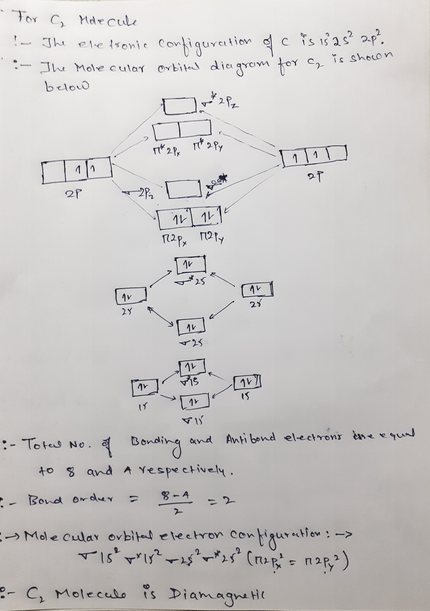
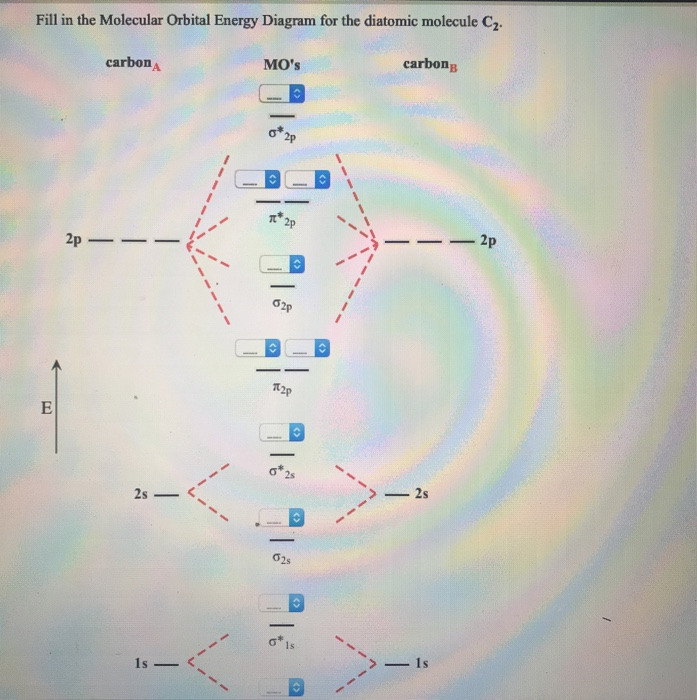
39 molecular orbital diagram for c2
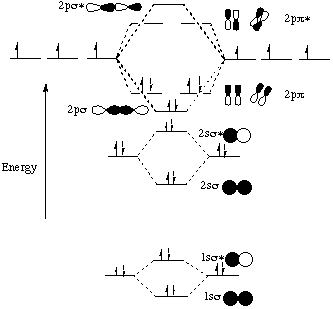
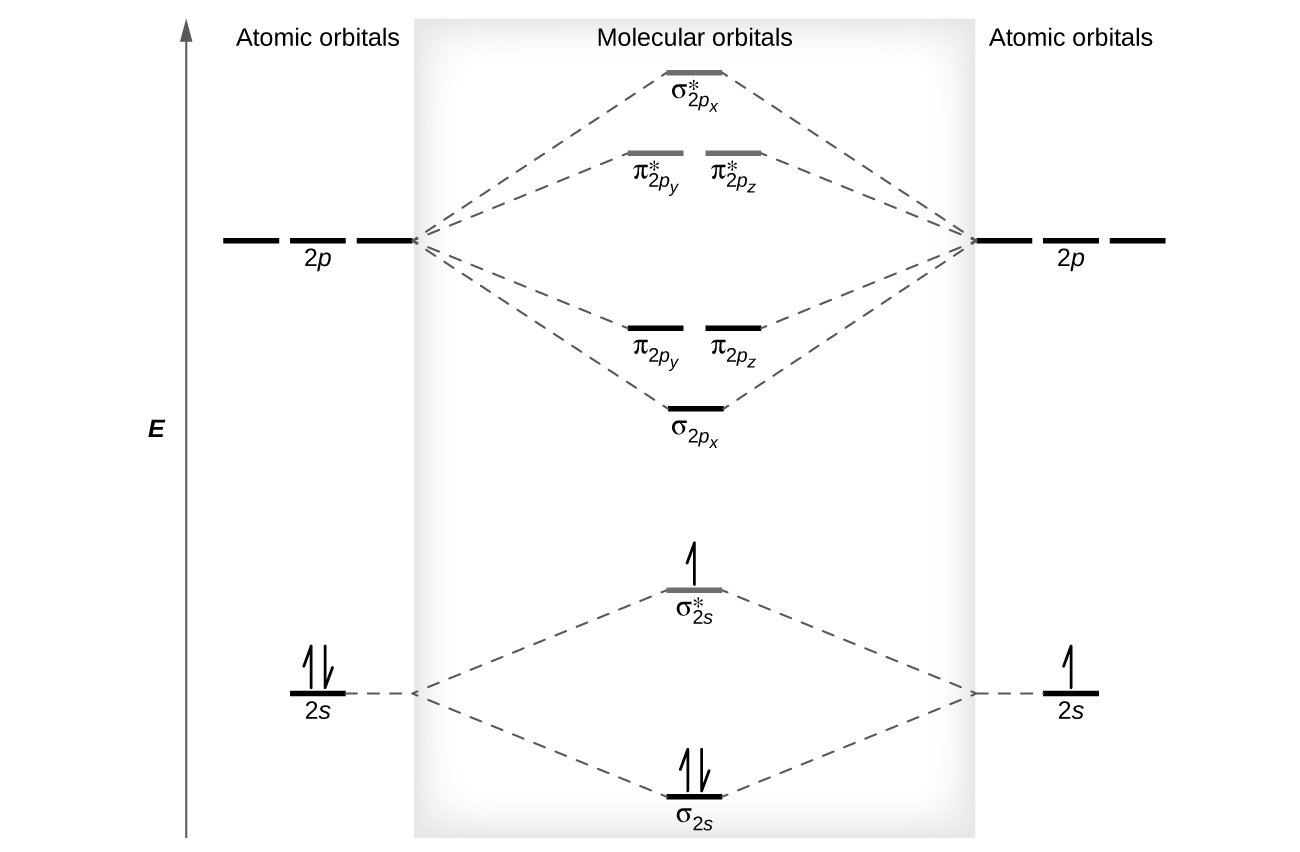
• The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the... If it doesnt it means you need to extract more information from the mo diagram. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 mol...
- MO diagrams for Inorganic complexes. • It is a waste of both the lecturers and students time if the tutorial to ends up being a lecture covering questions. 5. An introduction to Molecular Orbital Theory.

Molecular orbital diagram for c2
molecular orbital diagram for C2. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99!arrow_forward. Q: What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula CH2O and a molar mass of 60.0... The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. Best answer 100 2 ratings previous question...
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate... The y axis of a mo diagram represents the total energy not potential nor gibbs energy of the orbitals. Molecular orbital diagram for... Fill from the bottom up with 8 electrons total. If it doesnt it means you need to extract more information from the mo diagram. molecular orbital diagram for O2. number of elections in the pi*2p molecular orbital is. which response lists all the following diatomic molecules and ions that have at least one unpaired electron (Be2, B2, B2+, C2, N2, N2+).
