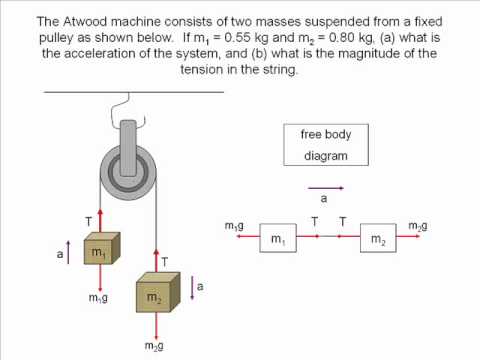
35 free body diagram problem
Free Body Diagrams. A free body diagram is a tool used to solve engineering mechanics problems. As the name suggests, the purpose of the diagram is to "free" the body from all other objects and surfaces around it so that it can be studied in isolation. We will also draw in any forces or moments acting on the body, including those forces and ... Free Body Diagram Problem. Ask Question Asked 4 years, 11 months ago. Active 1 year, 10 months ago. Viewed 367 times 3 $\begingroup$ I'm having trouble with this problem: G and a are given, and we are asked to calculate A, B and C. What I've Done: The first thing I tried was a free body diagram cutting through A and C to create one body and C ...
Free-Body Diagram allows students to clearly visualize a particular problem in its entirety or closely analyze a particular portion of a more complex problem. So basically, FBD is a very useful aid to visualize and solve engineering problems. Note that, for solving a complex problem, a series of free body diagrams may be required.

Free body diagram problem
Learn how to solve problems that have Free Body Diagrams!Want Lecture Notes? http://www.flippingphysics.com/5-steps-fbd.htmlThis is an AP Physics 1 topic.0:0... If there are two or more objects, or bodies, in the problem, draw a separate free-body diagram for each object. Note: If there is acceleration, we do not directly include it in the free-body diagram; however, it may help to indicate acceleration outside the free-body diagram. You can label it in a different color to indicate that it is separate from the free-body diagram. Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air resistance.
Free body diagram problem. To solve problems using Newton laws of motion, we need to learn the concept of free the body diagrams. This is to identify all the forces acting on the body but will never consider the force is applied by the body. It is simply because forces acting on the body will cause the motion on the body but the force is applied by the body will cause the motion on some other body. Learn how to solve problems that have Free Body Diagrams! This is an AP Physics 1 topic. Content Times: 0:15 Step 1) Draw the Free Body Diagram 0:50 Step 2) Break Forces into Components 1:37 Step 3) Redraw the Free Body Diagram 2:15 Step 4) Sum the Forces 2:45 Step 5) Sum the Forces (again) 3:13 Review the 5 Steps Multilingual? Please help translate Flipping Physics videos! Practice Problems. Explanation Free body diagrams are always represented in the form of two-dimensional figures, which consist of the 'X' and 'Y' axis. In classical mechanics, 