38 photosystem 1 and 2 diagram
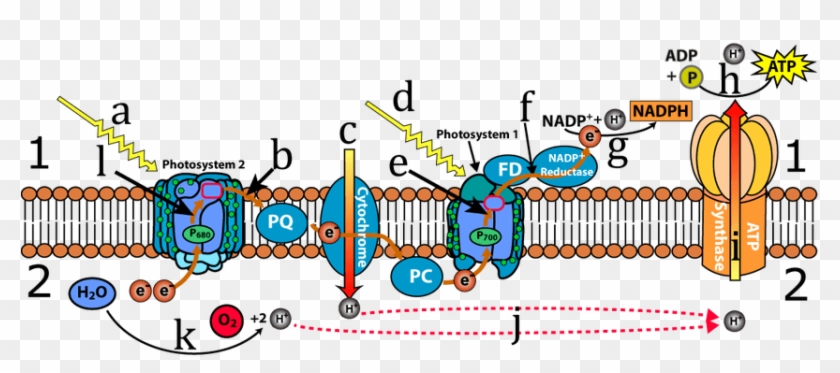
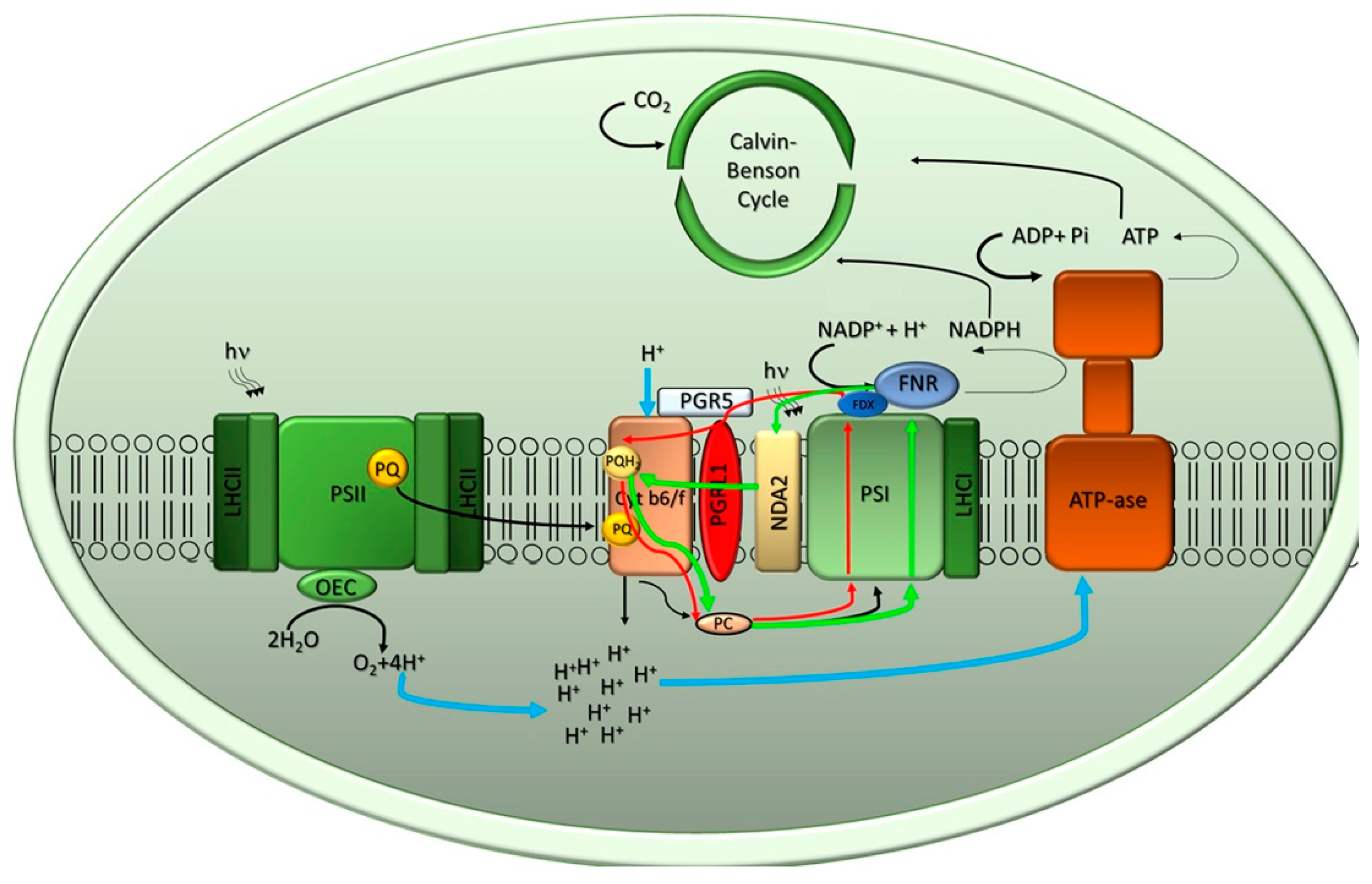
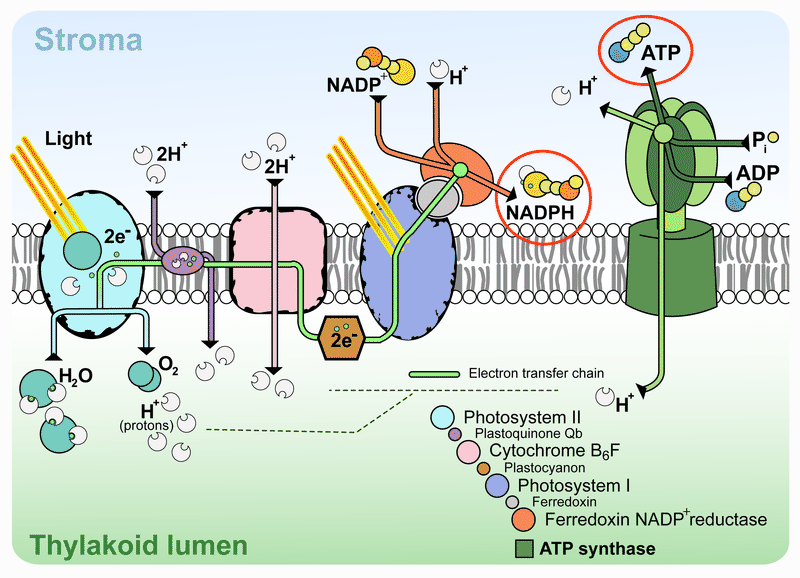
Download scientific diagram | 1. Diagram of photosystem II (PS II) representing the polypeptide composition, electron transport carriers and light-driven ... 1 2 O 2 + 2 H + H+ H + +H H H+ H+ H H+ H+ Photosystem II Electron transport chain Photosystem I ATP synthase Thylakoid space (high H+ concentration) Summary of the “Light” Reactions. 3. Light-independent (“Dark”) Reactions. The “Dark” Reactions A series of reactions called the Calvin cycle
1 Reaction centers · 2 Structure of PSI and PSII · 3 In oxygenic photosynthesis · 4 Photosystem Repair; 5 See also; 6 References ...
Photosystem 1 and 2 diagram
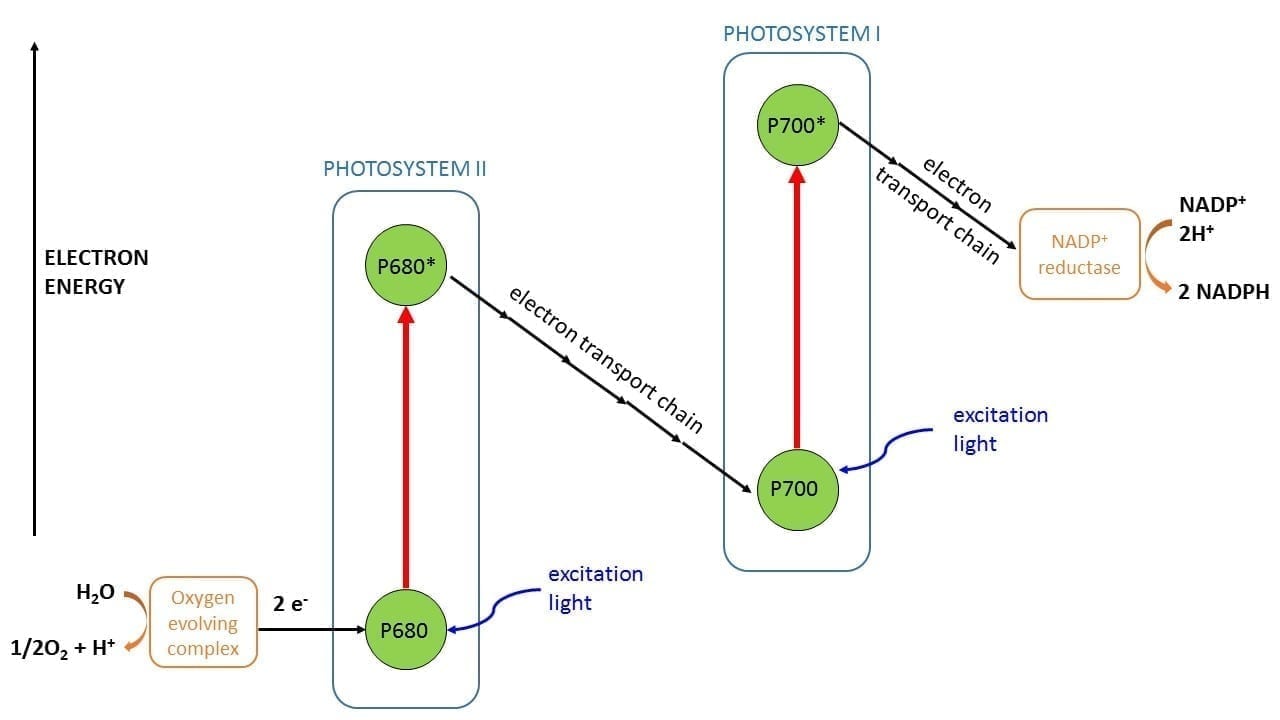
Regarding your questions #1 ("Is the primary pigment reaction centre in both photosystems a pair of chlorophyll a molecules?") and #3 ("How can it be that it absorbs at a different wavelength in the two photosystems if it is the same molecule?"Both reaction centers in Photosystem I and Photosystem II contain only chlorophyll a. According to Lodish (Molecular Cell Biology): Photosystem constitutes two main parts. Antenna Complex: It is a light- harvesting complex which comprises proteins and many molecules of cholorophyll a, cholorophyll b and carotenoids. Reaction Center: It has one or more molecules of cholorophyll a along with primary