37 pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram
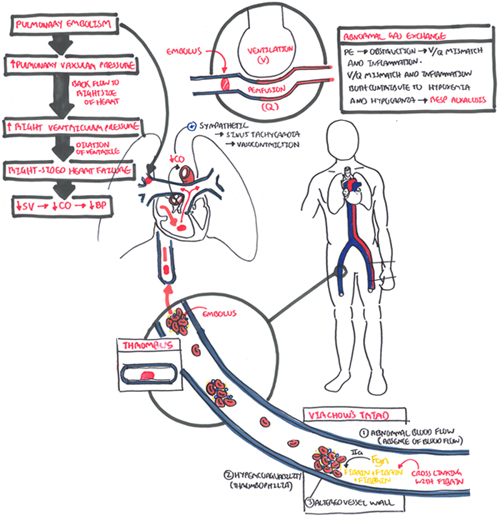
Pulmonary Embolism • Occlusion of a pulmonary artery (ies) by a blood clot. • Results from DVTs that have broken off and travelled to the pulmonary arterial circulation. • PE is one of the leading causes of preventable deaths in hospitalized patients. 20/01/20164. 5. 20/01/20165. 6.
Thrombotic pulmonary embolism is not an isolated disease of the chest but a complication of venous thrombosis. Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism are therefore parts of the same process, venous thromboembolism. Evidence of leg DVT is found in about 70% of patients who have sustained a pulmonary embolism; in most of the remainder, it is assumed that the whole thrombus has ...
