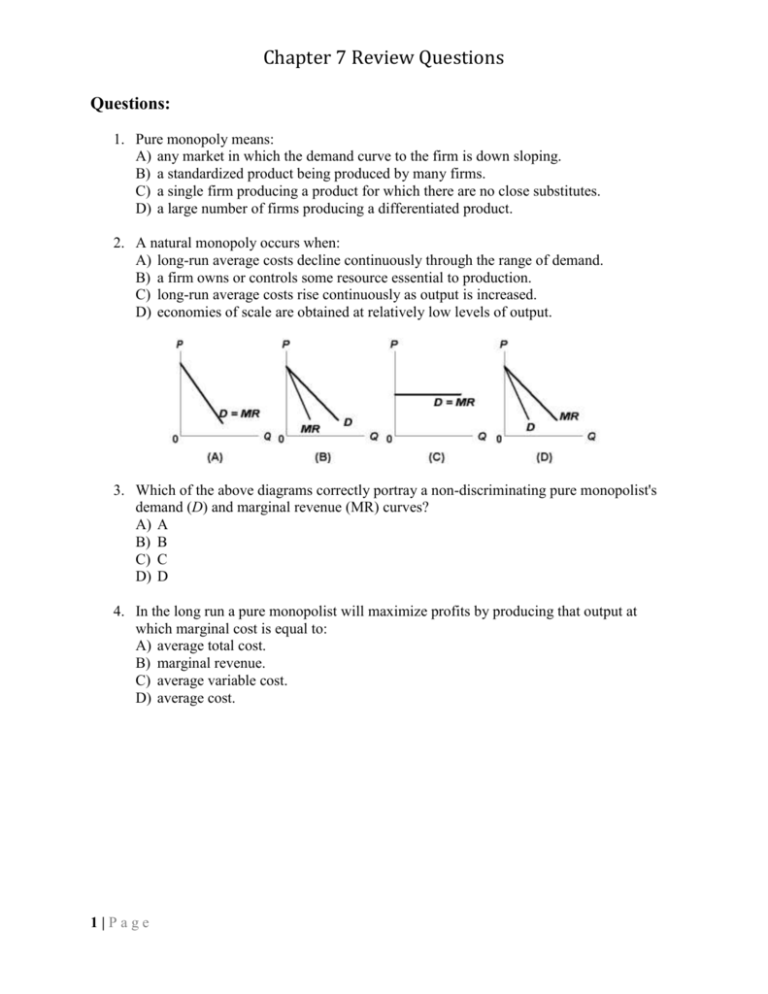
Therefore, the monopolist will be in equilibrium at output OM where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost and the profits are the greatest. The corresponding price in the diagram is MP or OP. It can be seen from the diagram at output OM, while MP' is the average revenue, ML is the average cost, therefore, P'L is the profit per unit.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be; Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will; For a pure monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because: A price discriminating pure monopolist will attempt to charge each buyer (or group of buyers): For a pure ...
A) The pure monopolist will maximize profit by producing at that point on the demand curve where elasticity is zero. B) In seeking the profit-maximizing output the pure monopolist underallocates resources to its production. C) The pure monopolist maximizes profits by producing that output at which the differential between
Chapter 10 - Pure Monopoly 170. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B. price P3 and producing output Q3. C. price P2 and producing output Q2. D. price P1 and producing output Q1. 171.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be: Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. the profit-seeking monopolist will; If a pure monopolist is producing more output than the mr = mc output: At its profit-maximizing output, a pure nondiscriminating monopolist achieves; If a pure monopolist is operating in a range of output where demand is elastic: If a pure monopolist is producing at that output where p = atc, then
Monopoly Equilibrium in the long-run In a pure monopoly, entrance into the market by potential competitors is not possible. Thus, whether or not a monopolist earns a profit in the short-run, no other producer can enter the market in the hope profit is not eliminated in the long-run. Ref. Ferguson pg 307. Discriminating Monopolist A monopolist may charge different prices less different markets ...
