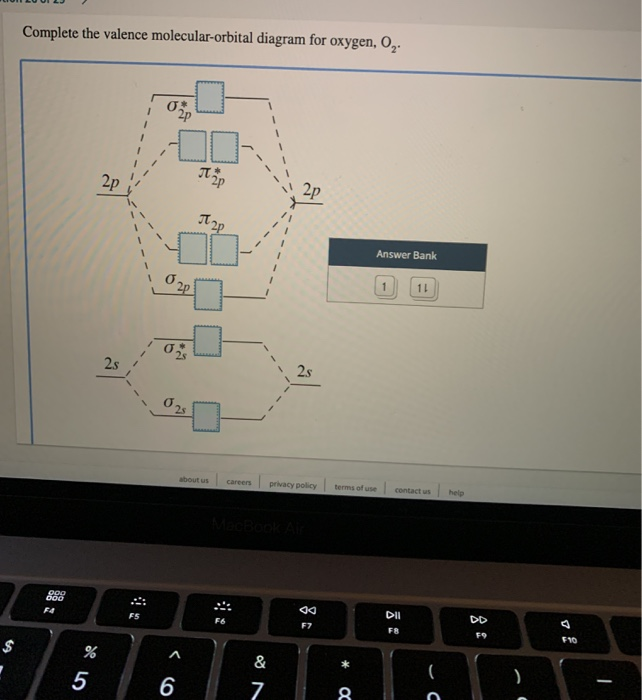
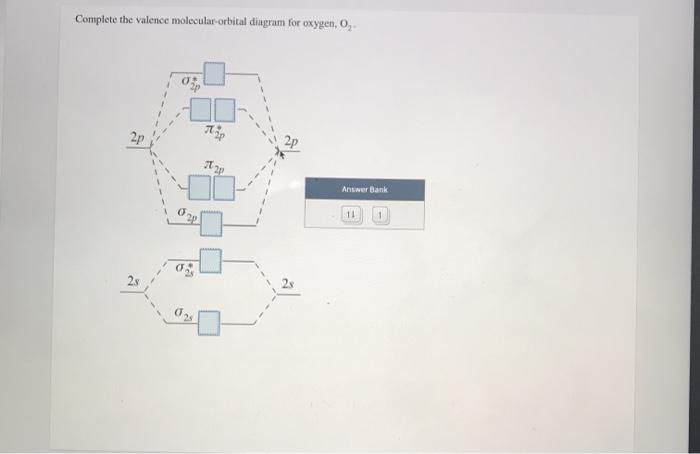
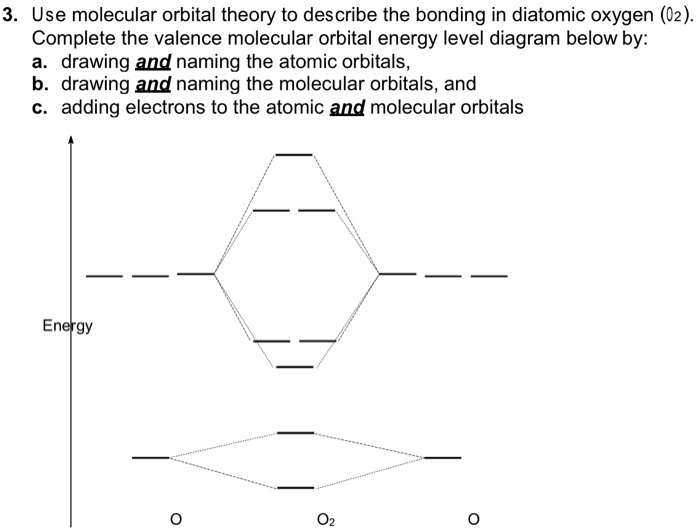
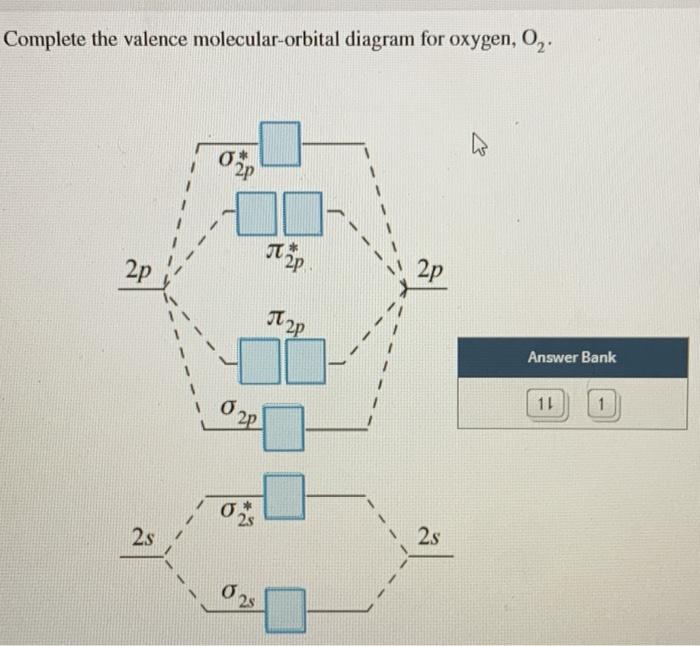
34 complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2
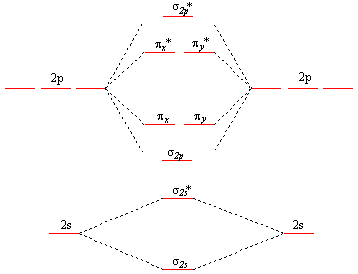
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond.
