34 mo diagram for cn
$\begingroup$ No, $\ce{CN-}$ is the case in point. From an MO picture, there is no non-bonding "lone pair." There's nothing to donate. Coordination between a metal and $\ce{CN-}$ in MO-world and Lewis structure world look very different. The end-result of MO and Valence Bond may be similar, but the interpretations are different. $\endgroup$ Molecular Orbital Mixing. More detail was added to this answer in response to input and questions from students in the class of 2008. If you have suggestions or contributions please e-mail me. First of all while the stage 1 (pre mixing diagram) of diatomics is very easy to produce, the mixing in diatomics is very difficult to evaluate because more than two orbitals are involved. The total ...
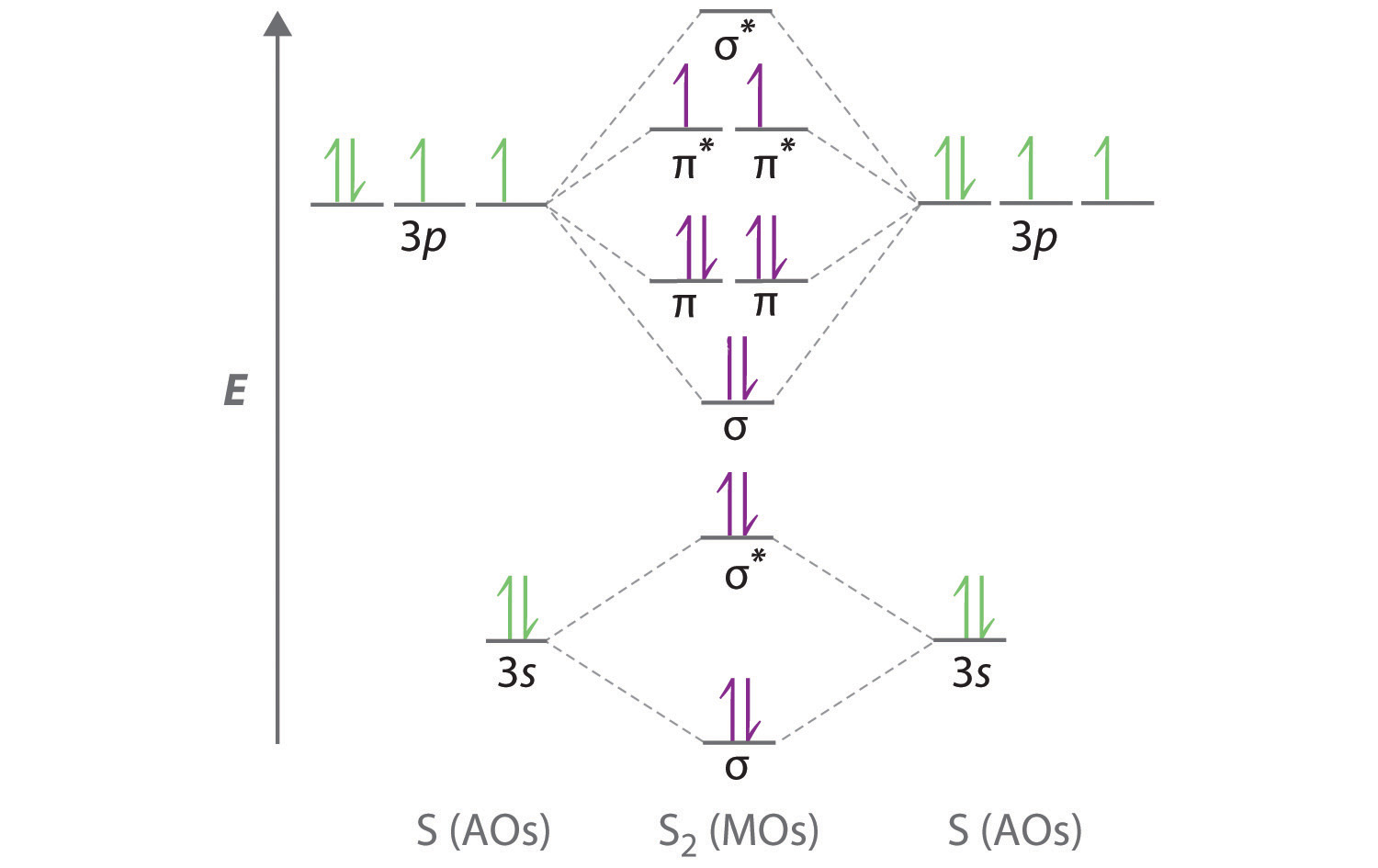
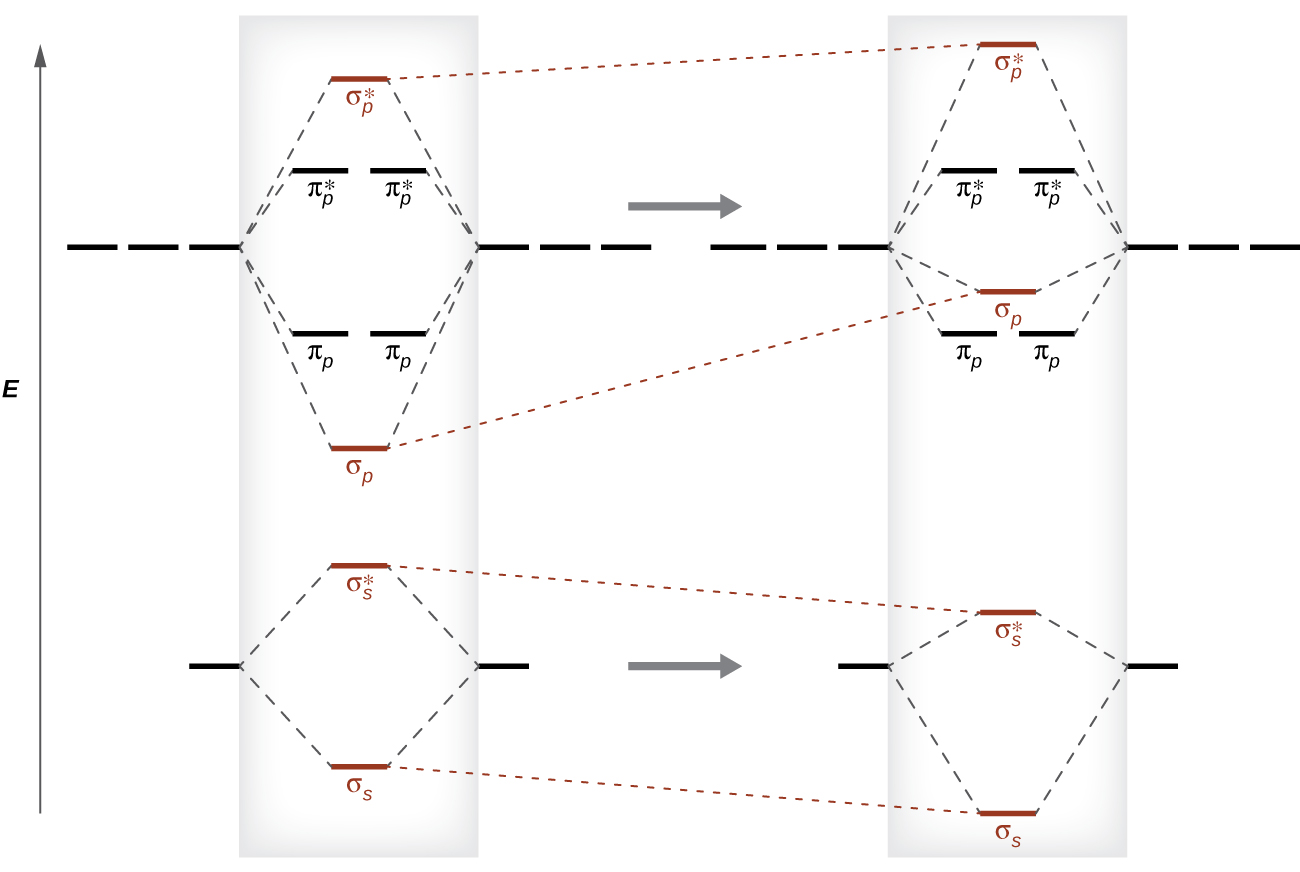
MO Diagrams. Now we're ready to look at MO diagrams for the first row series. Note that the molecules that aren't common and stable might still be more stable in the gas phase than single atoms. For instance, in a gas of Li metal, diatomic molecules will form. The figure shows a summary of the energy levels, so we can see how they change.