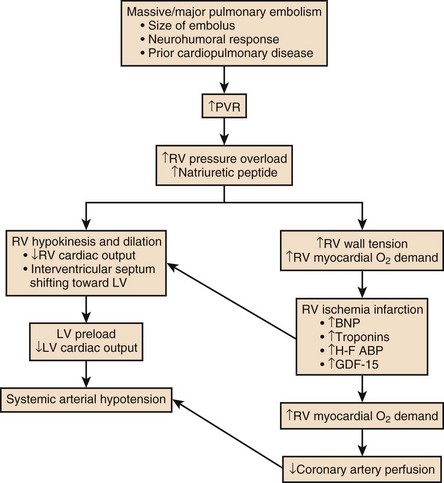
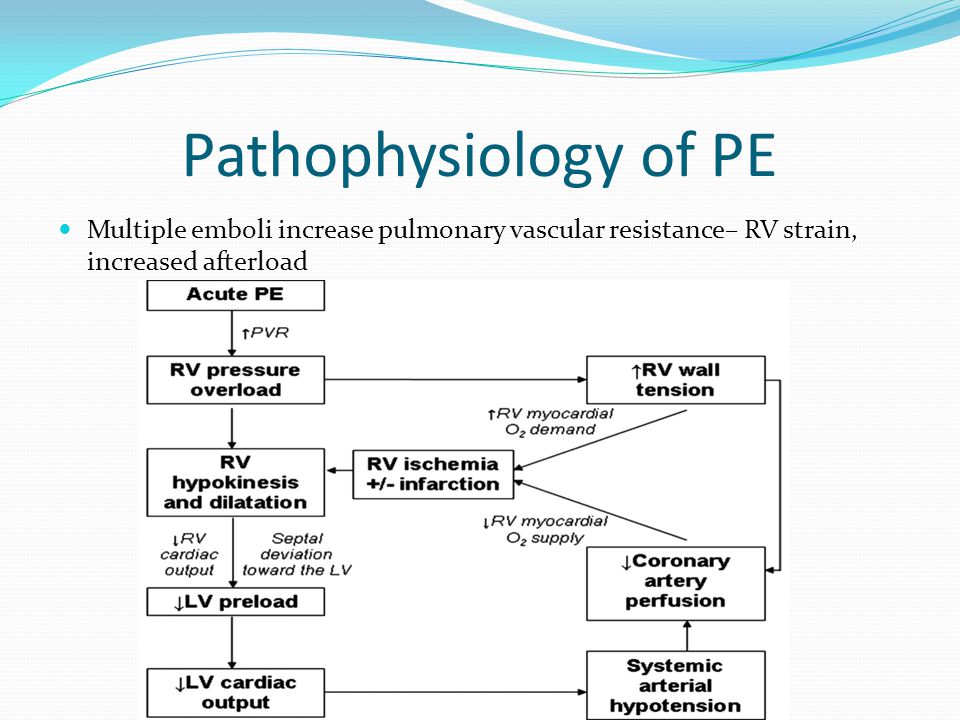
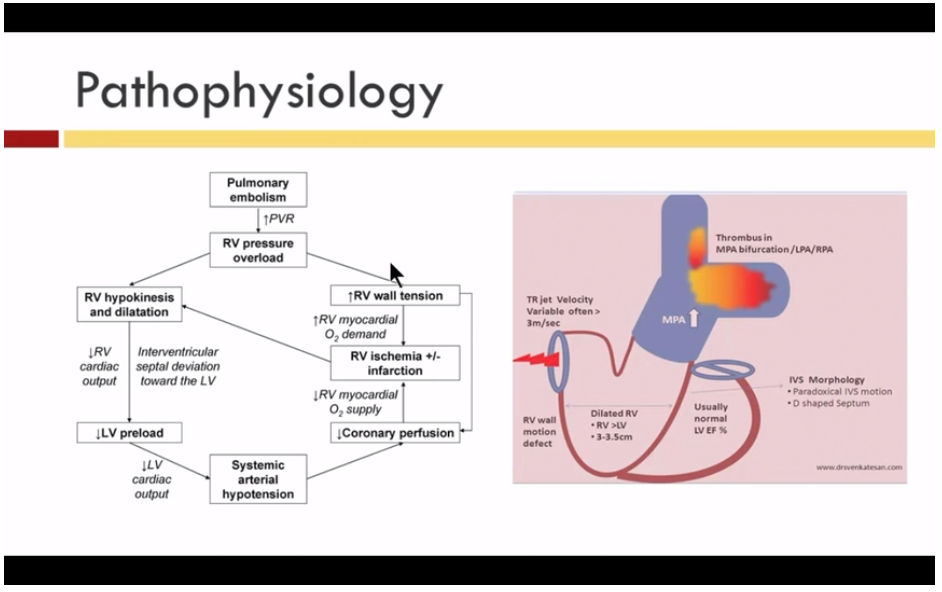
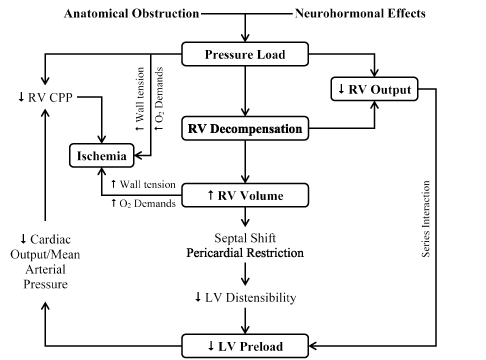
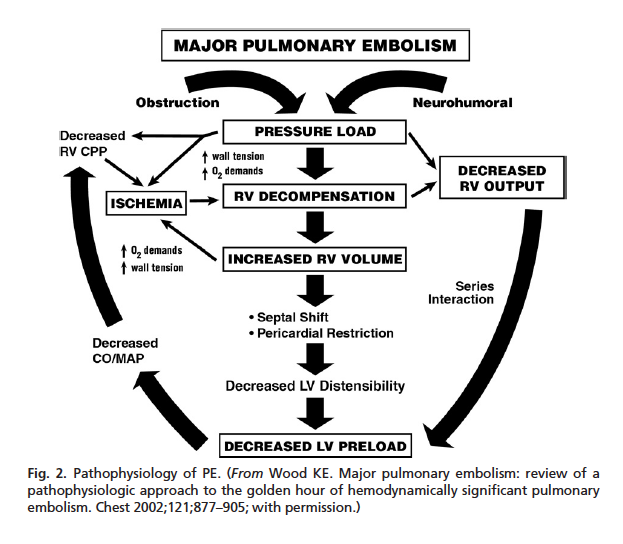
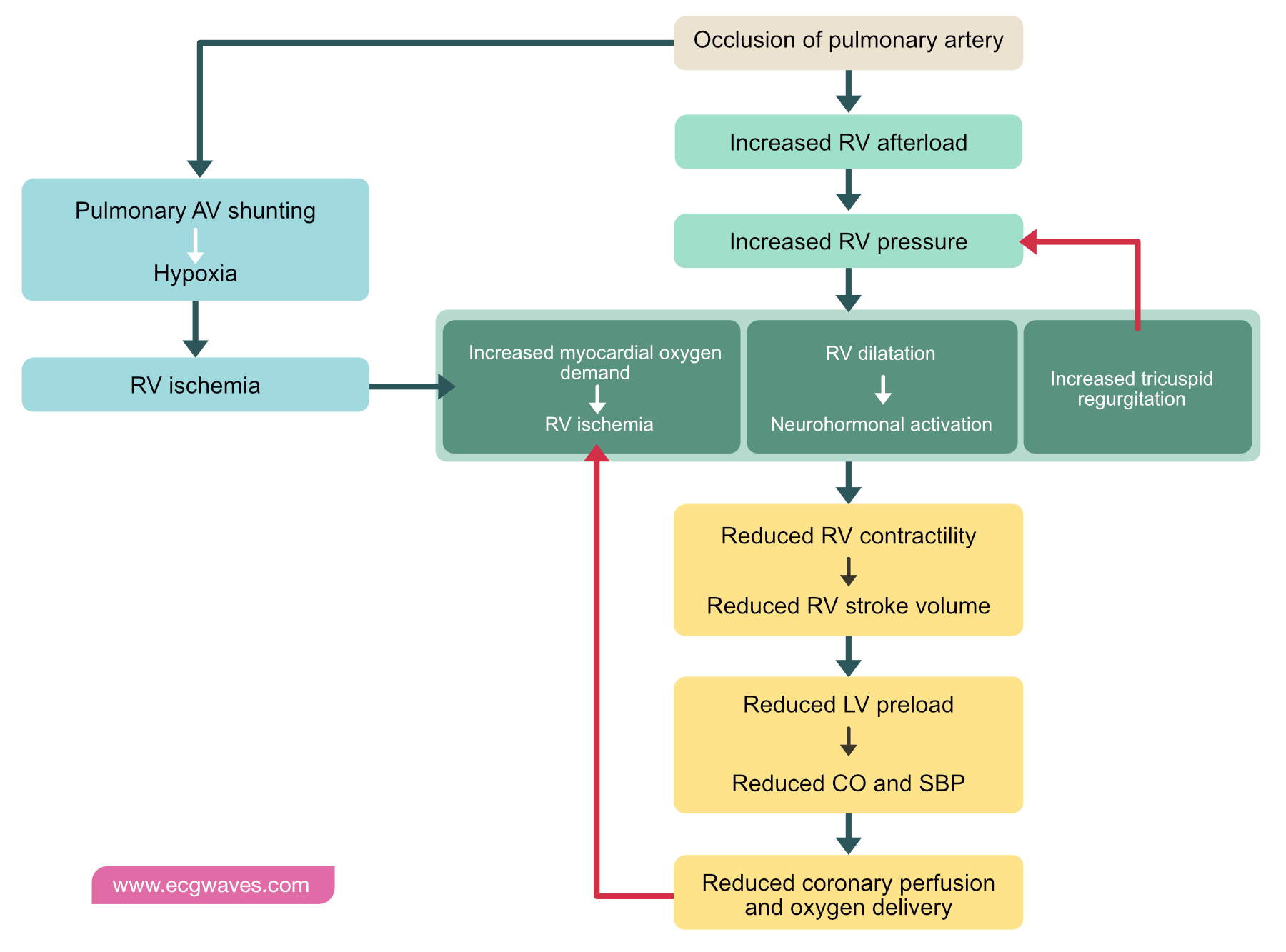
Pathophysiology of right ventricular failure in acute pulmonary embolism and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a pictorial essay for the interventional radiologist Yolanda C. Bryce1*, Rocio Perez-Johnston1, Errol B. Bryce2, Behrang Homayoon3 and Ernesto G. Santos-Martin1 Abstract

Pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram
Get clarity on pulmonary embolism(PE) with memorable illustrations from Dr. Roger Seheult. Watch the rest of this course free: https://www.medcram.com/course
😍🖼Animated Mnemonics (Picmonic): https://www.picmonic.com/viphookup/medicosis/ - With Picmonic, get your life back by studying less and remembering more. M...
Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism. Click the image to enlarge. Obstruction. When a thrombus completely or partially obstructs the pulmonary artery or its branches, the alveolar dead space is increased. Impairment. The area receives little to no blood flow and gas exchange is impaired. Constriction.
Pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram.
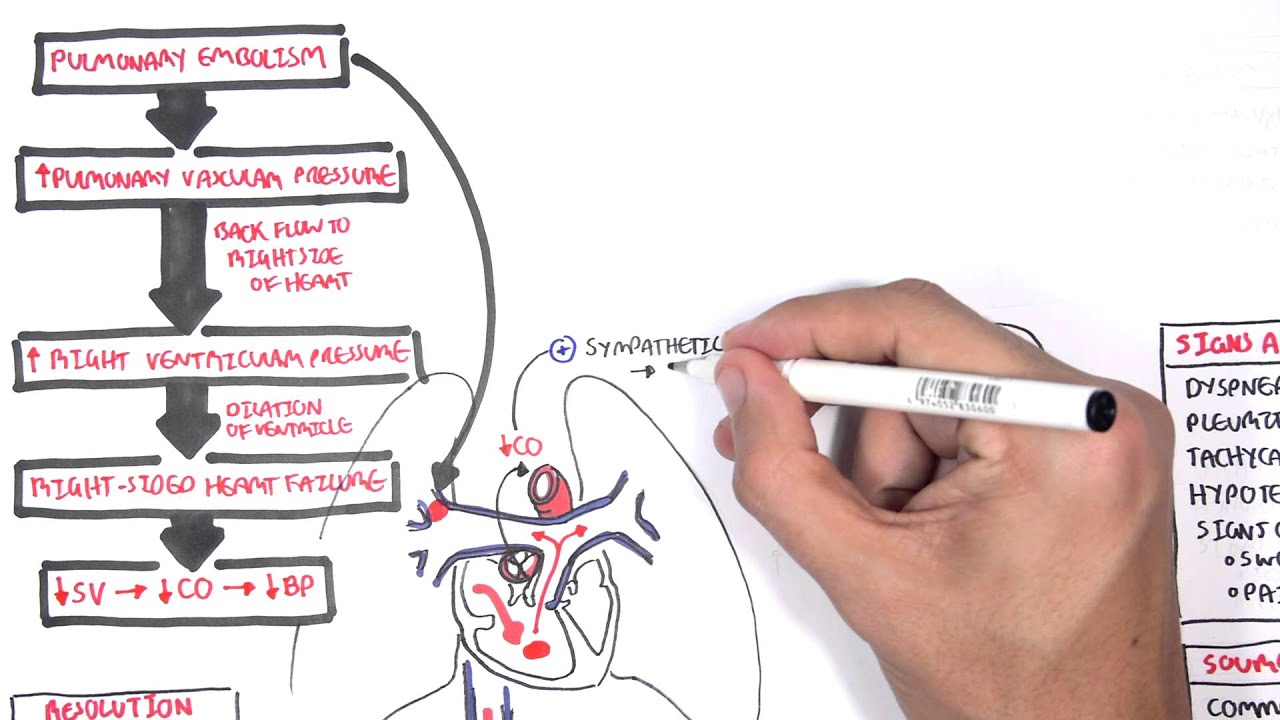
PULMONARY EMBOLISM PRESENTED BY Dr. RAHUL GUPTA. 2. DEFINITION It is an obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by a thrombus that originates somewhere in the venous system or in the right side of heart It is most common preventable cause of death among hospitalized patient. 3.
17 Aug 2015 — Pulmonary Embolism PART I (Overview). 361,339 views361K views. Aug 17, 2015. 4.2K. Dislike. Share. Save. Armando Hasudungan.
March 31, 2017 - External validation of a simple ... embolism. Thromb Res 2015; 135: 796–801. ... . Incidence of venous thromboembolism: a community-based study in Western France. Thromb Haemost 2000; 83: 657–660. ... Kerr KM, et al. Pulmonary endarterectomy: part I. Pathophysiology, clinical ...
Acute pulmonary embolism 1: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis Martin Riedel German Heart Center, Munich, Germany Table 1 Risk factors for venous thromboembolic disease Venous stasis or injury,secondary hypercoagulable states: Immobilisation or other cause of venous stasis—for
Overinflation of the air sacs is a result of a breakdown of the alveoli walls. It causes a decrease in respiratory function and breathlessness. Damage to the air sacs can't be fixed. It causes permanent holes in the lower lung tissue. Pulmonary emphysema is part of a group of lung diseases called ...
December 19, 2020 - Pulmonary embolism is often caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs. Prevention is aimed at stopping clots from forming in the legs.
Advances in recognition and treatment ... spent in the hospital. This article will review the risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, evaluation, and treatment of PE. Keywords: Pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, venous thromboembolism...
by DC Sabiston Jr · 1965 · Cited by 65 — Diagrammatic illustration of thrombosis in situ which occurs both proximal and distal to a pulmonary embolus. The proximal thrombosis extends to the first major ...