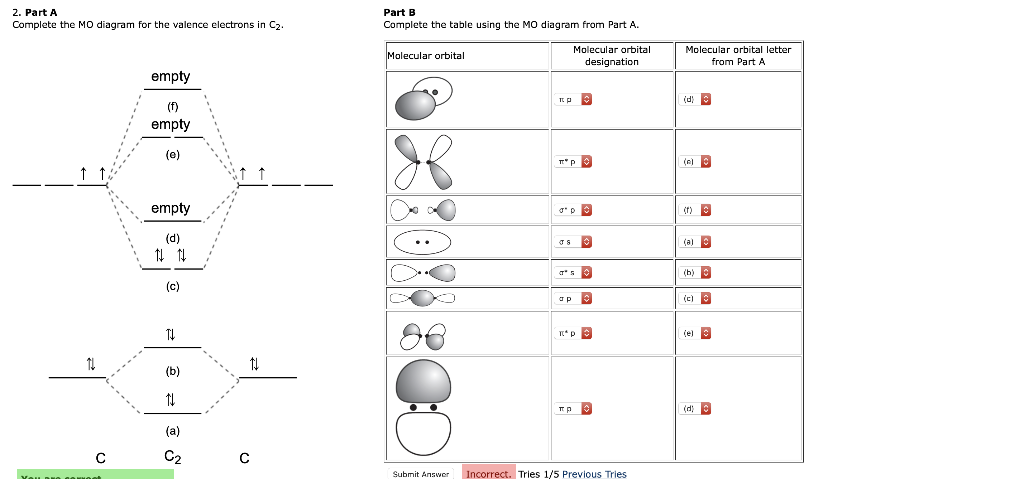
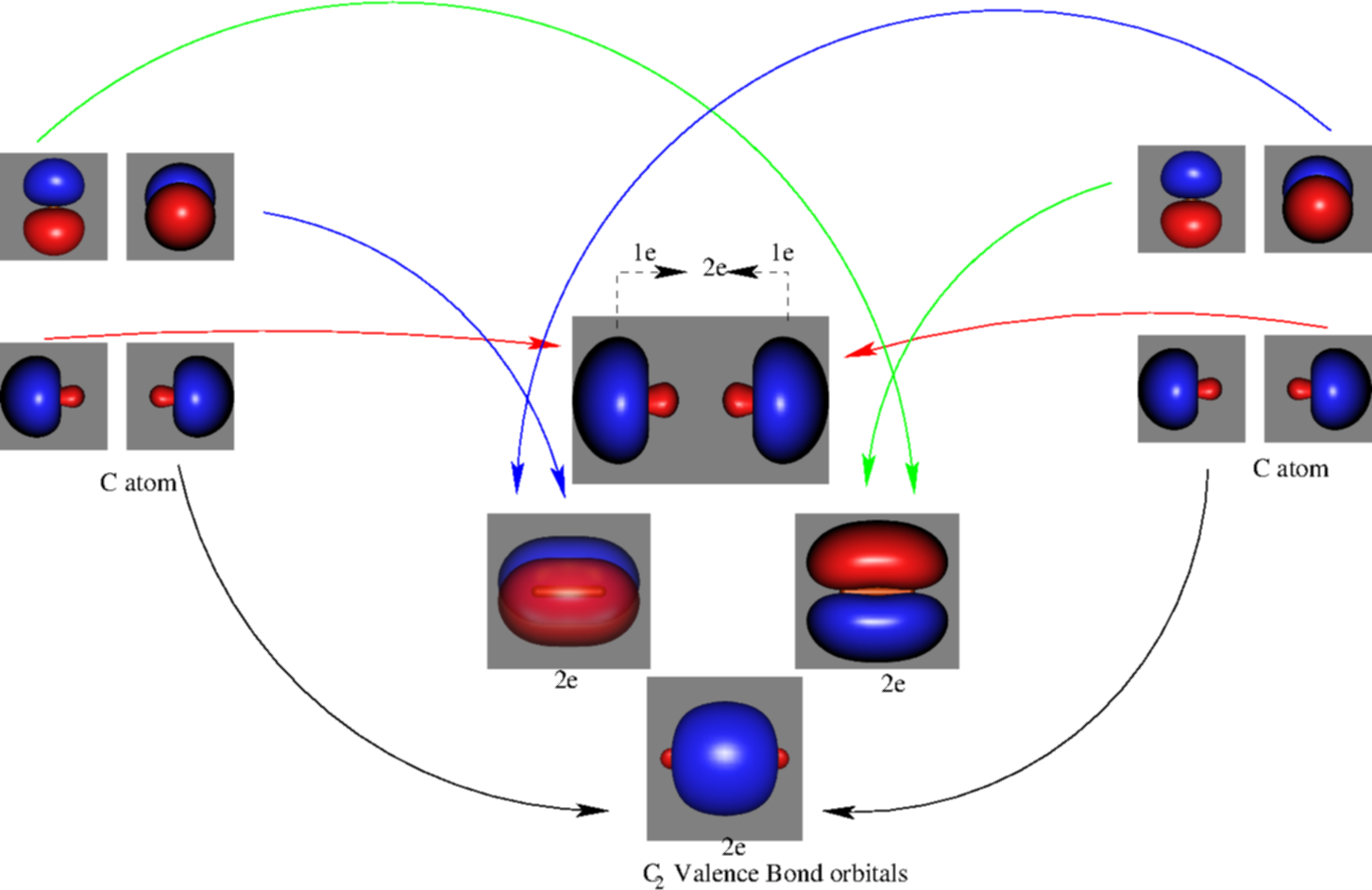
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. I've been brooding on some MO theory concepts that my inorganic chemistry class has absolutely failed to address. I've spent the last week obsessively looking for answers to these questions to no avail. **Questions**: 1. How can both 1s(sigma) bonding and antibonding orbitals coexist? How about 2p(pi) bonding/antibonding coexisting? I don't understand the physical/spacial manifestation of both the bonding and antibonding orbitals being filled at the same time. I would prefer a drawing or...
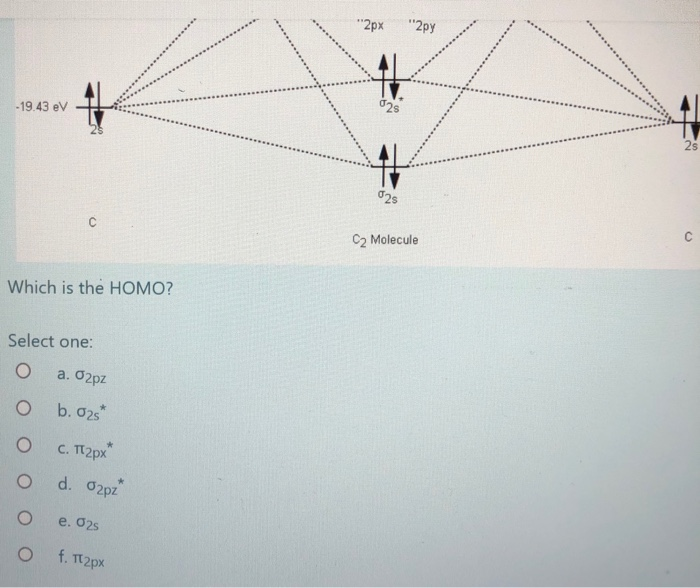
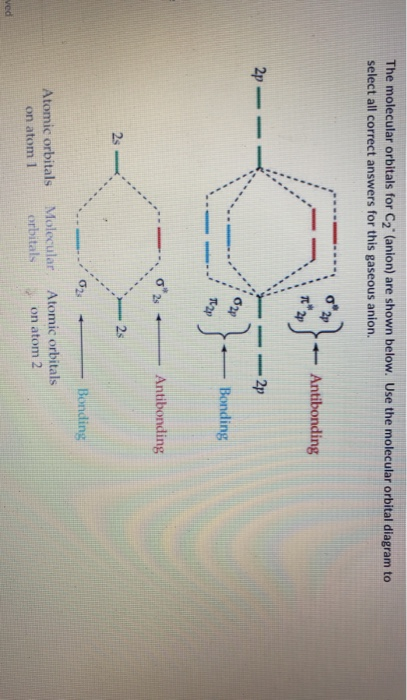
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2p_(sigma), so that is where the extra electron will be added. The problem provides you with the MO diagram for the #"C"_2# molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2. Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer c2. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules. Valence Molecular Orbital... The molecular orbital diagram for c22 this problem has been solved. The answer is c2 because of bond orders when we draw the c2 mo we have everything up till the pipy orbitlal filled and From the molecular orbital diagram of n 2 predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic.
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in 2,Molecular Orbital Theory shows that there are two sets of paired electrons in a degenerate pi bonding set of orbitals. This gives a bond order of 2...
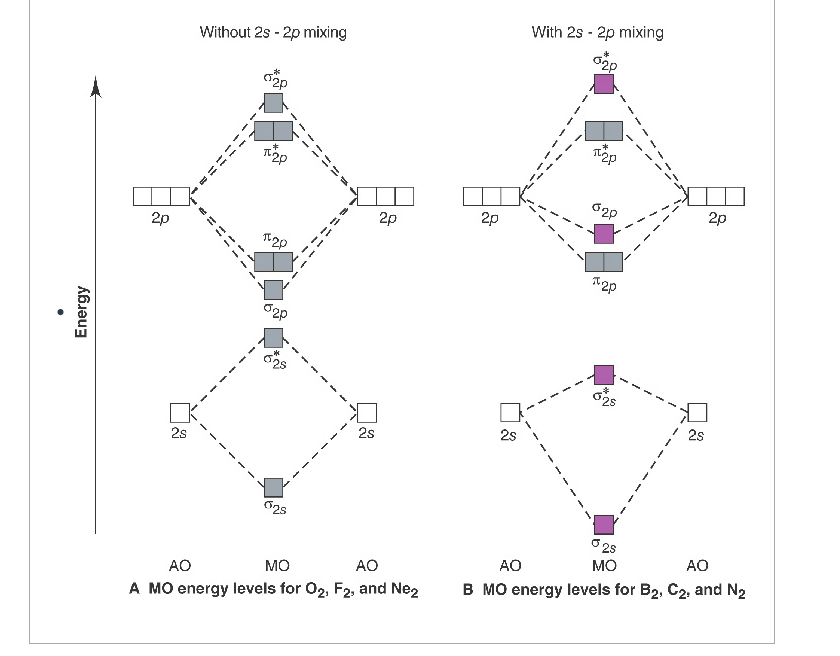
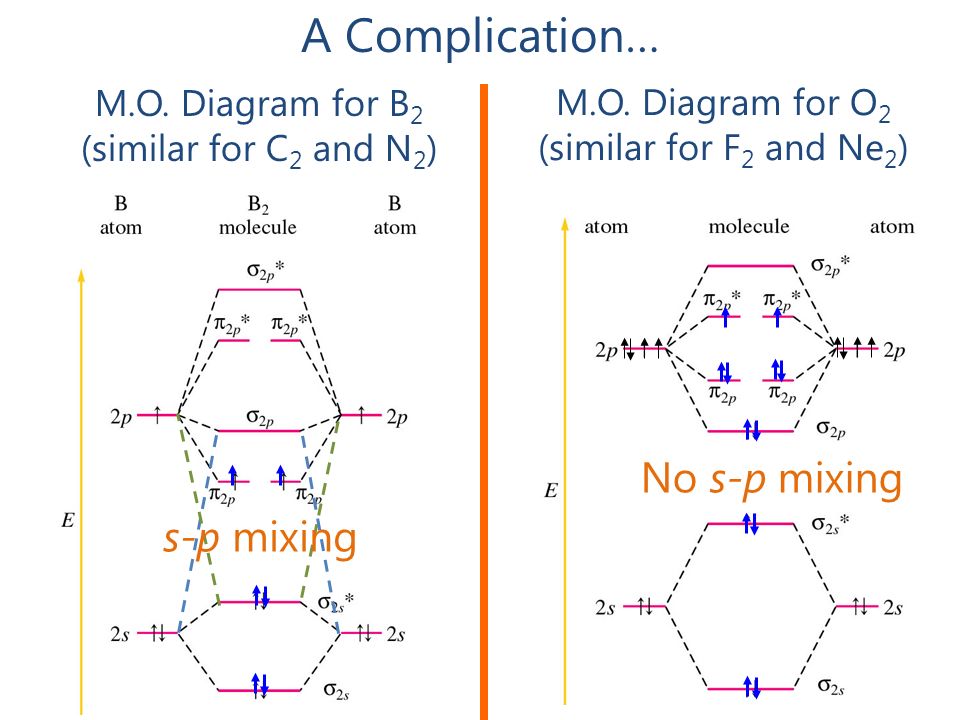
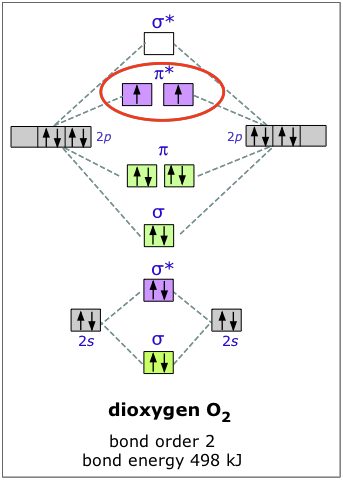
The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions Experiments have shown that O2 and F2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but B2, C2, and N2 are best described by a model that...
Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. Get 11 help now from expert chemistry tutors. Consider The Species O2 O2 And O2 W...
Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. A bond involving molecular orbitals which are symmetric with respect to ro...
Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw So here, I basically ask, how do I draw a correlation diagram? Like, how do I know how many electrons to put in the bonding atomic orbital and antibonding atomic orbital?
In this diagram, as in all the orbital diagrams in this book (such as Table 2.3 and Figure 2.6), the signs of orbital lobes are indicated by shading or color. nodes of the resulting molecular orbitals. In the p* antibonding case, four lobes result that are similar in appearance to a d orbital, as in Figure 5.2(c).
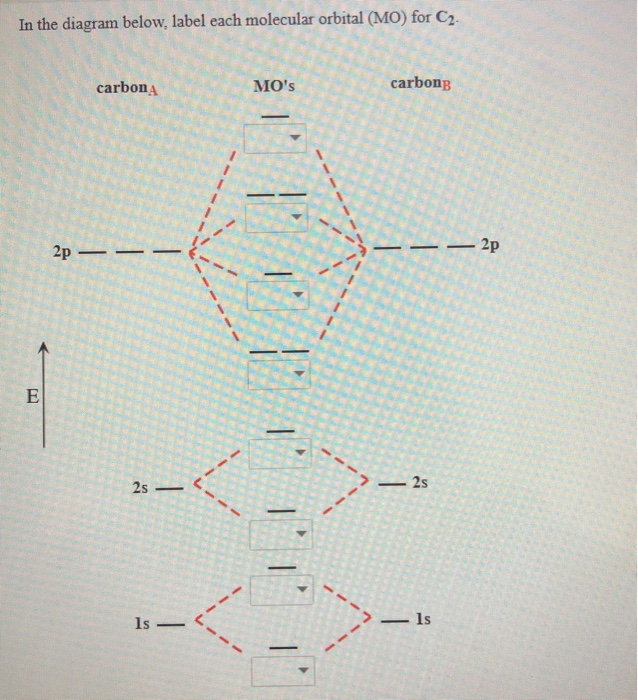
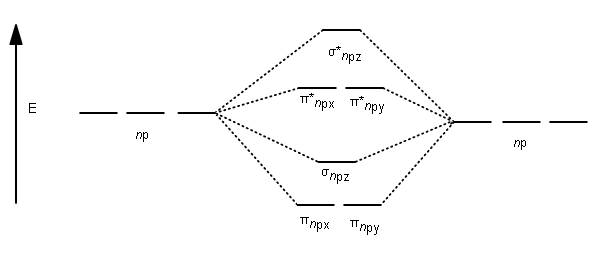
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. For example, homonuclear diatomic molecules of second row elements like Li2, Be2, B2 , C2, N2 , the σ 2pz MOs is higher in energy than π 2px and π 2py MOs.
molecular orbital diagram c2. Watch. 1 answer·0 watching·0 views.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Carbon Dimer (C2).Fill from the bottom up, with 8 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s...
Draw The Mo Diagram For Acetylide Ion C2 2 And Calculate Its Bond Order Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon.
Draw the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for this system. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the Na2− ion. A Because sodium has a [Ne]3s1 electron configuration, the molecular orbital energy-level diagram is qualitatively identical to the diagram for the interaction of...
A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. Best answer 100 2 ratings previous question...
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.
molecular orbital diagram for C2. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99!arrow_forward. Q: What is the molecular formula of a compound with the empirical formula CH2O and a molar mass of 60.0...
Solved 5 Draw Complete Molecular Orbital Diagrams To Compare The Bonding In C2 F2 And Cf A What Is The Bond Order Of Each B Which Of The Thre Course Hero














0 Response to "39 molecular orbital diagram for c2"
Post a Comment