Mo diagram for cn
MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in carbon is six. What do the molecular orbitals of cyanide look like, compared with those ... MO Theory • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection. • The wavefunctions of properly-formed group orbitals can be ... Walsh diagram OH 2, SH 2, NH 2 8 Bent-, FH2 + NH 2, PH 2, CH 2 7 Bent-, OH2 + CH 2, SiH 2, BH 2 6 Bent-, NH2 + BH 2, AlH 2, CH 2 5 Bent BeH 2, BH 2+ 4 Linear LiH 2, BeH 2+ 3 Linear LiH 2+ 2 Bent No. of Shape valence electrons Molecular species Known shape of some AH 2 molecules Recall: a molecule adopts the structure that best stabilises the HOMO.
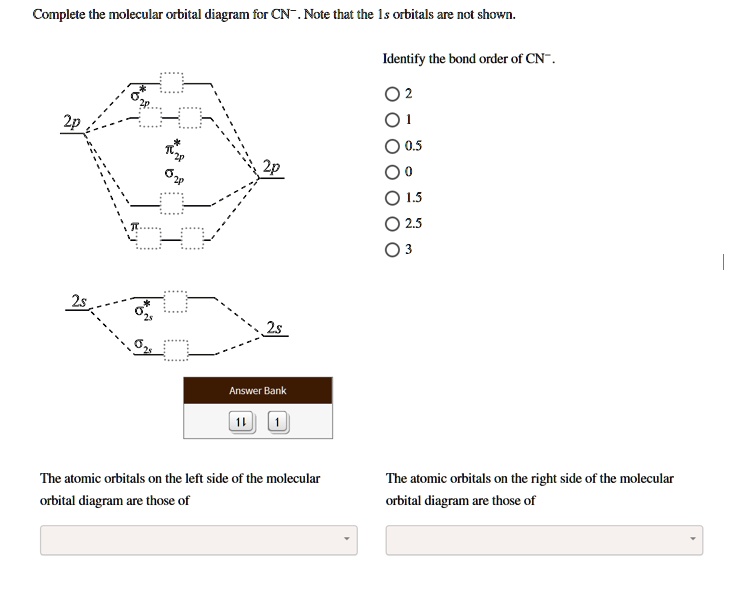
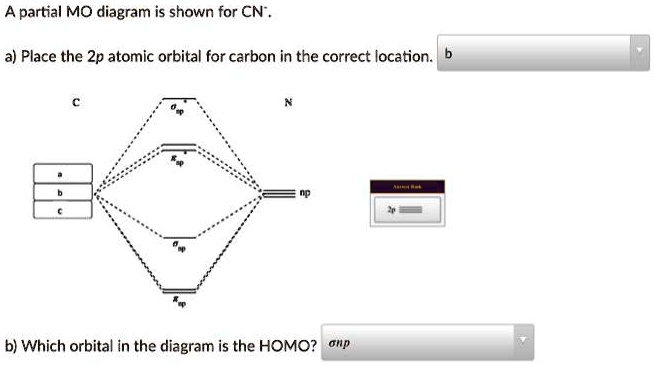
Mo diagram for cn. CN, CN+ and CN- , all are diatomic molecule or ions. So their bond order can be calculated on the basis of molecular orbital theory. Now , the total electron of ...6 answers · 40 votes: [math]\text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2}[/m ... The molecular orbital diagram of CN molecule is shown in the following figure: Reference: Essentials of Physical Chemistry /Arun Bahl, B.S Bahl and G.D. Tuli / multicolour edition. Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) Reviewed by تعرف على علم الكيمياء on 5/20/2019 Rating: 5 How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Assignment Score: 36.9% Resources Hint Check Answer < Question 7 of 16 > A partial MO diagram is shown for CN. Place the 2p atomic orbital for carbon in the correct location Which orbital in the diagram is the HOMO?
