35 electron positron annihilation feynman diagram
Career and Contributions [ edit ] A Feynman diagram showing an electron annihilating with a positron creating two gamma rays. Consider the process of annihilation of an electron-positron pair into two gamma rays, as shown in figure 7.9 . This is the lowest order in in which this process can occur, since pair annihilation to a single photon cannot conserve energy and momentum: but . The diagrams can be view as Compton scattering turn on its side.
Electron-positron annihilation in classical electrodynamics ... Left side of this diagram is the same for annihilation into pairs of muons The ratio of cross sections is called R . ... Feynman, Yang, Bjorken •Quark content of the proton and neutron led to a question how
Electron positron annihilation feynman diagram
In the Stückelberg-Feynman interpretation, pair annihilation is the same process as pair creation. Møller scattering. electron-electron scattering. Bhabha scattering. electron-positron scattering. Penguin diagram. a quark changes flavor via a W or Z loop. Tadpole diagram. One loop diagram with one external leg. Download scientific diagram | Feynman diagram for the electron positron Annihilation into a photon followed by photon Disintegration into an electron ... The positron is the electron going back in time. This is what the arrow means. But you have to remember that in physics, cause and effect are not by the direction of the arrows, but by the direction of entropy increase, which is up in the diagram regardless of which way the particles go relative to their own proper time.
Electron positron annihilation feynman diagram. Figure 8: A Feynman diagram demonstrating an annihilation of an electrons (e–) and a positron (e+) into a photon (γ) that produces a bottom quark (b) and anti- ... An internal line in a Feynman diagram represents the exchange of a virtual particle. In this diagram, there is a virtual electron / positron involved in the process. A virtual particle is a short lived excitation which is allows you to realize a sub-process which would normally violate energy and momentum conservation, so long as at the end of ... Electron positron annihilation into W bosons ... Generate Feynman diagrams. Nicer typesetting. ... The Higgs diagram is needed to cancel the divergence that goes like m_e*Sqrt[s] in the high energy limit. If we neglect the electron mass, then this particular diagram does not contribute. ... on R value in electron positron annihilation ... Electron-positron annihilation diagram ... Feynman diagram of electron and positron annihilation
Diagram (d) shows the process of positron-electron annihilation, e ... Feynman diagram for the process of photon-electron scattering. 1 This process is electron-photon scattering, known as the Compton effect. When it was discovered by Arthur Compton in 1923, it added strong support to the photon concept of light. ... Electron–positron annihilation - Quantum Electrodynamics, Mathematical ... Great introduction to particle physics by learning to draw Feynman diagrams. Is electron-positron annihilation time reversible? Is electron-positron annihilation time reversible? ... Feynman diagram for the $phi^3$ scalar Field ... Electron positron annihilation feynman diagram. Electron positron annihilation is the process in which a positron collides with an electron resulting in the annihilation of both particles. Ask question asked 3 years 4 months ago. Schroeder 29 october 2002. Photon can pair produce an electron and a positron. Active 3 years 4 months ago.
Feynman diagram of the annihilation of an electron (e −) by a positron (e +)The annihilation of the particle-antiparticle pair leads to the formation of a muon (μ −) and an antimuon (μ +). Both antiparticles (e + and μ +) are represented as particles moving backward in time; that is, the arrowheads are reversed. Electron Positron Annihilation e- e+ Consider the process: e+e- + - - •Work in C.o.M. frame (this is appropriate for most e+e- colliders). •Only consider the lowest order Feynman diagram: e- - e+ Feynman rules give: NOTE: •Incoming anti-particle •Incoming particle •Adjoint spinor written first •In the C.o.M. frame have ... Just a quick question regarding the tree level Feynman diagram(s) contributing to this process - I am wondering if I wanted to compute the ... Feynman diagram of electron-positron annihilation ... In my mind he is always connected to Feynman diagrams, but one of the more amazing things about ...
Tree Level Feynman Diagrams of Electron Positron Interaction 7 Why does an electron react differently to a virtual photon in the interaction between two electrons and between an electron and a positron?
Particle Annihilation Feynman Diagrams Explained by James Dann for CK12.org CC-BY-SA.
Electron-Positron Annihilation D. Schroeder, 29 October 2002 ... Interpretation of Bhabha'sformula (R. P. Feynman, 1949): =(const.) × 2 Each diagram representsa complex number that dependson E and
Feynman used Ernst Stueckelberg's interpretation of the positron as if it were an electron moving backward in time.
Feynman Diagrams Feynman Rules The Calculation Spin Higher-Order Diagrams Extensions and Further Examples Turning Amplitudes into Probabilities Other QED Processes Inventory of Particles and Interactions Electron-Positron Annihilation into Hadrons Lepton-Hadron and Hadron-Hadron Collisions Here is a large ...
Electron-positron annihilation to two photons Feynmann diagramms for the electron -positron annihilation in two photons: (43) Matrix elements can be evaluated similar to Compton scattering, but with the substitution: (44)
Feynman diagrams are symbolic representations for interactions among elementary particles. ... Feynman diagram can represent alternative sequences of ...
Example 2: Electron-positron annihilation into fermions ... where the electron-positron pair fuses into a gauge ... There are two Feynman diagrams The two internal lines, on the amplitude level, behave like if M is the mass of the particle and Γ is its width.
Feynman diagram for annihilation. So if you are more familiar with viewing feynman diagrams where time increases to the right this problem is easily solved. This is an annihilation of a positron and an electron. Just rotate the diagram by 90 degrees when you are interpreting it.
Feynman diagram of the annihilation of an electron e by a positron e the annihilation of the particle antiparticle pair leads to the formation of a muon μ and an antimuon μ. Electron positron annihilation is the process in which a positron collides with an electron resulting in the annihilation of both particles. Feynman Diagrams.
A Feynman diagram represents a perturbative contribution to the amplitude of a quantum transition from some initial quantum state to some final quantum state. For example, in the process of electron-positron annihilation the initial state is one electron and one positron, the final state: two photons.
Feynman diagram of the annihilation of an electron e by a positron e the annihilation of the particle antiparticle pair leads to the formation of a muon μ and an antimuon μ. Positrons are the antimatter equivalent of an electron produced from b decay. Both antiparticles e and μ are represented as particles moving backward in time.
... Feynman, this isn’t Neville.) Then he goes on to say: ... Time runs left to right in this Feynman diagram of electron–positron annihilation.
A Feynman diagram for electron-positron annihilation. ... Feynman, pictured above, imagined a way of thinking in which there is only one electron : ...
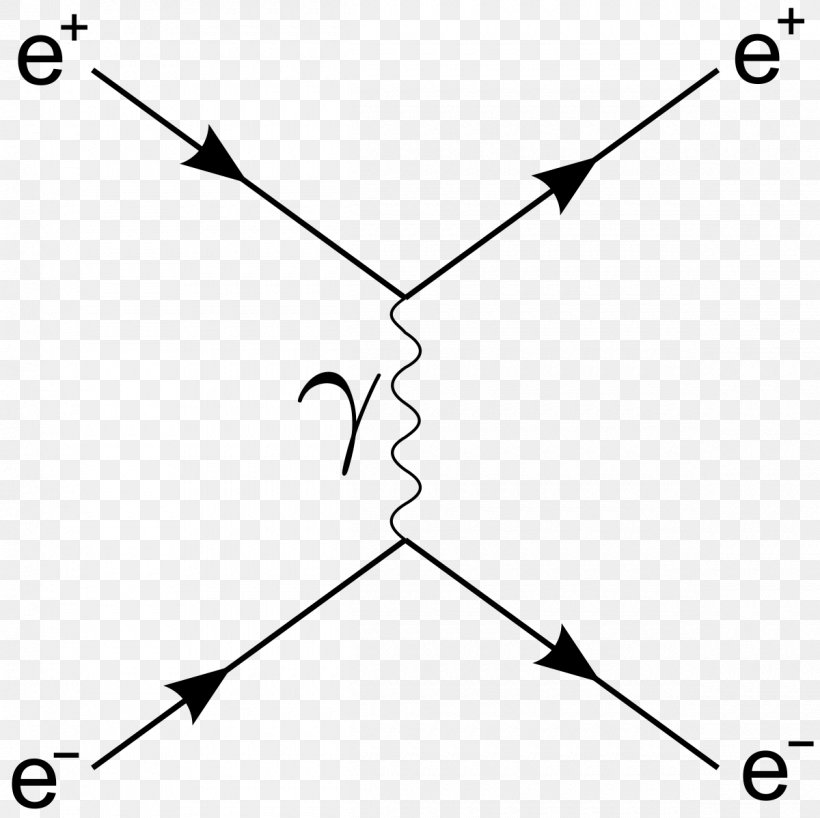
Feynman Diagram Bhabha Scattering Electron Positron Annihilation Png 1200x1198px Feynman Diagram Area Beak Bhabha Scattering Black
The positron is the electron going back in time. This is what the arrow means. But you have to remember that in physics, cause and effect are not by the direction of the arrows, but by the direction of entropy increase, which is up in the diagram regardless of which way the particles go relative to their own proper time.
Download scientific diagram | Feynman diagram for the electron positron Annihilation into a photon followed by photon Disintegration into an electron ...