electron acceptor and associated electron carriers of electron transport system. PC. What happens as the electron goes the ETC. The energy state lowers as the electron travels through proteins and is absorbed by ATP. What is the main function of B6F complex. To get the electron from photosystem 2 to photosystem 1. Where is this photon from. An outside source (sun) What is the function of P700.
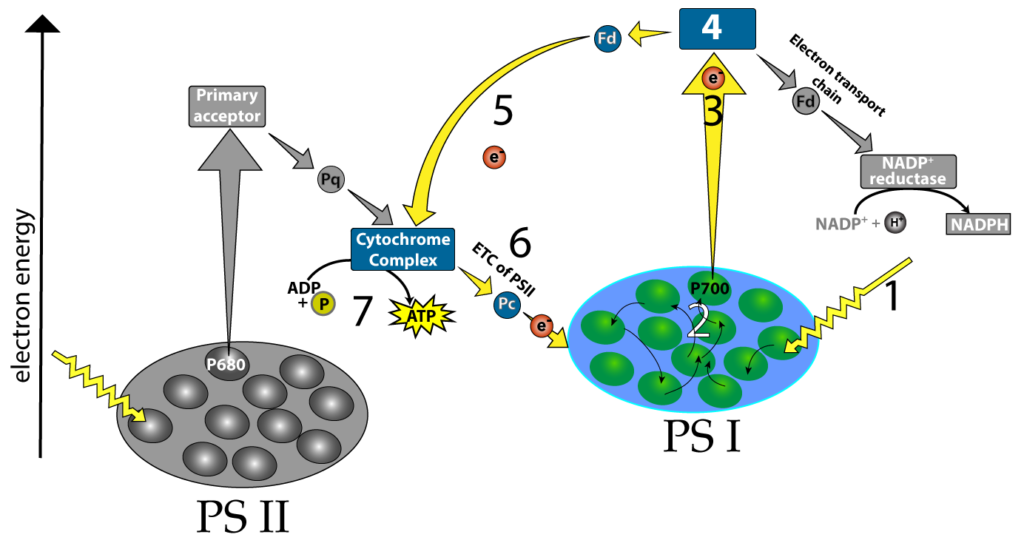
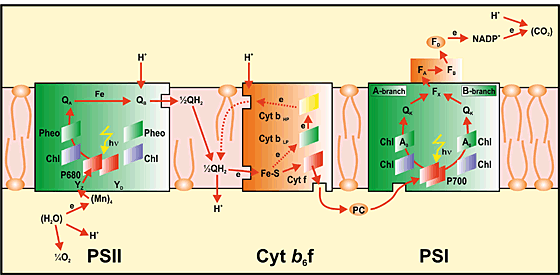
Photosystem 1 and 2 diagram. 1. PHOTOSYSTEM STRUCTURE. 1.1. Brief Overview on the Evolution and Structure of the Plant Photosystem Reaction Centers. ... Most common values to describe the successive reaction leading to oxidation of Pheo – and reduction of Q A, are in the range of 2-10 ns-1 (e.g., 62, 201, 209-211, 215, ... The Electron Transport Pathway from Water (H 2 O) to NADP+ (the Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate, oxidized form). Many versions of the Z-scheme are available in the literature.This particular diagram was developed by Wilbert Veit and Govindjee, 2000, and can be also found at molecadv.com. ... Photosystem I or PS 1 contains chlorophyll A-670, chlorophyll A-680, chlorophyll A-695, chlorophyll A-700, chlorophyll B, and carotenoids. Photosystem II or PS 2 contains chlorophyll A-660, chlorophyll A-670, chlorophyll A-680, chlorophyll A-695, chlorophyll A-700, chlorophyll B, xanthophylls and phycobilins. The light-dependent reactions involve two photosytems (II and I) and an electron transport chain that are all embedded in the thylakoid membrane. Light that is harvested from PSII causes an excited electron of the chlorophyll. a. special pair to be passed down an electron transport chain (Pq, Cyt, and Pc) to PSI.
Difference # Photosystem I (PS I): 1. Photosystem I (PS I) is involved in the cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation. 2. Photosystem I (PS I) receives the electrons from photosystem II. This system produces a strong reductant which reduces NADP+ to NADPH 2. 3. Molecular oxygen is not evolved in this system. 4. Main Difference – Photosystem 1 vs 2. Photosystem I (PS I) and photosystem II (PS II) are two multi-subunit membrane-protein complexes involved in oxygenic photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is the pigment involved in capturing light energy. PS 1 contains chlorophyll B, chlorophyll A-670, Chlorophyll A-680, chlorophyll A-695, chlorophyll A-700 and carotenoids. The structural and photochemical properties of the minimum particles capable of performing light reactions I and II have received much study. Treatment of ... PC. What happens as the electron goes the ETC. The energy state lowers as the electron travels through proteins and is absorbed by ATP. What is the main function of B6F complex. To get the electron from photosystem 2 to photosystem 1. Where is this photon from. An outside source (sun) What is the function of P700.
Photosystem constitutes two main parts. Antenna Complex: It is a light- harvesting complex which comprises proteins and many molecules of cholorophyll a, cholorophyll b and carotenoids. Reaction Center: It has one or more molecules of cholorophyll a along with primary electron acceptor and associated electron carriers of electron transport system. Regarding your questions #1 ("Is the primary pigment reaction centre in both photosystems a pair of chlorophyll a molecules?") and #3 ("How can it be that it absorbs at a different wavelength in the two photosystems if it is the same molecule?"Both reaction centers in Photosystem I and Photosystem II contain only chlorophyll a. According to Lodish (Molecular Cell Biology):

Pdf Molecular Mechanism Of Oxidation Of P700 And Suppression Of Ros Production In Photosystem I In Response To Electron Sink Limitations In C3 Plants Semantic Scholar

Biochemical And Spectroscopic Characterization Of Highly Stable Photosystem Ii Supercomplexes From Arabidopsis Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Pdf Achieving Solar Overall Water Splitting With Hybrid Photosystems Of Photosystem Ii And Artificial Photocatalysts Semantic Scholar
Ap Bio Photosynthesis Light Reaction Flow Chart Elegant Photosystem 1 And 2 Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download












0 Response to "38 photosystem 1 and 2 diagram"
Post a Comment