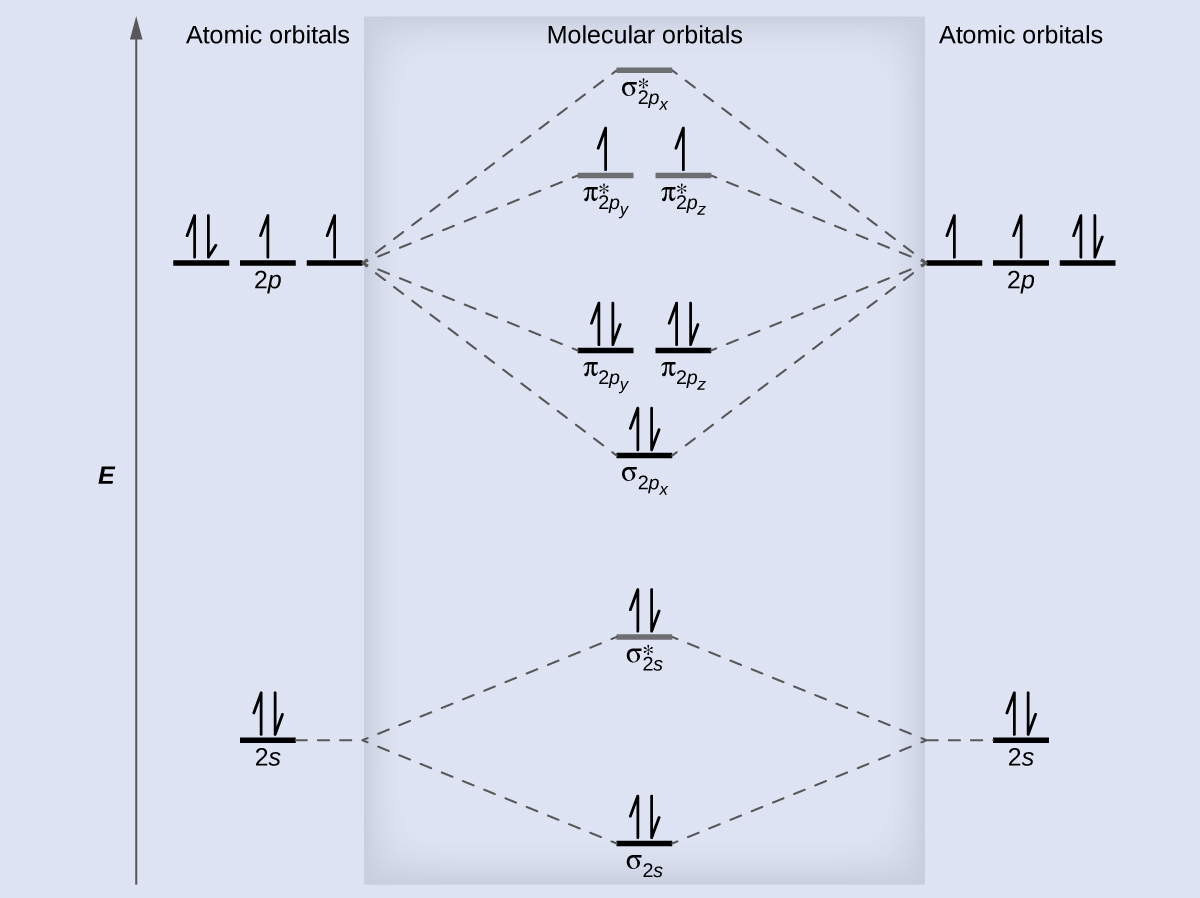
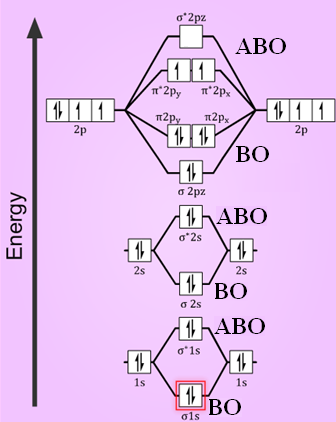
The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. Learn about the molecular orbital diagram for o2 using these free and printable molecular orbital diagram as your reference in understanding the mo of oxygen.

Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2
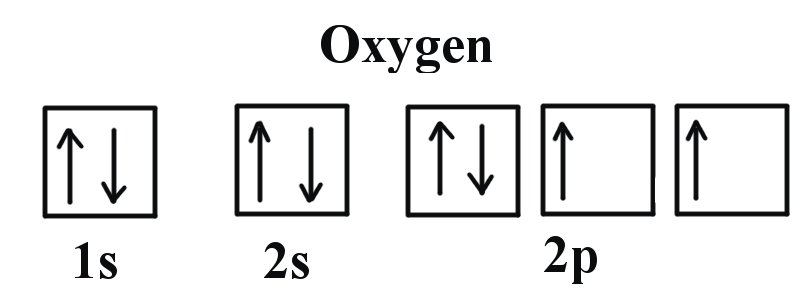
In order to draw oxygen's molecular orbital diagram, you need to start by taking a look at what atomic orbitals you have for an oxygen atom, #"O"#.. As you know, oxygen is located in period 2, group 16 of the periodic table and has an atomic number equal to #8#.This means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for #8# electrons.
Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2. The first compound in the diagram has two blue and three red atoms. The second compound has two blue and ... O2, oxygen I2, iodine. F2, fluorine. Magnesium reacts with oxygen to give (yield) magnesium oxide. The reactants are Mg and O2. The product is MgO.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2).Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s*...
Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2.
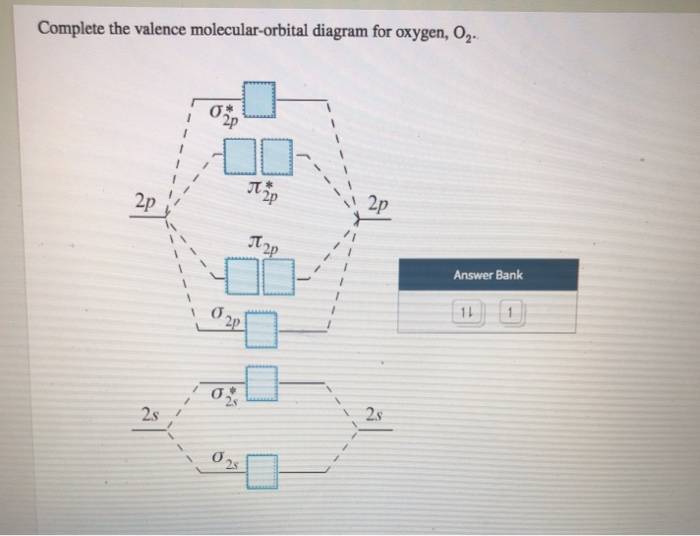
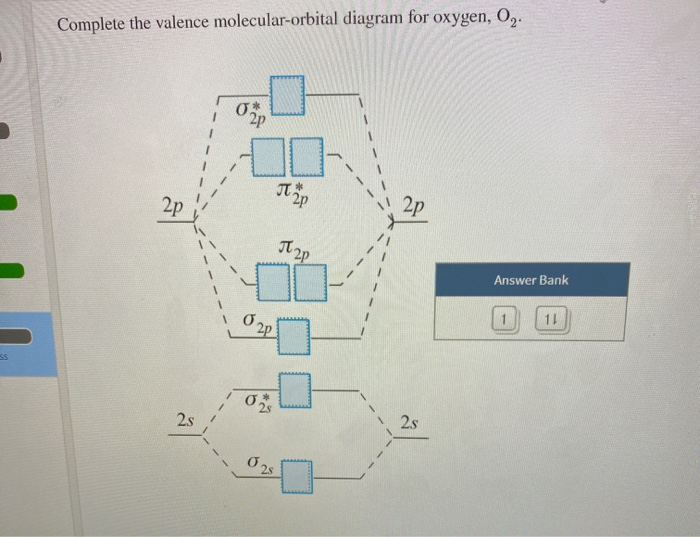
FREE Answer to Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason The concept used to solve this problem is based on molecular orbital diagram. A molecular orbital diagram is used to explain ...
All molecular orbitals except the highest would be occupied by molecular orbitals in the diagram .. and 10 in the ozone diagram in the Problem answer. Valence MO diagram (not all tie-lines drawn): nb. H(A). 2pBe . Ozone. Ozone is planar, so there will be one p orbital from each oxygen atom.
Aug 20, 2015 — From the molecular orbital diagram, we observe that oxygen has two unpaired ... so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence ...4 answers · 8 votes: Four electrons in the lowest levels, sigma-1 and sigma*-2 (bonding and antibonding), two in ...What is the molecular orbital diagram for O2- and ...5 answersMar 27, 2017What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2 ...6 answersMar 12, 2017Why is the molecular orbital diagram for O₂ ...2 answersAug 1, 2019How many molecular orbitals are there in O2? - Quora5 answersJun 4, 2019More results from www.quora.com
You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of O2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get O2. Two 2s orbitals combine to give a σ2s bonding and σ* 2s antibonding MO.
Problem Details. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He 2 and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons. Bond order: a) 0. b) 0.5. c) 1. d) 1.5. e) 2.
electronic state. Complete the molecular orbital diagram for NO by filling in the valence electrons in the occupied orbitals. Sketch the shape of the π and π* orbitals, clearly showing all nodes. Determine the bond order of NO and whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Marks 6 MO orbital energy level diagram for NO Sketch of the π MO
Atomic oxygen has 6 valence electrons and 4 valence orbitals (2s, 2p x, 2p y, and 2p z). We can draw a Lewis structure of molecular oxygen with a double bond between the oxygen atoms and 2 non-bonding pairs of electrons on each atom. However, experimentally we can determine that O 2 has 2 unpaired electrons. The Lewis structure seems to be ...
This means that the electron configuration of a neutral oxygen atom must account for 8 electrons. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. image via upload.wikimedia.org. image via upload.wikimedia.org.
The energy of σ 2 p z molecular orbital is greater than and molecular orbitals in nitrogen molecule. Write the complete sequence of energy levels in the increasing order of energy in the molecule. Compare the relative stability and the magnetic behavior of the following species: N 2 , N 2 + , N 2 − , N 2 2 +
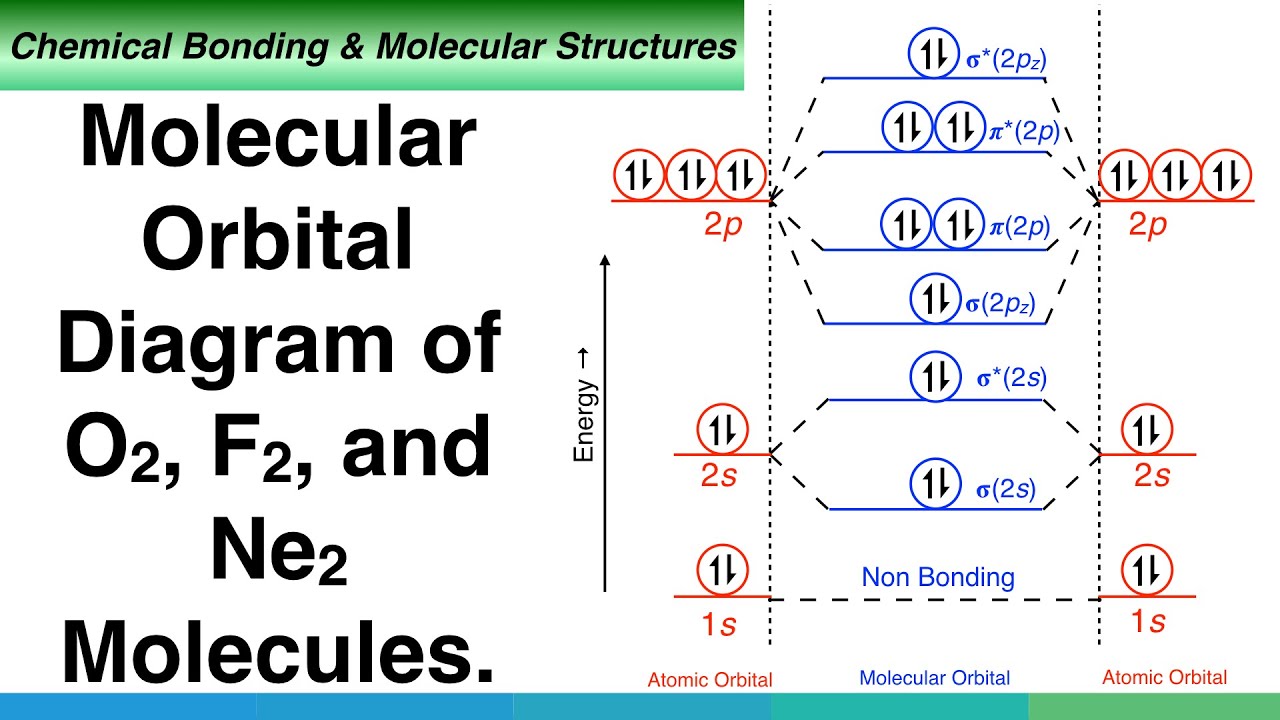
We know that Oxygen has atomic number = 8. Thus, the electronic configuration for an atom of oxygen in the ground state can be given as - $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}$ One atom of oxygen has 8 electrons. Thus, two atoms will possess 16 electrons i.e. Oxygen molecules will have 16 electrons. The molecular orbital diagram of an Oxygen molecule is as -
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...
Complete these structures by adding bonds and lone pairs as necessary. Apr 25, 2018 · You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of O2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get O2.
number of valence electrons) with O2. Therefore, NF is predicted to be paramagnetic with a bond order of 2. The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold
As we studied above that one oxygen atom has a deficiency of two valence electrons, it readily accepts two electrons. So, a single oxygen molecule has six electrons in its octet. If we look for O2, then the number will be O2: 6+6 = 12. In total, an O2 molecule needs four valence electrons to complete its octet and achieve a stable condition.
molecular orbitals can be formed by the combination of multiple atomic orbitals, allowing electrons to be _____ or shared between several atoms. the molecular orbital model therefore allows a better description of the bonding in _____ structure than valence bond theory, which depicts electrons as being _____ between two atoms at a time
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed.
So we're gonna have to bonds in our Louis structure. ... Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, 02- 2p Answer Bank 2s 2s.4 answers · Top answer: okay for this question, we are going to be drawing the Louis structure of H two s. We're gonna ...
Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, 0,. 2p 2p ´2p 2p T 2p Answer Bank 11 1 2p * Ở. 2.s 2s 2s
Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O, Answer Bank. Complete the valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O, Answer Bank Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order.
The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbital s. image via upload.wikimedia.org image via upload.wikimedia.org Question: Below is a molecular orbital diagram for O2.
The period of oxygen is 2 and it is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of oxygen(O) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of oxygen, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem
Aug 21, 2018 — More molecular orbital diagrams for 02 are provided below. Complete this valence molecular orbital diagram for oxygen o2. Click the blue boxes ...
We can use the molecular orbital diagram of oxygen molecules to explain the paramagnetic behaviour of oxygen atoms. We also have to know that for the paramagnetic nature of a molecule, it should contain a minimum of one unpaired electron. Complete answer: The valence bond theory could not explain the paramagnetic nature of oxygen molecules.
Triplet Oxygen Wikipedia . Youll need the molecular orbital MO diagram of O2. Valence electron configuration of o2. 79 211 ratings FREE Expert Solution. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and pay attention to the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals.
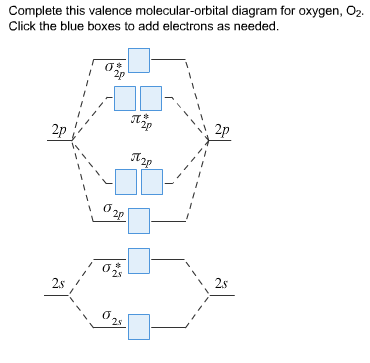
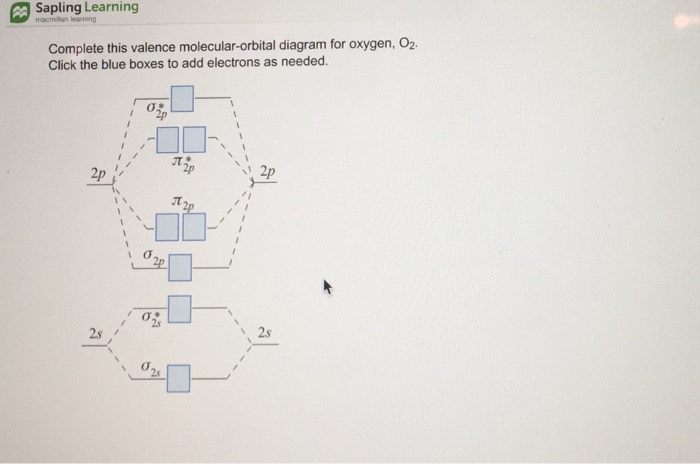











0 Response to "34 complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen o2"
Post a Comment