Videos (1) Pulmonary embolism is the blocking of an artery of the lung (pulmonary artery) by a collection of solid material brought through the bloodstream (embolus)—usually a blood clot (thrombus) or rarely other material. Pulmonary embolism is usually caused by a blood clot, although other substances can also form emboli and block an artery.
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) » Pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) » Pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism. Posted September 26, 2012 by Eric Wong.
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and potentially fatal form of venous thromboembolism that can be challenging to diagnose and manage. PE occurs when there is obstruction of the pulmonary vasculature and is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States. A combination of acquired a …
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease that is preventable and treatable. COPD is characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens with everyday activities such as walking or …
What is the pathophysiology? Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when one or more emboli, usually arising from a thrombus (blood clot) formed in the veins, are lodged in and obstruct the pulmonary arteries. When a PE is present, the lung tissue is ventilated but not perfused, resulting in an intra-pulmonary dead space and impaired gas exchange ...
Atrial fibrillation (AF or A-fib) is an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by rapid and irregular beating of the atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal beating, which become longer or continuous over time. It may also start as other forms of arrhythmia such as atrial flutter that then transform into AF.
Pathophysiology of Disease - An Introduction to Clinical Medicine, 7th Ed
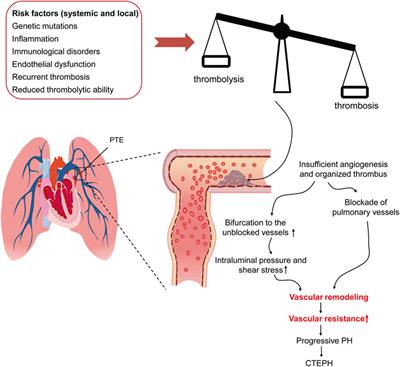
June 4, 2018 - The prognosis from PE depends on ... the pathophysiology helps in risk-stratifying patients and determining treatment. Though the natural history of thrombus is resolution, a subset of patients have chronic residual thrombus, contributing to the post-PE syndrome. Keywords: Pulmonary Embolism, venous ...
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when there is an acute obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches. It is commonly caused by a venous thrombus that has dislodged from its site of formation and embolized to the arterial blood supply of one of the lungs. The process of clot formation and embolization is termed thromboembolism.
In the first 24 hours, chest x-rays and pulmonary function tests are not definitive for a pulmonary embolism. Oximetry and arterial blood gas typically show hypoxemia. Echocardiography may show right ventricle strain. Serum D-dimer levels will test positive for thrombus degradation by-products; fibrinogen and fibrin.
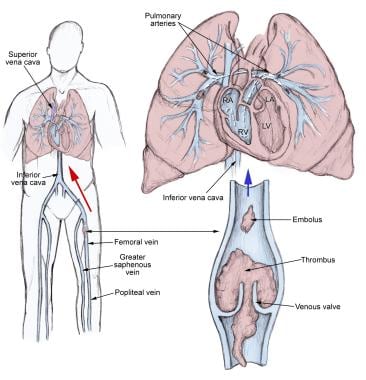
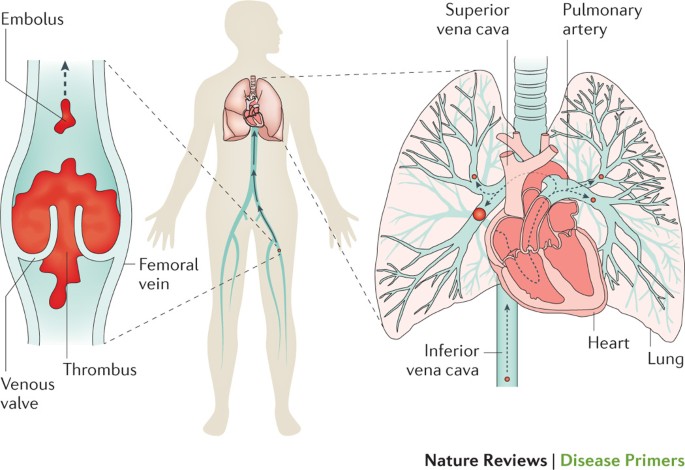
Eric Wong and Sultan Chaudhry. Faculty reviewer: Dr. Peter L. Gross, Associate Professor, Division of Hematology and Thromboembolism, Department of Medicine (McMaster University) Definition. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are manifestations of the same pathological entity, called venous thromboembolism (VTE). An embolus is any intravascular material that migrates from ...
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a thrombus dislodges from a vein, flows through the veins and typically lodges in the lung. Most thrombi form in one of the deep veins of the lower limb or those of the pelvis; this condition is referred to as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The thrombi lodge in the lungs because veins get larger as they flow to ...
July 11, 2006 - Acute pulmonary embolism: part I: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis. Circulation. 2003; 108: 2726–2729.LinkGoogle Scholar · 14 Dunn KL, Wolf JP, Dorfman DM, Fitzpatrick P, Baker JL, Goldhaber SZ. Normal D-dimer levels in emergency department patients suspected of acute pulmonary ...
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmona...
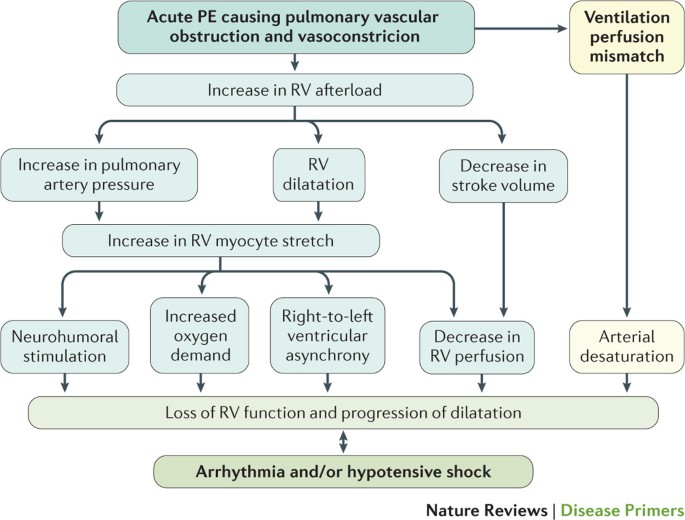
December 2, 2003 - This New Frontiers article reviews the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of pulmonary embolism (PE) in 2 parts. In this first section we summarize the mechanisms of right ventricular dysfunction, arterial hypoxemia, and other abnormalities of gas exchange.
Pulmonary emboli often arise from thrombi originating in the deep venous system of the lower extremities or pelvis. A blood clot dislodges and is swept into the pulmonary circulation and lodges in a p... more
September 2, 2021 - Mechanism: thrombus formation (see “Virchow's triad.”) → deep vein thrombosis in the legs or pelvis (most commonly iliac vein) → embolization to pulmonary arteries via inferior vena cava → partial or complete obstruction of pulmonary arteries [1] Pathophysiologic response of the lung ...
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is defined as a circulatory disorder of the pulmonary arteries, characterized by embolic occlusion of one or more pulmonary arteries most commonly caused by venous thrombi in the legs. PE is not a disease; rather, it is a complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). It is defined as a circulatory disorder of the pulmonary ...
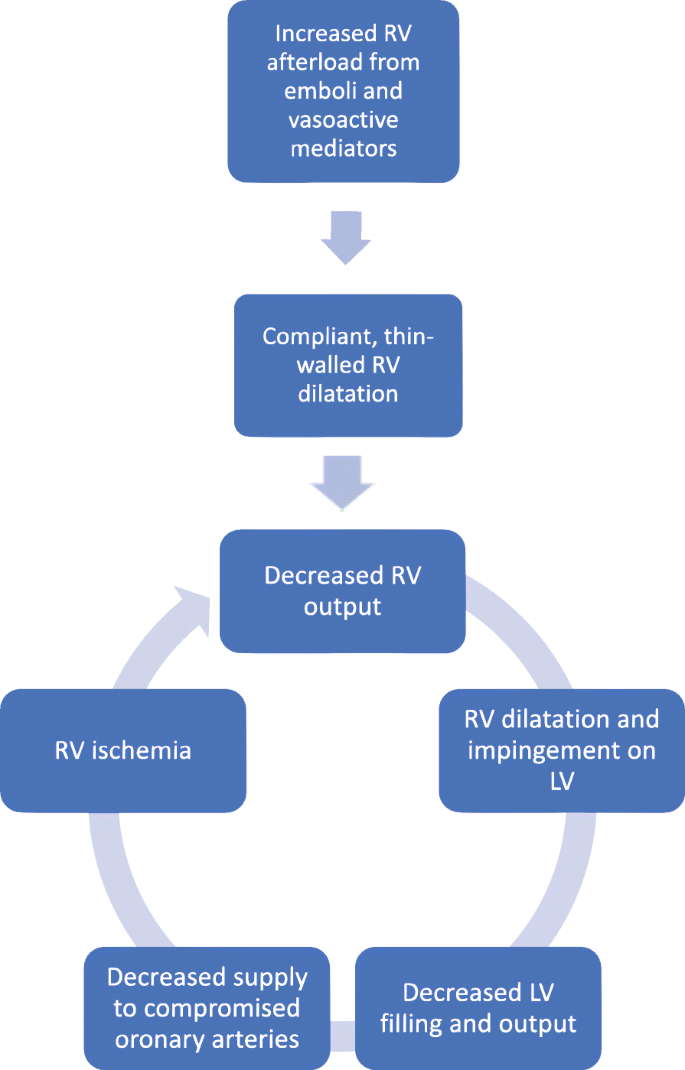
Acute right ventricular (RV) failure and impaired gas exchange (mainly hypoxaemia) can be two important issues clinicians are confronted with in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. An acute increase in RV afterload due to mechanical obstruction and vasoconstriction is the crucial factor ...
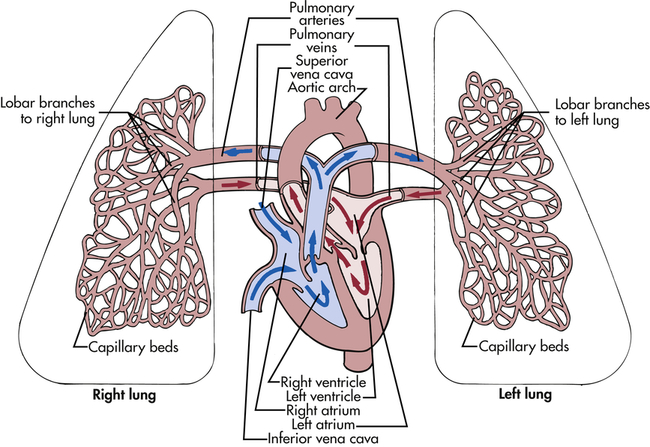
Pulmonary veins are thinner than the arteries because the muscular is not well developed. The pulmonary arterioles branch out to form capillaries which runs across several alveoli before forming venules. These venules run through the connective tissue which surrounds the alveoli. Therefore, each venule drains a number of alveoli. The venules unite to form progressively …
Mechanisms of Thrombosis Maureane Hoffman, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology . Blood clotting where it shouldn't or when you don't want it to. Things You Should Know:\r\(1\) Arterial \(and sometimes venous\) Thrombosis and Atherosclerosis \(Plaque Rupture\) - I consolidated things she said throughout the lectures on Slides 2 & 30\r\(2\) Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism - Slides 4, 5 & 8\r\
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is when a blood clot (thrombus) becomes lodged in an artery in the lung and blocks blood flow to the lung. Pulmonary embolism usually arises from a thrombus that originates in the deep venous system of the lower extremities; however, it rarely also originates in the pelvic, renal, upper extremity veins, or the right heart chambers (see the image below).
Chapter 129 Pulmonary Vascular Disease Figure 129.5 The histological appearance of pulmonary edema. PULMONARY EMBOLISM osms.it/pulmonary-embolism PATHOLOGY & CAUSES Blockage of pulmonary artery by a substance brought there via bloodstream Thrombus in remote site embolizes → lodges in pulmonary vascular tree → "pulmonary embolism" Obstruction of blood flow distal to embolism ...
Pathophysiology Arterial gas embolism is a major cause of death in diving and the initiating cause (pulmonary barotrauma) usually goes undetected. Caused most often by the expansion of respiratory gases during ascent, it also occurs when the breath is held during ascent from a dive, when there is local pulmonary pathology, when there is dynamic […]
11.01.2021 · Pathophysiology 'Diagram of the human heart) Normal valves: This video shows a normal aortic valve on the left and mitral valve on the right. Video from the Visible Human Heart: All cardiac valves have similar well defined interstitial cell layers, covered by endothelium. The three cell layers have specific features, and are named fibrose, spongiosa, and the …
Vascular obstruction (e.g., pulmonary embolism) The following diagram shows diseases or conditions that may result in reduced cardiac output, or those related to abnormal vascular function. ... To understand more fully the physiology and pathophysiology of hypotension, see the Blood Pressure Regulation Tutorial.