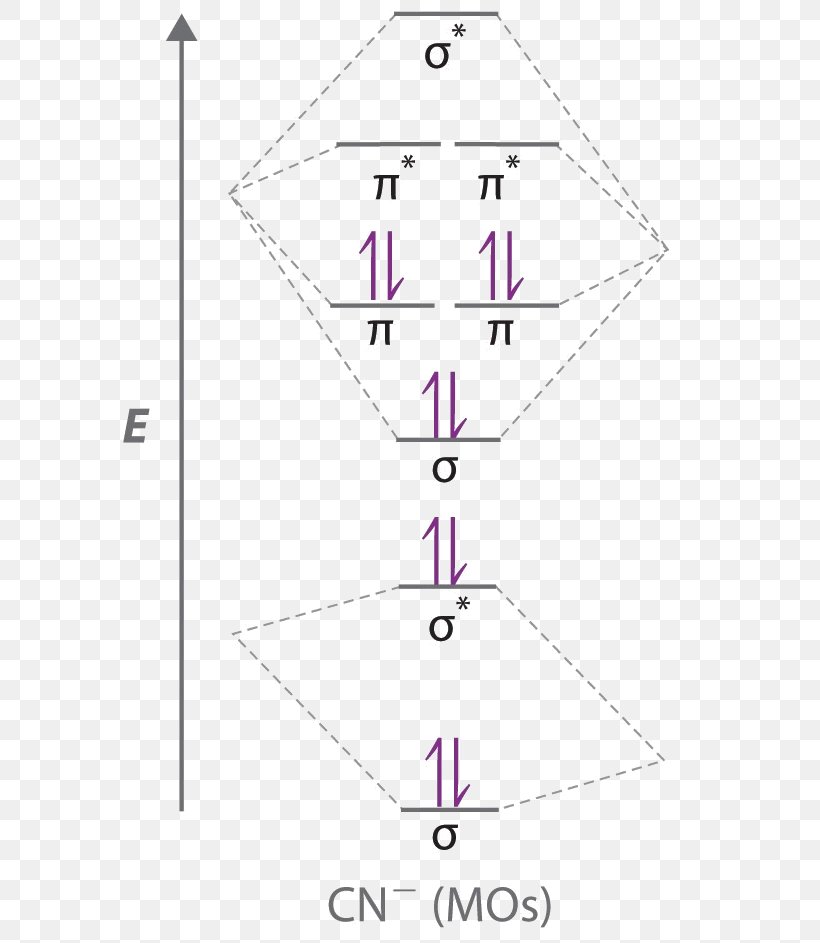
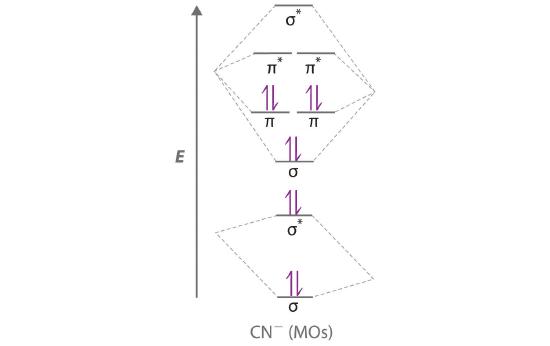
Module Two Chem 101 Problems. Carbon dioxide is a _____ compound composed two types of _____ atoms. Carbon dioxide is a molecular compound composed of two oxygen atoms with covalent double bonds to a central carbon atom. Both C and O are to the right of the "staircase" on the periodic table, as nonmetals. Classify the following compounds as ... Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 11. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic ... MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine. Relative AO Energies for MO Diagrams H He Li Be B C N O F Ne B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar Al Si P S Cl Ar ... Tania Havenga. University of South Africa. Here is the MO for CN-, just take away a single electron from the MO since CN is neutral. Vijayta Gupta is right, the N atom is lower in energy. http ...
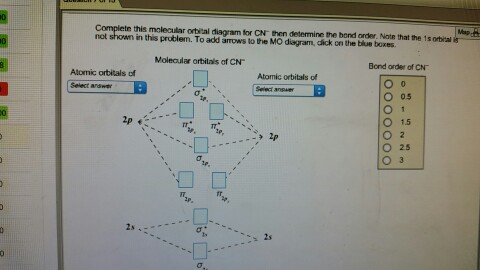
1 answerWe're being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN- and then determine the bond order. To do so, we shall follow these steps: Step 1: Calculate ... #3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron. Interactive Exercise: Drawing the MO diagram of CN-Right, you have been asked to draw the MO diagram for CN-, a heteronuclear diatomic. Don't panic! Take it one step at a time and you will have a complete MO diagram before you know it. This is meant to be an interactive exercise, so arrange for some pieces of blank paper, a pencil, a pen and an eraser. We will go through each of the steps in ... Explain the MO diagram for NO molecule. chemical bonding; class-11; Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. 1 Answer +1 vote . answered Dec 23, 2020 by Taashi (15.8k points) selected Dec 24, 2020 by Aashi01 . Best answer. 1. Electronic configuration of N atom is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3 . 2. ...
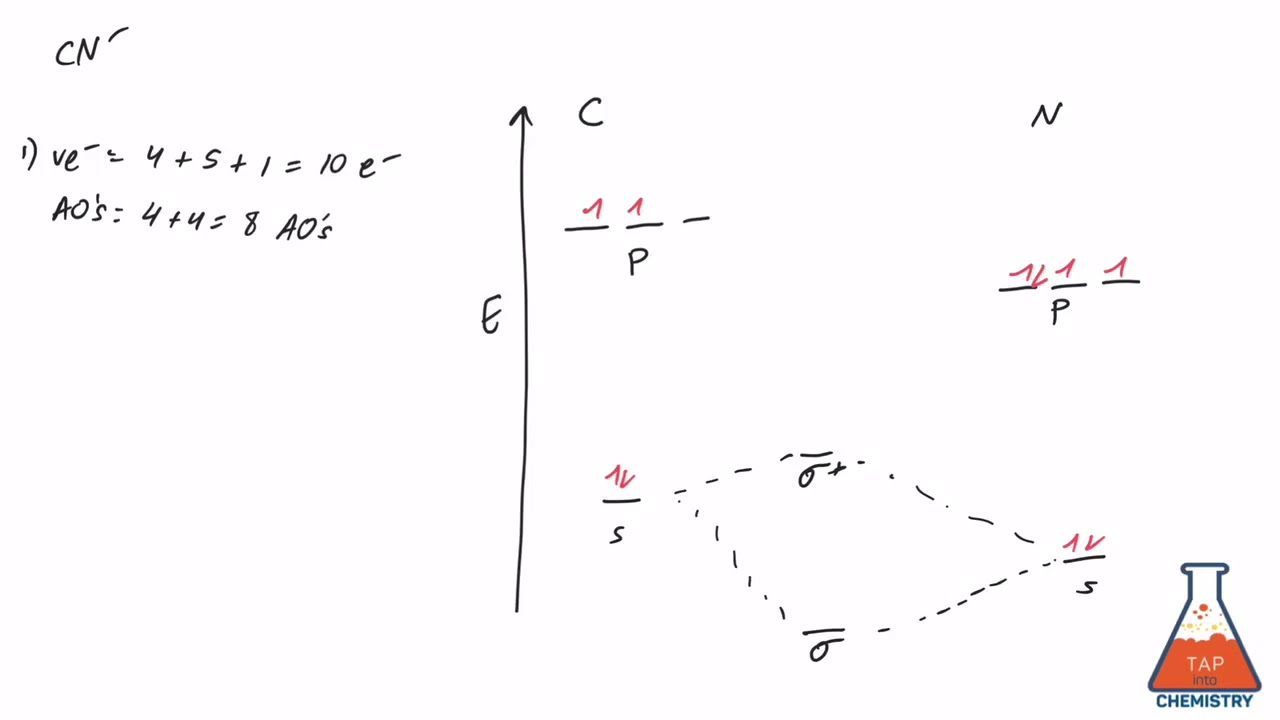
Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero ...
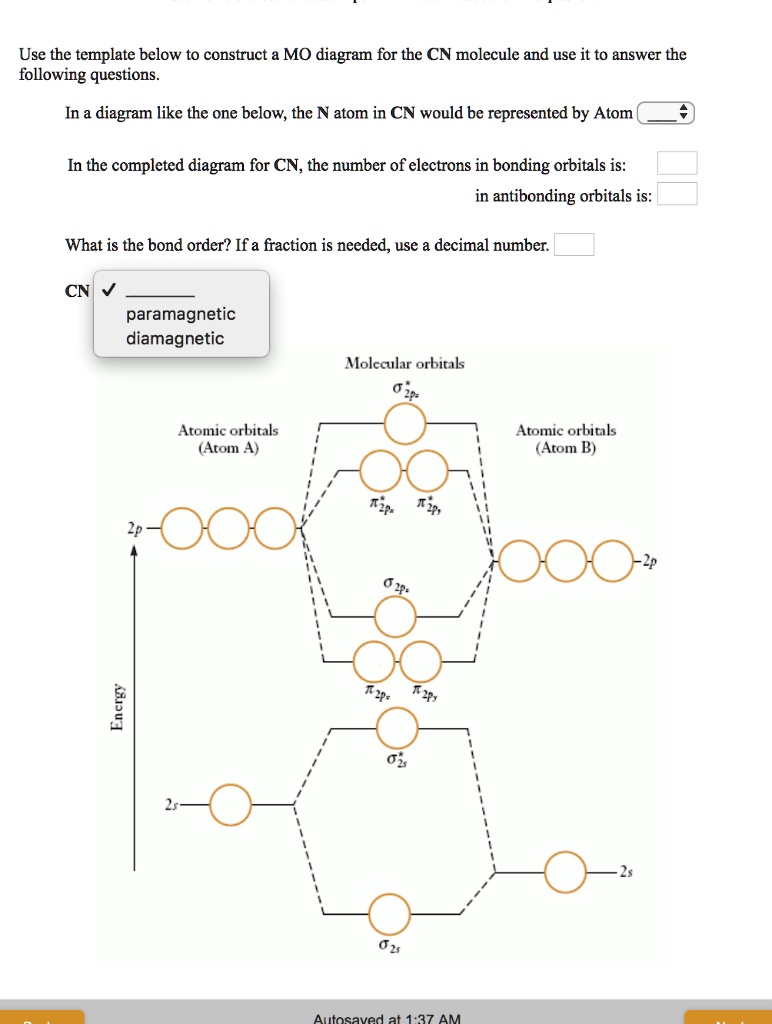
CN is Molecular orbitals 02 Atomic orbitals (Atom A) Atomic; Question: Use the template below to construct a MO diagram for the CN molecule and use it to answer the following questions. In the completed diagram for CN, the number of electrons in bonding orbitals is: in antibonding orbitals is: What is the bond order?
Answer (1 of 8): You didn't specify the kind of theory you are considering. VB theory (Lewis dots) will give a different bond order than MO theory. In VB theory, you end up getting three bonds and a pair of electrons on one atom, C\underline{=}N: so three (Or maybe four if you put the lone pair ...
The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion). Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for \(\ PageIndex{12}\) to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). In the traditional Lewis picture there are two lone pairs on the cyanide ion. In the MO diagram though there appear to be no non-bonding. What do the molecular orbitals ...
Example: Constructing a MO for Hexammine 2+Ruthenium, [[(Ru(NH 3) 6] NH 3 NH 3 2+ H 3N Ru NH 3 point group = O h H 3N NH 3 h 48 Ru bonding AOs O h E 8C 3 6C 2 6C 4 3C 2 i6S 4 8S 6 3 h 6 d /h 60 02 20004 2 = A 1g: 5s T 1u: (5p x , 5p y, 5p z) E g: (4dx2‐y2, 4dz2) A 1g 6001260001212481 A 2g 6 0 0 -12 6 0 0 0 12 -12 0 0 E g 1200012000240 48 1 Pd non‐bonding AOs
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
Problem 1: (a) Prepare the MO diagram for the cyanide ion, CN −.Use sketches to show clearly how the atomic orbitals interact to form MOs. (b) What is the bond order, and how many unpaired electrons does cyanide have? (c) Which molecular orbital of CN − would you predict to interact most strongly with a hydrogen 1 s orbital to form an H-C bond in the reaction: CN − + H + → HCN?
When two atomic orbitals combine, two molecular orbitals are formed. One is known as bonding molecular orbital and the other is called an anti-bonding molecular ...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason • The molecular orbital theory explains the bonding in terms of the combination and organization of atomic orbitals of an atom which ...
Molecular orbital Diagram Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory heteronuclear ...
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN-
Figure 11.5. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Part (a) in Figure 11.5. 3 shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
Answer (1 of 5): The total number of electron of CN- ion is ( 6+7+1) = 14 . According to molecular orbital theory, the electronic configuration of CN - ion is as follows, From the above electronic configuration , it has been found that , the number of bonding electron is 10 and the the number of...
"O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram.
here is the final diagram (below), please answer a few more questions about the tutorial to help improve it, go to feedbackgo to feedback
Walsh diagram OH 2, SH 2, NH 2 8 Bent-, FH2 + NH 2, PH 2, CH 2 7 Bent-, OH2 + CH 2, SiH 2, BH 2 6 Bent-, NH2 + BH 2, AlH 2, CH 2 5 Bent BeH 2, BH 2+ 4 Linear LiH 2, BeH 2+ 3 Linear LiH 2+ 2 Bent No. of Shape valence electrons Molecular species Known shape of some AH 2 molecules Recall: a molecule adopts the structure that best stabilises the HOMO.
MO Theory • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection. • The wavefunctions of properly-formed group orbitals can be ...
MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in carbon is six. What do the molecular orbitals of cyanide look like, compared with those ...


















0 Response to "34 mo diagram for cn"
Post a Comment