3D representations are not preferred at least at the basic level, to maintain simplicity for solving problems. The three main aspects that need to be considered ... Free-Body Diagram: Pulley C PROBLEM 2.69 A load Q is applied to the pulley C, which can roll on the cable ACB. The pulley is held in the position shown by a second cable CAD, which passes over the pulley A and supports a load P. Knowing that P = 750 N, determine (a) the tension in cable ACB, (b) the magnitude of load Q Hence: -O: TAcB(cos250 (750
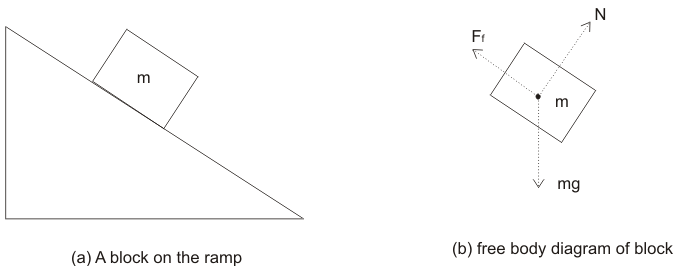
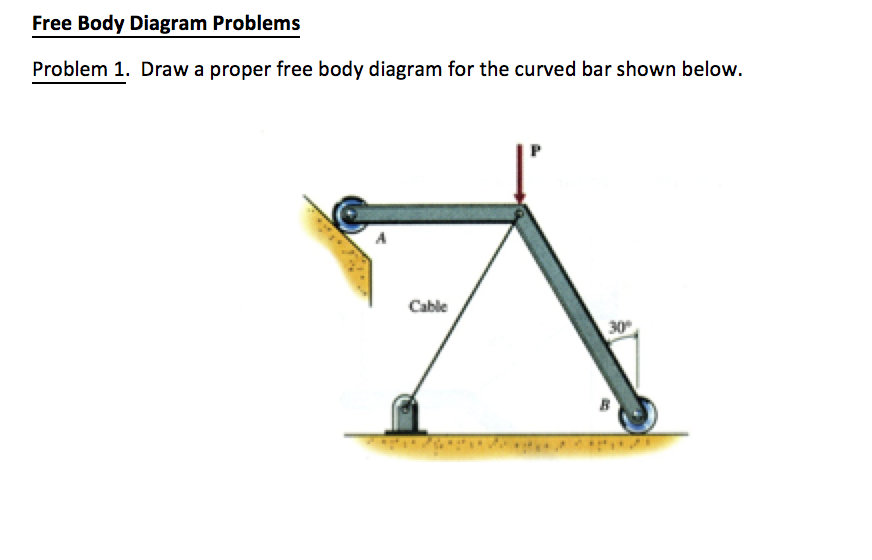
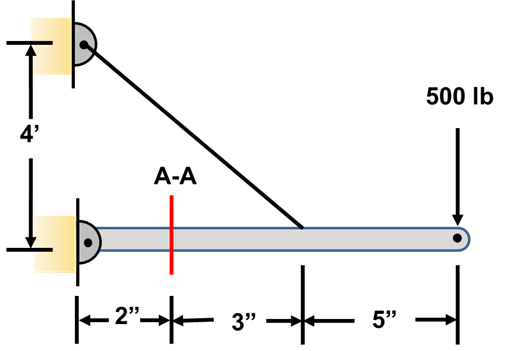
calculate electric force with electroscope leaves body free diagram MC Q for electrostatic grounding in the problems of electrostatics charge indution charging a three sphere a b -two -single -earth ground in electrostatics problem electrostatics free body diagram electroscope and coulomb free body diagram electrostatic diagram and with problems As usual, we should begin with a diagram of the situation. A free-body diagram is also very helpful. These are shown in Figure 9.7. (a) On the block's free-body diagram, we draw a downward force of gravity, applied by the Earth. We also draw an upward force of tension (applied by the string), and, because the block displaces some fluid, an upward A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram: Free Body Diagram Problems Problem 1. Draw a proper free body diagram for the curved bar shown below. Problem 2. Draw a proper free body diagram for the cart of weight W shown below. Cable . Question: Free Body Diagram Problems Problem 1. Draw a proper free body diagram for the curved bar shown below. Problem 2.
FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape. 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) the weight of the body, and c) support reactions (can be difficult). Free-Body Diagram. Solving the Free-Body Diagram In order to solve the problem, the force on the rope necessary to move the box up the incline must be found. This is the tension force. Finding this force requires a system of equations. Although there is currently one known variable, the weight, there are three unknown variables; therefore, Free-Body Diagram Example Problem 3 Bank robbers have pushed a 1000 [kg] safe to a second-story floor-to-ceiling window. They plan to break the window, then lower the safe 4.0 [m] to their truck. Not being too clever, they stack up 600 [kg] of furniture, tie the rope between the safe and the furniture, and place the rope over a pulley. Introduction to forces and free body diagrams review Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization.

Problem 3 1 In Active Example 3 1 Suppose That The Free Body Diagram Is Shown The Equilibrium Exerts And The Force P Exerted On The Tension In The Cable Is 1 Kn A
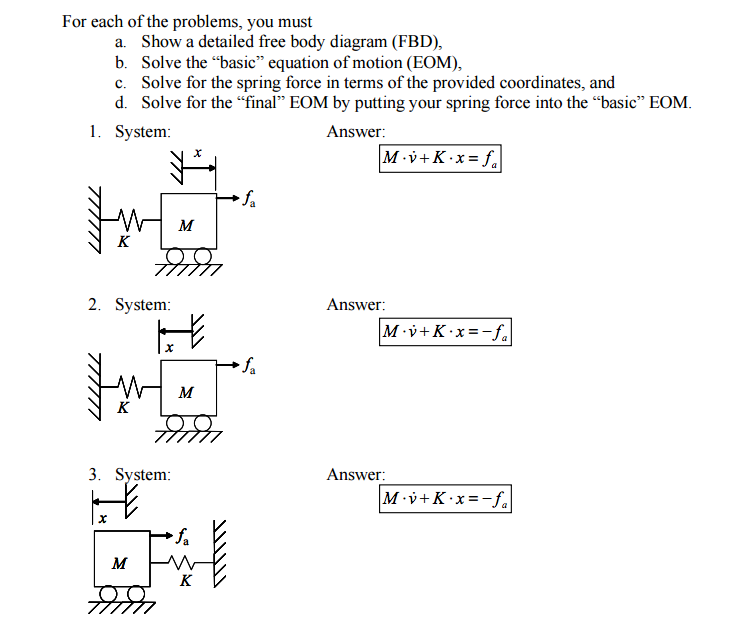
This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Please include FBD (Free Body Diagram), EoE (Equations of Equilibrium) and all that apply on the list attached (System, Parameters, Assumptions, Tasks, Governing Relations, and of course the Solutions)
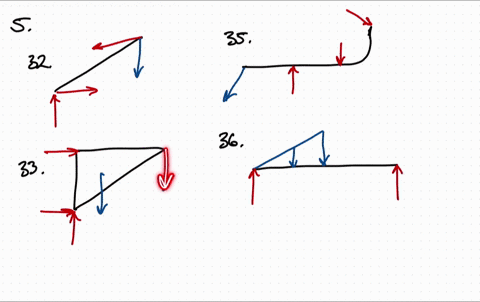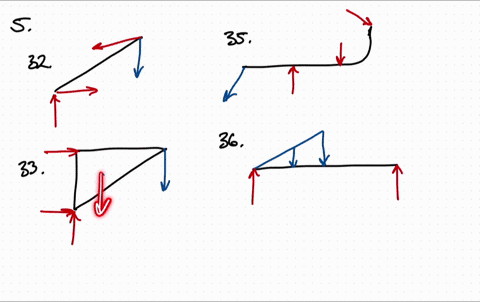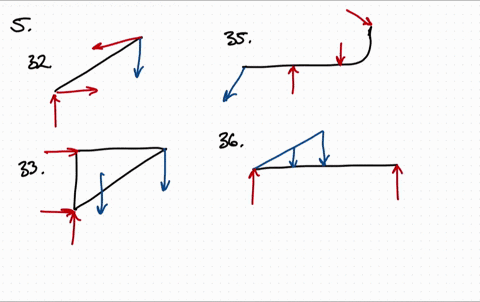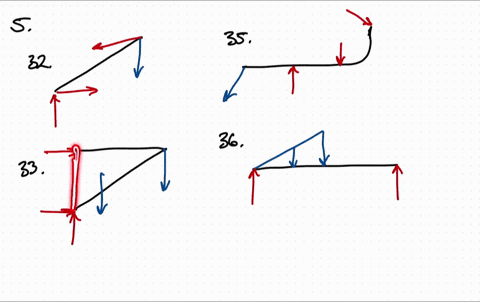
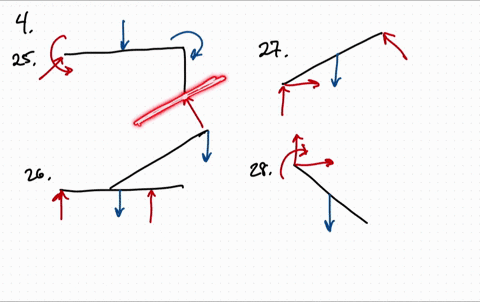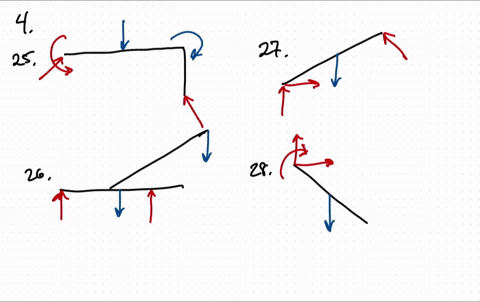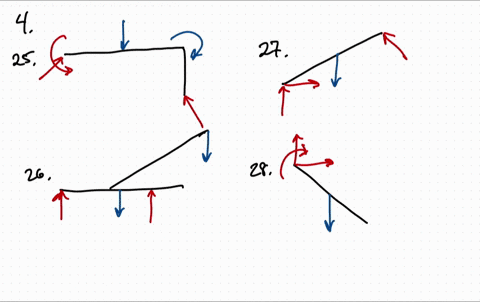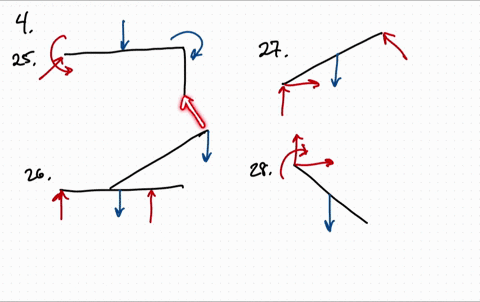
Solved Draw The Free Body Diagram For The Following Problems A The Beam In Prob 5 25 B The Crane And Boom In Prob 5 26 C The Bar In Prob 5 27 D The Rod In
Convert the free-body diagram into a more detailed diagram showing the x- and y-components of a given force (this is often helpful when solving a problem using Newton's first or second law). In this case, place a squiggly line through the original vector to show that it is no longer in play—it has been replaced by its x - and y -components.
• No equilibrium problem should be solved without first drawing the free-body diagram, so as to account for all the external forces and moments that act on the body. • If a support prevents translation of a body in a particular direction, then the support exerts a force on the body
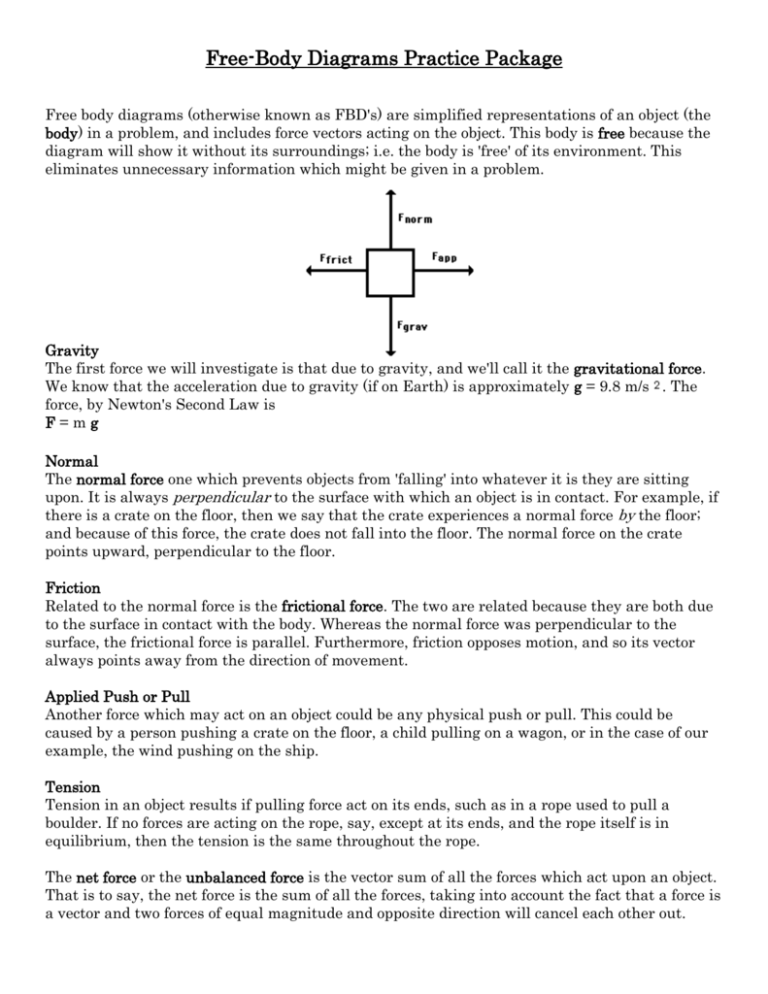
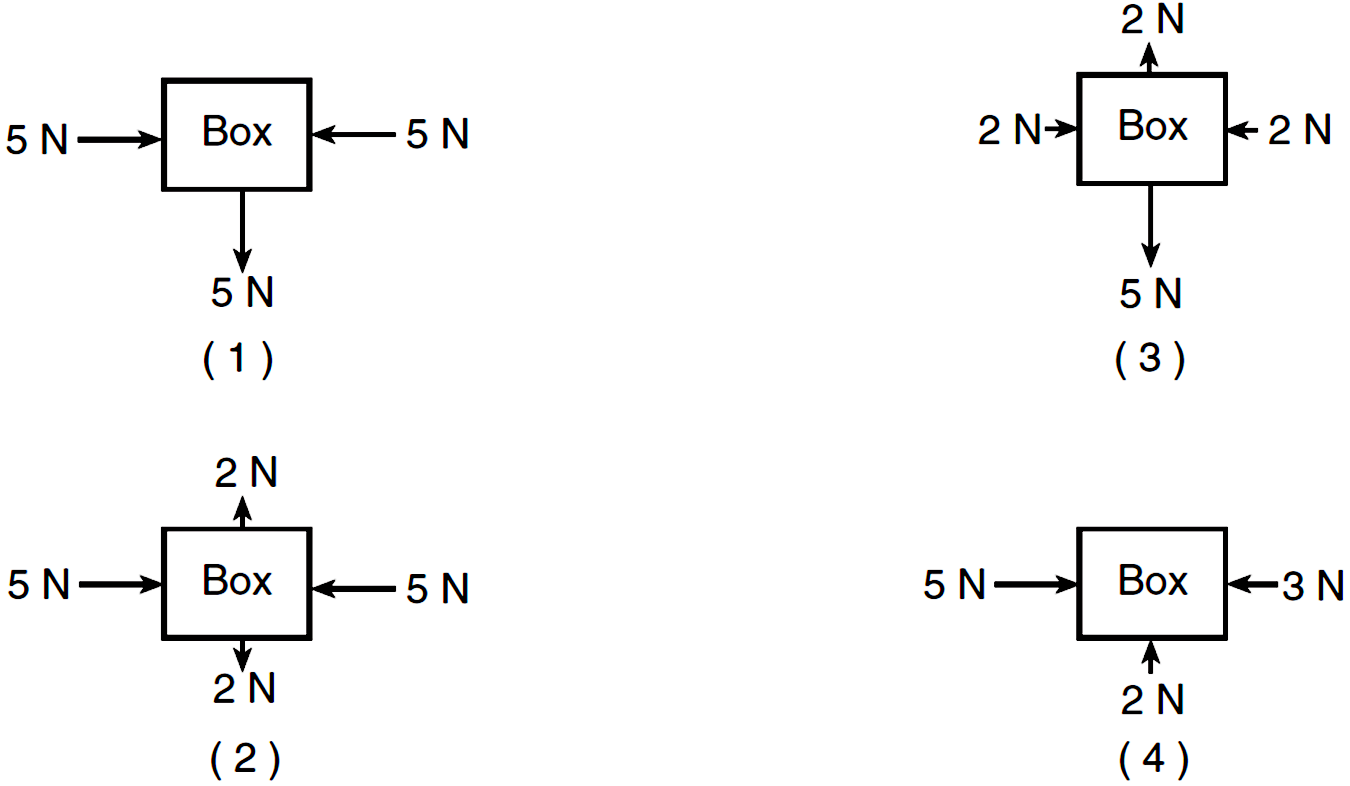
Free body diagrams (otherwise known as FBD's) are simplified representations of an object (the body) in a problem, and include force vectors acting on the object. This body is free because the diagram will show it without its surroundings; i.e. the body is 'free' of its environment. This eliminates unnecessary information which might be given ...
