34 blank molecular orbital diagram
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
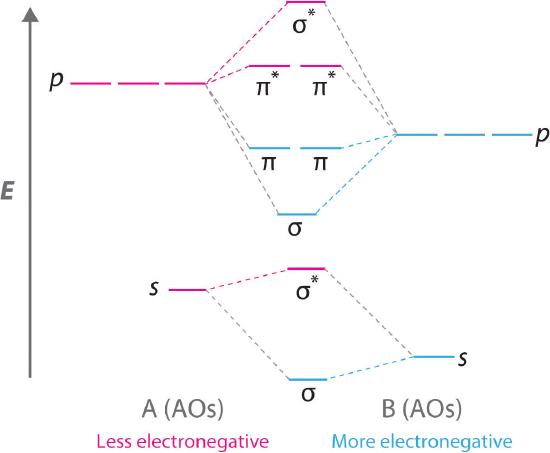
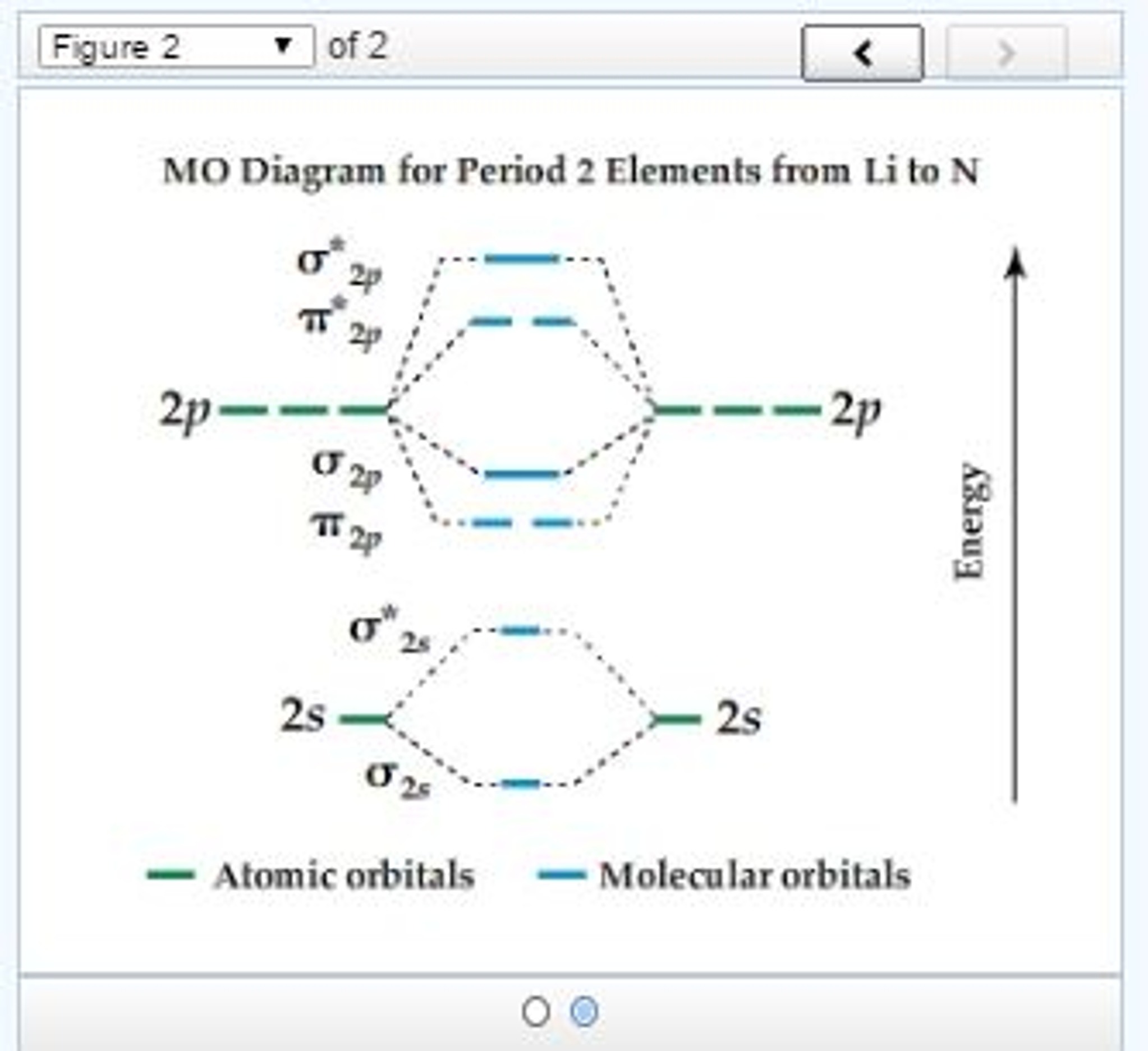
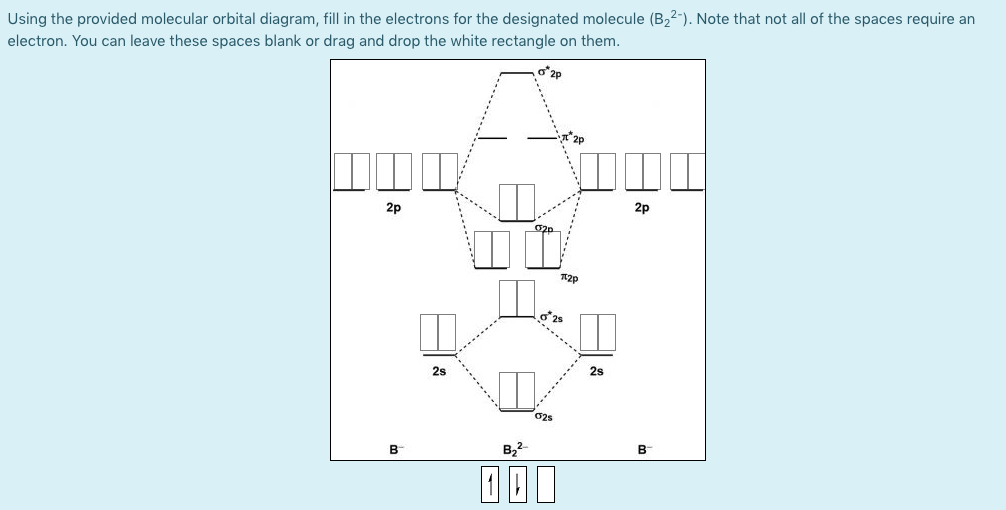
The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to the valence of diatomic boron, carbon, or nitrogen Part A What is the bond order of C? Express the bond order numerically. View Available Hint(s) VE ΑΣφ t h ? Figure < 1 of 1 Submit Part B - 2p an Is paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
Blank molecular orbital diagram
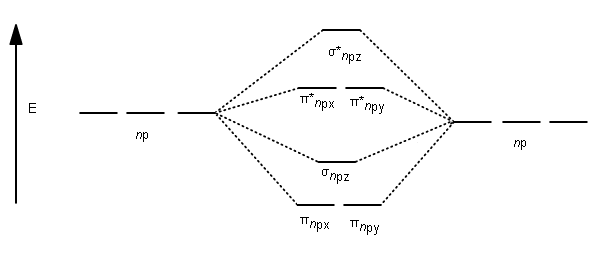
For this we need to picture atomic and molecular orbitals. l = 0 2. ATOMIC ORBITALS 2p x 2p y 2p z l = 1 x y z n = 2 This is an accurate representation of a 2p x orbital. This is a common picture of a p x orbital This simplifi ed p x orbital is often useful. A hand drawn version does not have to be exact.
Problem Details. The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to have valence of diatomic boron, carbon, or nitrogen. What is the bond order of C2^-? Express the bond order numerically. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos.