In the Stückelberg-Feynman interpretation, pair annihilation is the same process as pair creation. Møller scattering. electron-electron scattering. Bhabha scattering. electron-positron scattering. Penguin diagram. a quark changes flavor via a W or Z loop. Tadpole diagram. One loop diagram with one external leg.




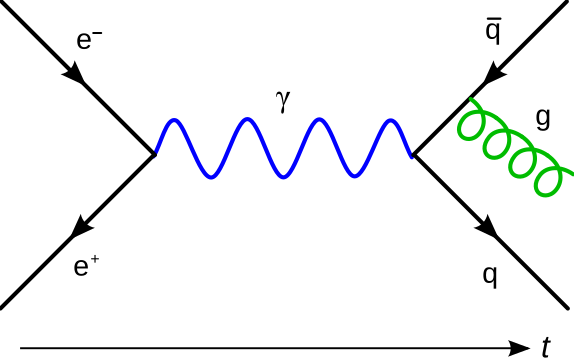

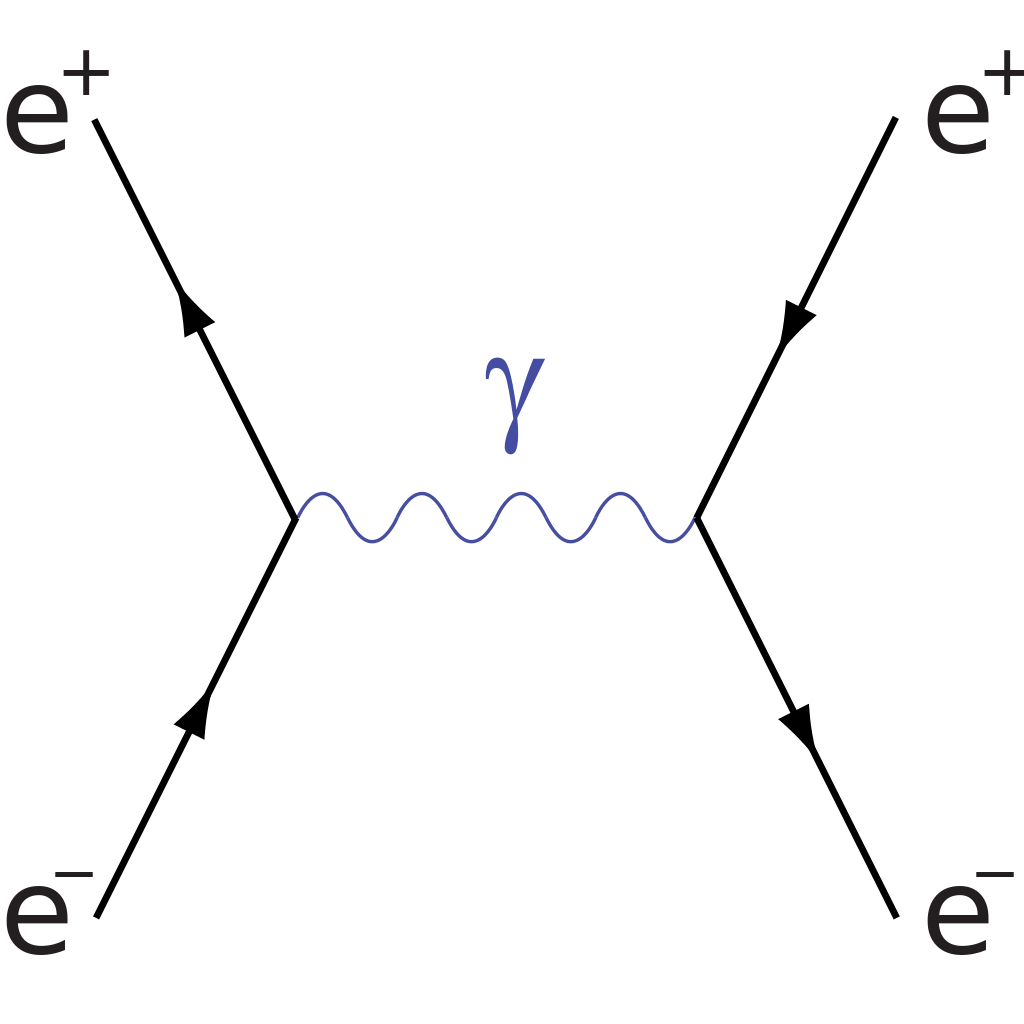

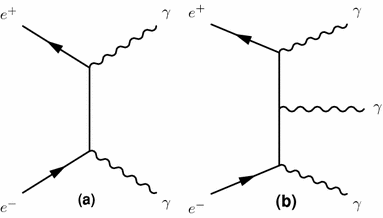














0 Response to "35 electron positron annihilation feynman diagram"
Post a Comment