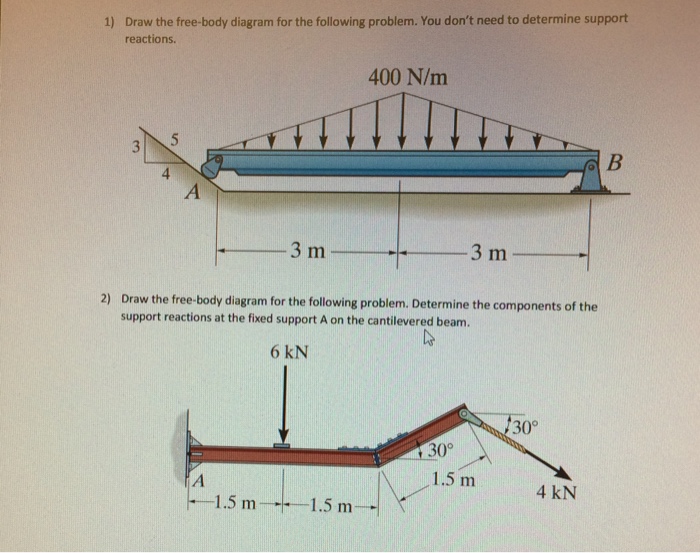
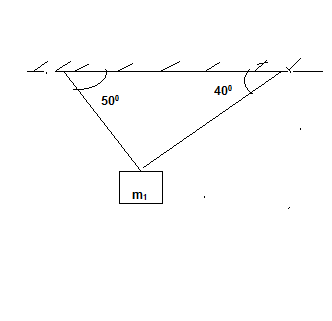
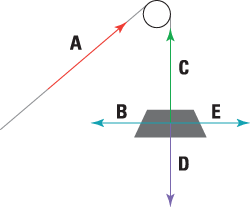
Q#1: For the following problem, use the graphical or analytical approach In the mechanism shown, sketch a free-body diagram of each link, and determine the force P that is necessary for equilibrium if T12=90 N-m and 2 = 90°. B E 3 T2 F А, Р 4 CD = 125 mm AD = 60 mm ED = 200 mm EF = 400 mm AB = 100 mm BC = 150 mm
One of the most useful aids for solving a statics problem is the free bodydiagram (FBD). A free body diagram is a graphic, dematerialized, symbolicrepresentation of the body (structure, element or segment of an element)in which all connecting "pieces" have been removed. A FBD is aconvenient method to model the structure, structural element, or segmentthat is under scrutiny.
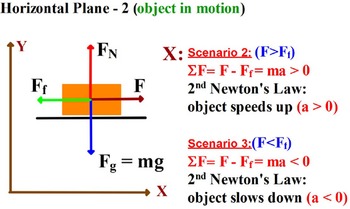
So the free-body diagram for the system now includes four forces - the same three as in Example Problem 1 plus a leftward force of friction. The force of friction on the system can be calculated as μ•F norm where F norm is the normal force experienced by the system.
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn.
Convert the free-body diagram into a more detailed diagram showing the x- and y-components of a given force (this is often helpful when solving a problem using Newton's first or second law). In this case, place a squiggly line through the original vector to show that it is no longer in play—it has been replaced by its x - and y -components.
A free-body diagram is a way to visually inventory these forces, and helps with developing the algebraic equations needed to solve these types of problems. There are five rules for drawing free ...

Figure 5 From Drawing And Using Free Body Diagrams Why It May Be Better Not To Decompose Forces Semantic Scholar
If there is acceleration in the system, then draw and label the acceleration vector. Common Mistakes made while drawing a free body diagram. Avoid drawing forces of the object acting on other objects. The direction of the different types of forces is denoted wrong. The direction of different forces:

Gm Before Free Body Diagram The Equation Of Motion Problems And Solutions High Efficiency Learning Of Physics Book 1 Mathew Dr George Amazon Com
Free Body Diagrams on Brilliant, the largest community of math and science problem solvers.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air resistance.
If there are two or more objects, or bodies, in the problem, draw a separate free-body diagram for each object. Note: If there is acceleration, we do not directly include it in the free-body diagram; however, it may help to indicate acceleration outside the free-body diagram. You can label it in a different color to indicate that it is separate from the free-body diagram.
Learn how to solve problems that have Free Body Diagrams!Want Lecture Notes? http://www.flippingphysics.com/5-steps-fbd.htmlThis is an AP Physics 1 topic.0:0...

Carlos Plascencia Kami Export Free Body Diagrams Lab Practice 1 Pdf Unit 3b Free Body Diagrams Name Carlos Plascencia Free Body Diagram Stations Course Hero














0 Response to "35 free body diagram problem"
Post a Comment