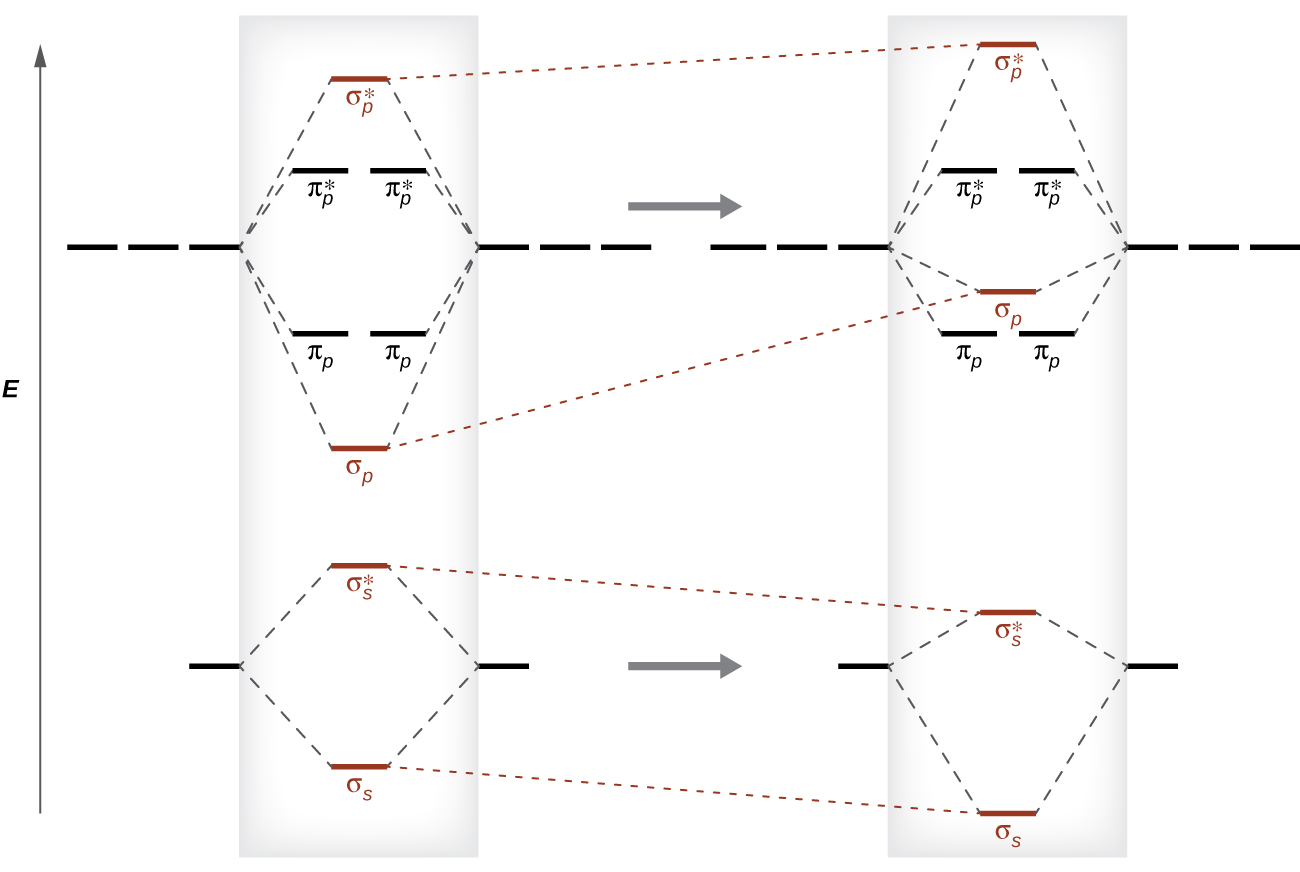
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Blank molecular orbital diagram.
A blank molecular orbital diagram has been provided to help you.Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.Molecular orbital (MO) theory is based in quantum mechanics and treats the orbitals found in a molecule in a manner similar to atomic orbitals in an atom.
The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to have valence of diatomic boron, carbon, or nitrogen. Is C2^- paramagnetic or diamagnetic? a) paramagnetic b) diamagnetic c) neither.
A large collection of various molecular orbital diagram is available in this post. Help yourself in understanding the chemical bonding in molecules through these 101 Diagramss!A molecular orbital diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular ...