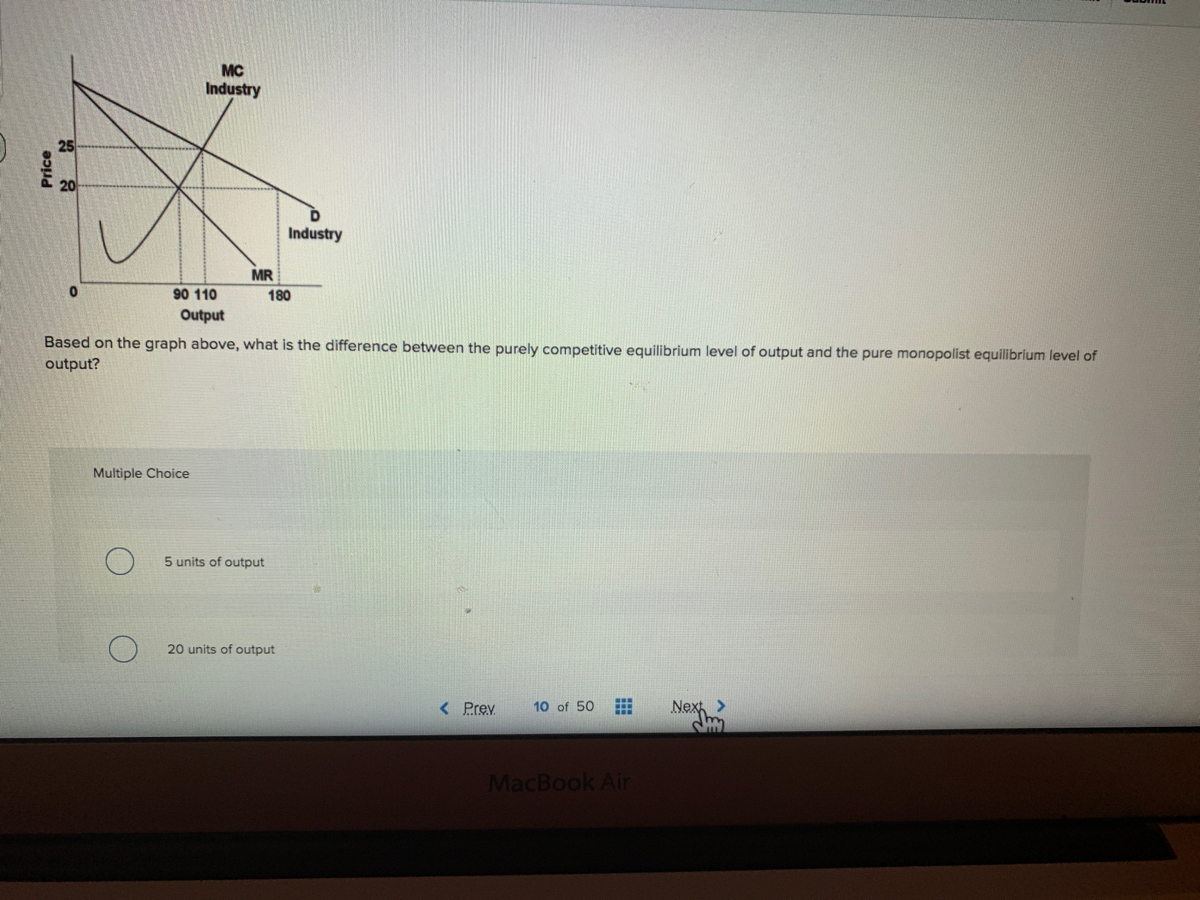
Economics questions and answers. Price g h Quantity Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be Multiple Choice 0 0 between fand g 0 < Prev 12 of 25 Next > MacBook Air MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be Multiple Choice between fand g. ООО where MR - MC < Prev 12 of 25 Next > MacBook ...
Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g. 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its profit-maximizing output, price will A) equal MR. B) be less than MR. C)
D) f . 32. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: a.cannot be determined from the information given. b.will be ae per unit sold. c.will be bc per unit sold. d.will be ac per unit sold. 33.
Refer to the diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by. producing Q2 units and charging a price of P2. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be. Nice work!



















0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be:"
Post a Comment