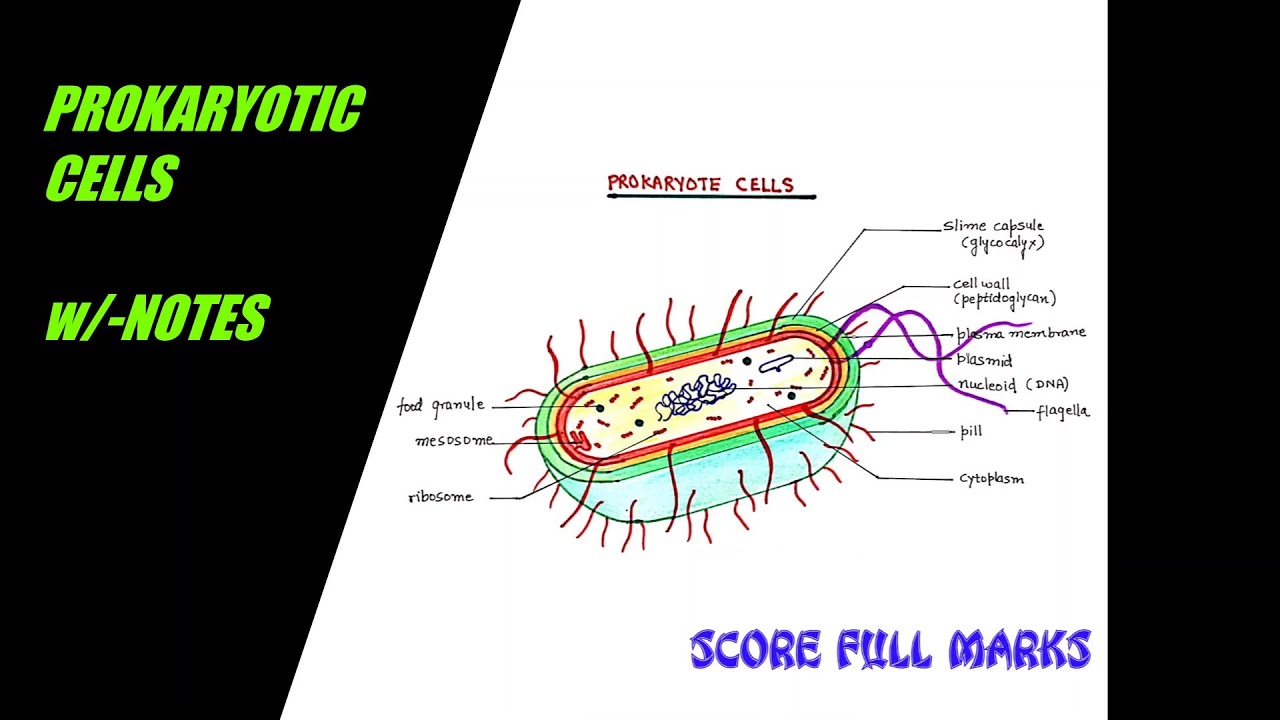
37 diagram of a prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotic Cells Diagram | Quizlet Prokaryotic Cells Diagram | Quizlet Prokaryotic Cells STUDY Learn Write Test PLAY Match Created by Mr_McFall TEACHER Terms in this set (7) Cilia ... Cell Wall ... Cell Membrane ... Flagella ... Ribosomes ... Cytoplasm ... DNA ... Sets found in the same folder Cell Organelles (Different Definitions T… 18 terms Mr_McFall TEACHER Animal Cell Diagram 1 Prokaryotic Cell Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Prokaryotic Cell. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Prokaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - Page 2 Prokaryotic Cell Diagram. to help you remember prokaryotes parts and pieces. - fimbriae: allow bacteria to adhere to target host cells, and play a major role in bacterial virulence. - conjugation pili: the tubes used to transfer plasmids from donor to recipient bacteria. This article has.