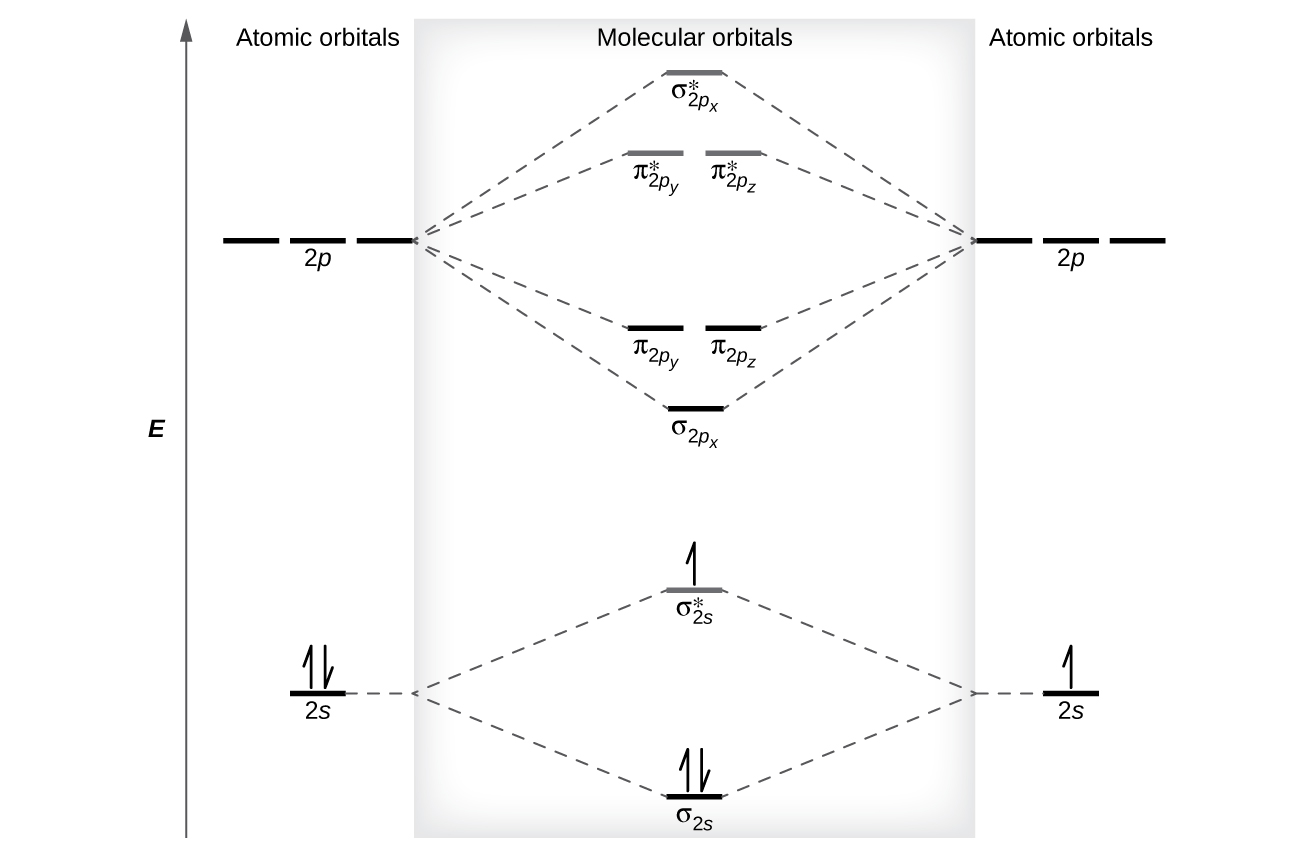
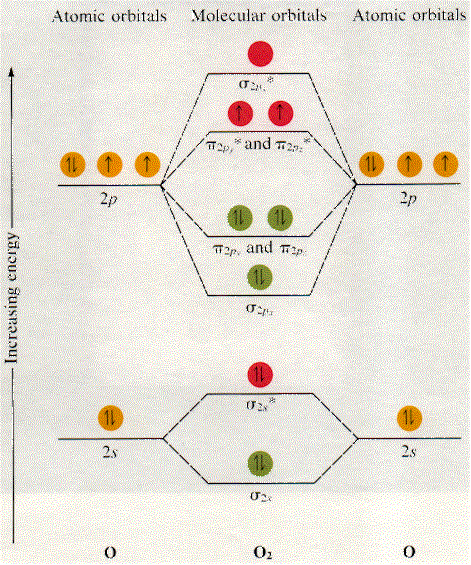
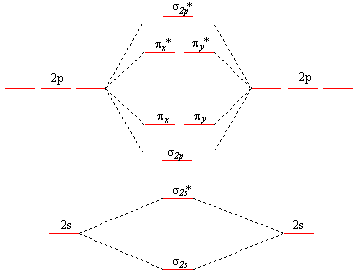
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Arrange the following in order of decreasing bond energy. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems MO ...