16.11.2021 · Pathophysiology of airflow limitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2004; 364:709. Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, et al. The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2004; 350:2645. Harkness LM, Kanabar V, Sharma HS, et al. Pulmonary vascular changes in asthma and COPD. Pulm …
A high incidence of thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism (PE), has been observed in COVID-19, which suggests that COVID-19 may induce intravascular coagulopathy [3–6]. PE may be a direct cause of death in patients with COVID-19, despite the use of antithrombotic prophylaxis [4, 6, 7].
Causes 1.thrombous 2. embolism 3.trauma 4. surgery 5. hypercoaguability 6. heart failure 7. pregnancy ( increase coaguability of BL 8. older than 50 years 9. atrial fibrillation · 4. Pathophysiology -When a thrombus completely or partially obstructs a pulmonary ...
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is the occlusion of pulmonary arteries by thrombi that originate elsewhere, typically in the large veins of the legs or pelvis. Risk factors for pulmonary embolism are conditions that impair venous return, conditions that cause endothelial injury or dysfunction, and underlying hypercoagulable states.
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot that gets into blood vessels in the lungs and prevents normal flow of blood in that area. This blockage causes problems with gas exchange. Depending on how big a clot and number of vessels involved, it can be a life-threatening event. Pulmonary Embolism Left atrium Left ventricle
Greenspan RH. Pulmonary angiography and the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1994 Sep-Oct; 37 (2):93–105. [Google Scholar] Hull RD, Raskob GE, Ginsberg JS, Panju AA, Brill-Edwards P, Coates G, Pineo GF. A noninvasive strategy for the treatment of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism.
Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism. Once deep venous thrombosis develops, clots may dislodge and travel through the venous system and the right side of the ...
September 6, 2020 - It seems to us that you have your JavaScript disabled on your browser. JavaScript is required in order for our site to behave correctly. Please enable JavaScript to use our site
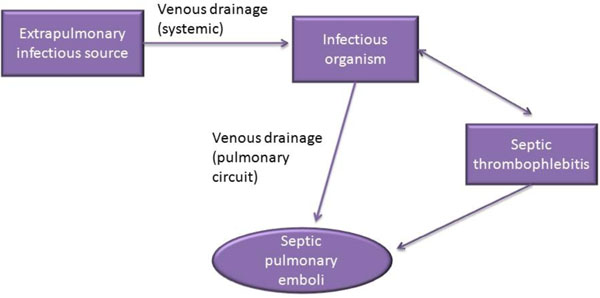
Pulmonary embolus is predominantly due to thrombus breaking off from deep veins or from within the right heart, lodging within large or small vessels within the pulmonary vasculature, causing a variable degree of clinical features ranging from asymptomatic through to shock and cardiac arrest. Non-thrombotic causes include air or fat embolism. Outcome is predicated by the degree of right ...
Pulmonary embolism is a common and potentially fatal cardiovascular disorder that must be promptly diagnosed and treated. The diagnosis, risk assessment, and management of pulmonary embolism have evolved with a better understanding of efficient use of diagnostic and therapeutic options. The use of either clinical probability adjusted or age adjusted D-dimer interpretation has led to a ...
Comparison of Effect of Ischemic Postconditioning on Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Treated With Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Versus Without Thrombectomy
Pulmonary embolus can be devastating leading to acute and chronic RV failure. Understanding the pathophysiology of RV failure in massive and submassive PE and CTEPH is the key factor in the justification for percutaneous interventions in selected patients. In addition, it aids communication ...
Healthy human lungs are normally the sites of fluid and solute filtration across the pulmonary capillary endothelium. Unlike other organs, the filtrate in the lungs is confined anatomically within adjacent interstitial spaces, through which it moves by a built-in pressure gradient from its site of formation to its site of removal through pulmonary lymphatic channels.
28.02.2020 · Pulmonary embolism: Tricuspidal regurgitation: Pneumothorax: Pericardial effusion : Pathophysiological differences between HFpEF and HFrEF. Only in HFrEF but not in HFpEF evidence-based therapy offers improvement in symptoms and prognosis. These differences highlight the need for understanding the differences in the pathophysiology between HFrEF …


















0 Response to "37 pulmonary embolism pathophysiology diagram"
Post a Comment