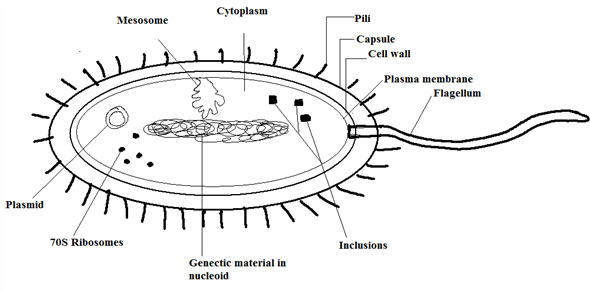
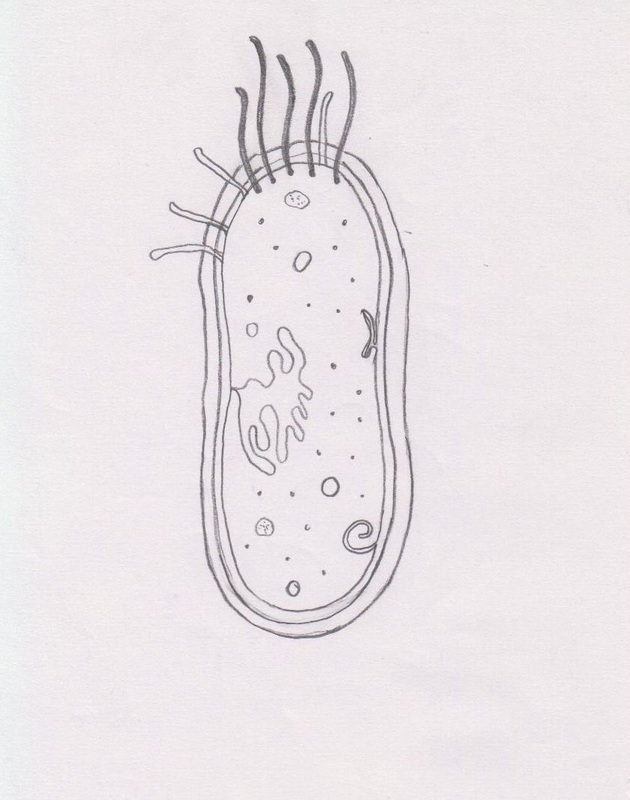
Diagram of a prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotic Cells: Structure, Function, and Definition They have no true nucleus as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell, but is coiled up in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell shapes. The most common bacteria shapes are spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral. PDF Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Venn Diagram Worksheet Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells . Title: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Venn Diagram Worksheet Author: Brandon Linn Created Date: 9/19/2018 6:59:56 PM ... PDF Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function Prokaryotes-CellShapes Most bacteria are classifies according to shape: 1. bacillus (pl. bacilli)= rod-shaped 2. coccus(pl. cocci… sounds like cox-eye)= spherical 3. spiral shaped a. spirillum(pl. spirilla) = spiral with rigid cell wall, flagella b. spirochete(pl. spirochetes)= spiral with flexible cell wall, axial filament
Diagram of a prokaryotic cell. Prokaryotes - Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells - Eduqas ... Prokaryotes Bacteria are amongst the simplest of organisms - they are made of single cells. Their cell structure is simpler than the cells of eukaryotes and cells are smaller, most are 0.2 μm - 2.0... › cells › bactcell_jsGet the Cell Model PowerPoints - CELLS alive Gram-positive Cell Wall. Gram-negative Cell Wall. Outer Membrane. Cytoplasmic Membrane. Membrane Proteins. Porin Prokaryotic cells Examples, Structure and Diagram - Jotscroll Prokaryotic cell labeled diagram showing the structures always present in all prokaryotes and those that are sometimes present Prokaryotic cell parts always present Cell wall Cell membrane Circular DNA Cytoplasm Ribosomes The above-listed parts of a prokaryotic cell are always present in all cells. Prokaryotic cell parts that are sometimes present Prokaryotic Cell: Definition, Features, Structure, Examples In 1957 Dougherty has divided cells into two types based on the organization in the nucleus of the cell. One is a prokaryotic cell (primitive cell) and the other is a Eukaryotic cell (ideal cell). Prokaryotic cells are the most primitive type and have no organized nucleus (lacking nuclear membrane, nucleolus, and nuclear reticulum).. The name Prokaryotic is derived from the Greek words Pro and ...
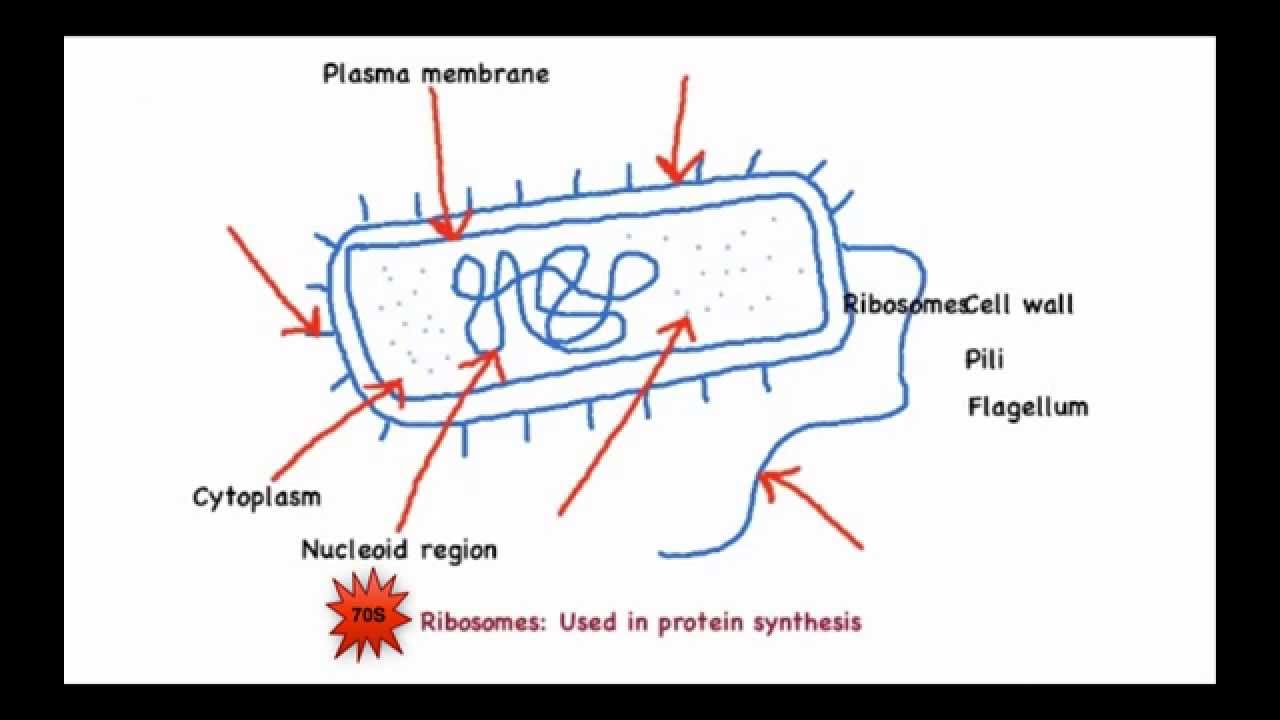
Prokaryotic cells (article) | Cells | Khan Academy The majority of prokaryotic is found in a central region of the cell called the nucleoid, and it typically consists of a single large loop called a circular chromosome. The nucleoid and some other frequently seen features of prokaryotes are shown in the diagram below of a cut-away of a rod-shaped bacterium. Prokaryote - Wikipedia Diagram of a typical prokaryotic cell A prokaryote ( / proʊˈkærioʊt, - ət /) is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό ( pro, 'before') and κάρυον ( karyon, 'nut' or 'kernel'). Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Prokaryotic Cells ... This figure shows the generalized structure of a prokaryotic cell. All prokaryotes have chromosomal DNA localized in a nucleoid, ribosomes, a cell membrane, and a cell wall. The other structures shown are present in some, but not all, bacteria. Most prokaryotes have a peptidoglycan cell wall and many have a polysaccharide capsule . The cell ... Prokaryote structure (article) | Khan Academy Structural features of prokaryotic cells. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Prokaryotic Cell - Definition, Examples & Structure ... Prokaryotic Cell Diagram The following image is a diagram of a prokaryotic cell; in this case, a bacterium. The Anatomy of a Bacterial Cell Prokaryotic Cell Structure Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus that contains their genetic material as eukaryotic cells do. Blank Prokaryotic Cell Diagram - schematron.org Basic Structures of Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotes, found in both Domain Archaea and Bacteria, are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles. Organisms that have prokaryotic cells are unicellular and called prokaryotes. The following image is a diagram of a prokaryotic cell; in this case, a bacterium. Structure of Prokaryotes | Boundless Biology Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack organelles or other internal membrane-bound structures. Therefore, they do not have a nucleus, but, instead, generally have a single chromosome: a piece of circular, double-stranded DNA located in an area of the cell called the nucleoid. Most prokaryotes have a cell wall outside the plasma membrane. scioly.org › wiki › indexCell Biology - Wiki - Scioly.org Oct 08, 2021 · While the cell membrane is essential to controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell, it also plays an important role in compartmentalizing the cell. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are surrounded by cell membranes, but eukaryotes also possess membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria or lysosomes. In these cases, the ...
Cell Structure: Prokaryotic Cells | Saylor Academy Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell: the nucleoid (Figure 4.5). Figure 4.5 This figure shows the generalized structure of a prokaryotic cell. All prokaryotes have chromosomal DNA localized in a nucleoid, ribosomes, a cell membrane, and a cell wall. The other structures shown are present in some, but not all, bacteria.
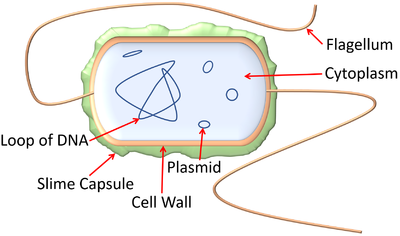
Prokaryotic cells Definition, Structure, Characteristics ... Structure of a prokaryotic cell. The prokaryotic cells is not so complex as cells of eukaryotic origin because they are cellular organelles. Most prokaryotic cells contain the following componentsor parts: Capsule. This is an extra external covering found in certain prokaryotic cells, which serves to guard the cells against foreign invaders.
› exams › prokaryotic-cellProkaryotic Cell: Definition, Functions, Diagram, Examples Prokaryotic Cell Definition. Prokaryotic cells are single-celled organisms that lacks a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. What is a Prokaryotic Cell? Prokaryotic cells are microorganisms that are known to be the earliest on earth. Kingdom Monera includes the prokaryotic cells. A teaspoon full of rich soil may contain billions of ...
Prokaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram Prokaryotic Cell Diagram to help you remember prokaryotes parts and pieces. Cytoskeleton: It's a relatively recent scientific discovery that rod-shaped bacteria and Archaea possess cytoskeletal proteins that function similarly to the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells.
microbenotes.com › plant-cellPlant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled ... Feb 16, 2022 · Eukaryotic cell sediment in the 90s while prokaryotic cell sediment in the 70s. Ribosomes found in the mitochondria and chloroplasts are as small as the prokaryotic ribosomes. Naturally, ribosomes are made up of two subunits i. e small and large subunits, both classified according to their sedimentation rates by the S unit.
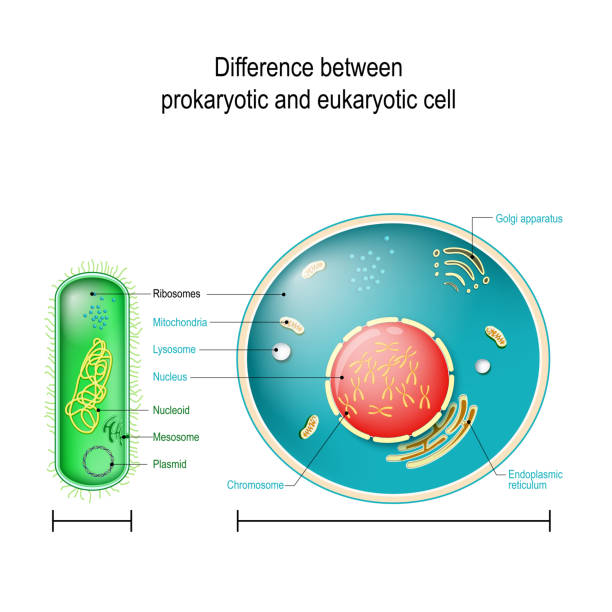
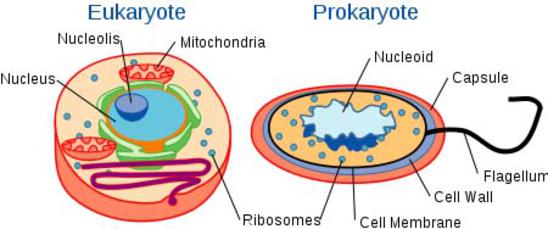
Structure of Prokaryotic Cells (2.1.5) | AQA A Level ... Animal and plant cells are types of eukaryotic cells, whereas bacteria are a type of prokaryote; Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells (between 100 - 1000 times smaller); They also differ from eukaryotic cells in having: A cytoplasm that lacks membrane-bound organelles; Their ribosomes are structurally smaller (70 S) in comparison to those found in eukaryotic cells (80 S)
Prokaryotic Cells: Structure, Components, Diagram and ... Diagram of a Prokaryotic Cell A bacterial cell is depicted in the prokaryotic cell diagram below. It is distinguished from a eukaryotic cell by the absence of a genuine nucleus and the presence of a flagellum. Diagram of a Prokaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell Components The four main components of prokaryotic cells are:
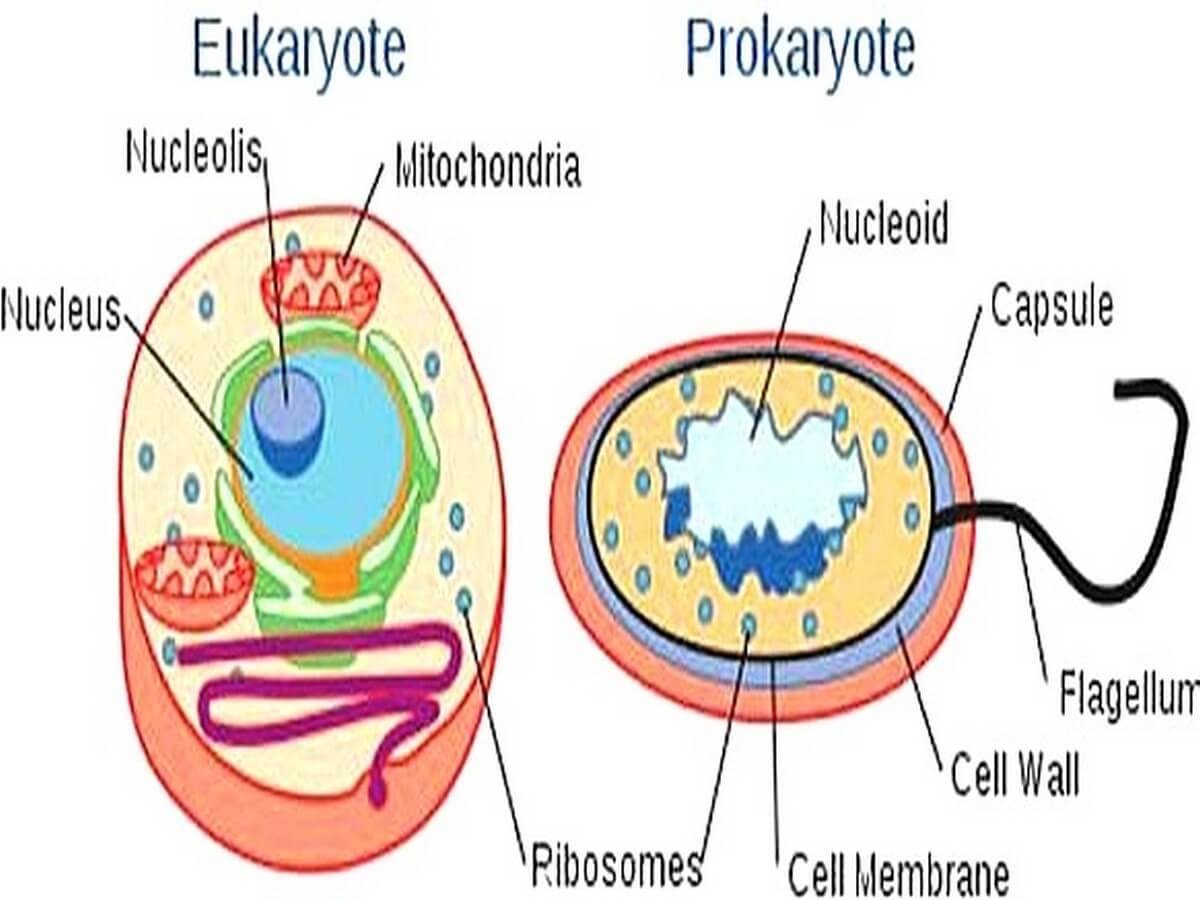
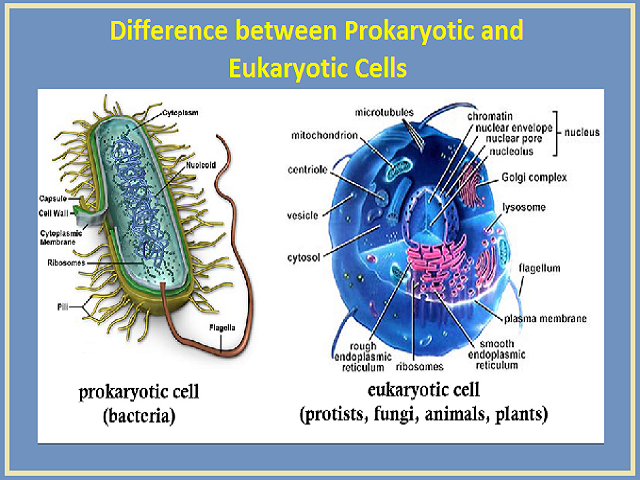
7.2: Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - Biology ... Cell Size. At 0.1-5.0 µm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10-100 µm (Figure 2). The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell. Similarly, any wastes produced within a prokaryotic ...
Structure of Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea ... The Prokaryotic Cell. Recall that prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles or other internal membrane-bound structures (Figure 2). Their chromosome—usually single—consists of a piece of circular, double-stranded DNA located in an area of the cell called the nucleoid. Most prokaryotes have a cell wall outside ...
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes - Cell structure - AQA - GCSE ... Eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Bacteria are amongst the simplest of organisms - they are made of single cells. Their cell structure is simpler than the cells of animals, plants and fungi.
byjus.com › biology › prokaryotic-cellsProkaryotic Cells- Definition, Structure, Characteristics ... The prokaryotic cell diagram given below represents a bacterial cell. It depicts the absence of a true nucleus and the presence of a flagellum that differentiates it from a eukaryotic cell. Prokaryotic Cell Diagram illustrates the absence of a true nucleus Components of Prokaryotic Cells The prokaryotic cells have four main components:
micro.magnet.fsu.edu › cells › bacteriacellMolecular Expressions Cell Biology: Bacteria Cell Structure Nov 13, 2015 · Cell Envelope - The cell envelope is made up of two to three layers: the interior cytoplasmic membrane, the cell wall, and -- in some species of bacteria -- an outer capsule. Cell Wall - Each bacterium is enclosed by a rigid cell wall composed of peptidoglycan, a protein-sugar (polysaccharide) molecule. The wall gives the cell its shape and ...
Prokaryotic Cell- Definition, Structure, Diagram, Example ... Prokaryotic Cell Diagram: it's far a bacterial mobile, which is prokaryotic. Prokaryotic Cell Parts: Prokaryotic cells, not like eukaryotic cells, lack a real nucleus that houses their genetic material. Prokaryotic cells, then again, have a nucleoid region, that is an irregularly formed area containing the cellular's DNA and is not ...
Differences Between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell ... Prokaryotic cells are comparatively smaller and much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus. ... In structure, both animal and plant cells are quite similar.
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe 13. Lysosomes are the single membranous structure filled with digestive enzymes which helps to digest worn-out cells and foreign bacteria and viruses. 14. Vacuoles are the membrane-bound structure present in the eukaryotic cell.In animal cells, there are numerous small vacuoles while in plant cells large vacuoles are present. Large vacuoles help in maintaining water balance and keep the cell ...
PDF Prokaryotic Cell Structure & Function Prokaryotes-CellShapes Most bacteria are classifies according to shape: 1. bacillus (pl. bacilli)= rod-shaped 2. coccus(pl. cocci… sounds like cox-eye)= spherical 3. spiral shaped a. spirillum(pl. spirilla) = spiral with rigid cell wall, flagella b. spirochete(pl. spirochetes)= spiral with flexible cell wall, axial filament
PDF Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Venn Diagram Worksheet Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells . Title: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Venn Diagram Worksheet Author: Brandon Linn Created Date: 9/19/2018 6:59:56 PM ...
Prokaryotic Cells: Structure, Function, and Definition They have no true nucleus as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell, but is coiled up in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell shapes. The most common bacteria shapes are spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bacteria_cell_drawing-5786db0a5f9b5831b54f017c.jpg)










/shigella-bacteria--illustration-758308491-5a02252f9e9427003c1759be.jpg)








0 Response to "37 diagram of a prokaryotic cell"
Post a Comment