Procedure: draw Lewis Structure, determine Steric Number (SN), Molecular Geometry and Hybridization SN = # of atoms bonded to the central atom plus # of lone pairs on the central atom (SN = the effective number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom). Note: If one s and one p orbital hybridize, they form two sp hybrid orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Diagram to basically describe what is molecular orbital and provide you with some example of it in diagram. Welcome to 101diagrams.com, the site that provide great resources of images for your education and knowledge about various kind of diagrams. Including the medical diagrams, mathematics diagrams symbol, biology diagrams ...
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
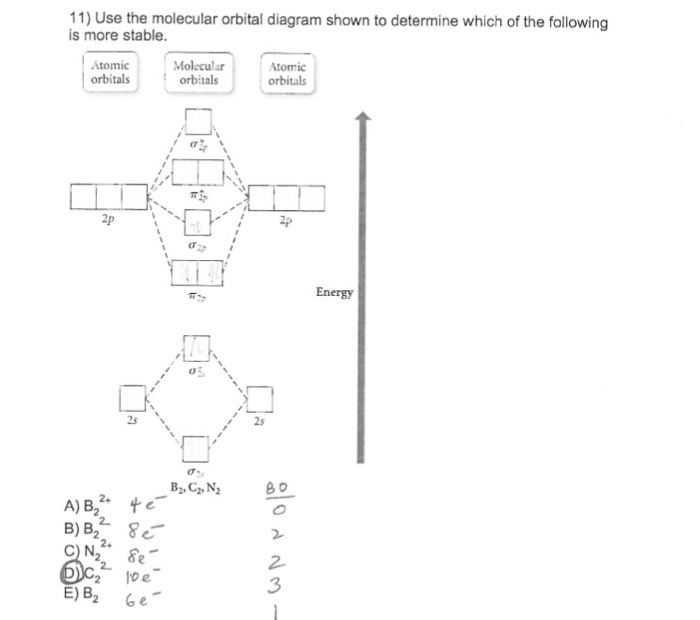

![Solved [MSW4PC] Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/2ad/2adcfa34-3cf5-420f-97eb-45dd8811750d/phpRFXM7l)




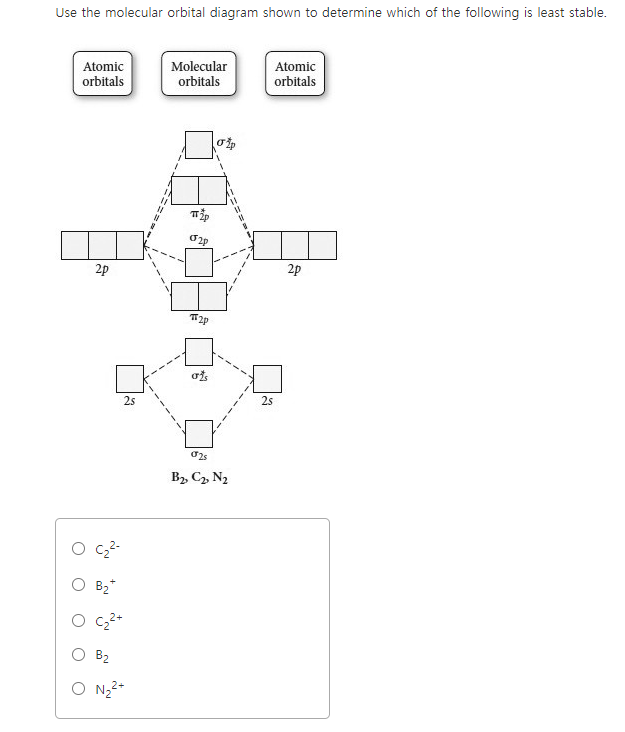











0 Response to "34 blank molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment