34 molecular orbital diagram for h2
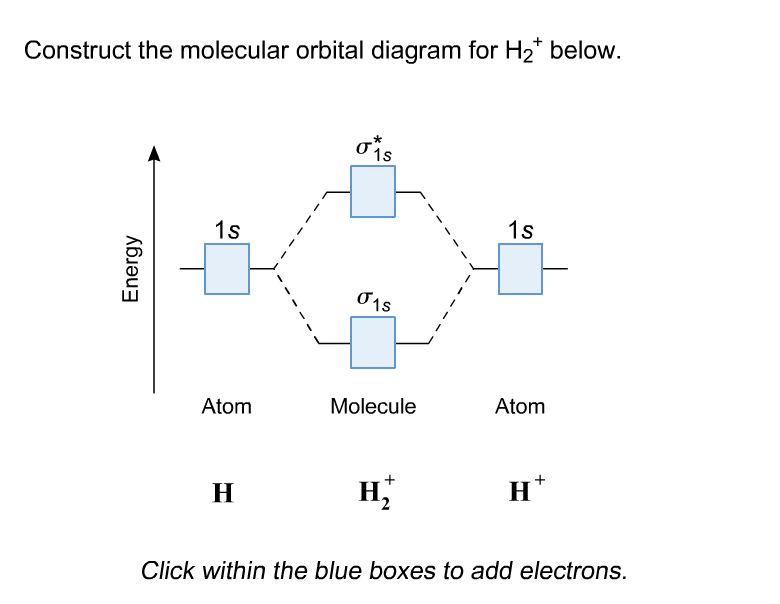
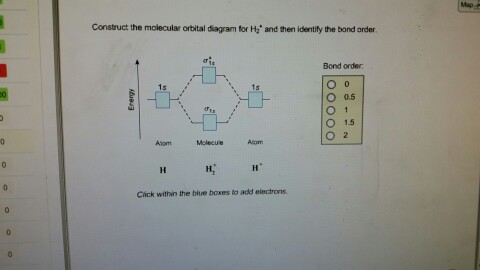
D.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^+ and then identify the bond order. *need before 7:00; Question: A.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^2+ and then identify the bond order. B.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, H 2), and the formation of H II regions.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion 1 Order of filling of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic molecules such as CO. Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure.

Molecular orbital diagram for h2
Answer (1 of 4): The bond order will be 3. Bond order is calculated as: (Bonding e - antibonding e) / 2 In normal O2, there are 6 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, making the bond order 2. By removing the 2 highest electrons, which reside in … Answer (1 of 4): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi... In H2, we have 2 hydrogen atoms, each with a 1s orbital. These orbitals are pointing at each other along the z axis, so they will make sigma orbitals. We can make molecular orbitals by combining these 2 atomic orbital to obtain 2 molecular orbitals. One orbital comes from addition, {H11s + H21s}, and the other comes from subtraction, {H11s - H21s}.
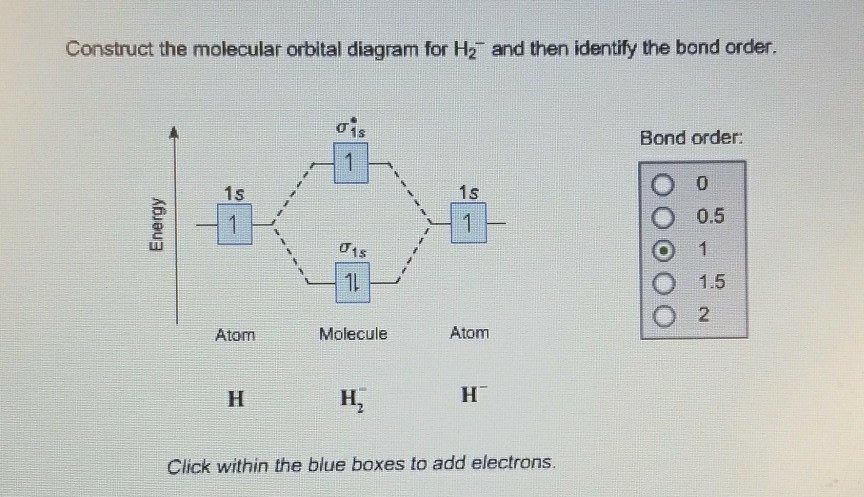
Molecular orbital diagram for h2. Answer (1 of 3): The two atomic orbitals overlap and they produce two molecular orbitals bonding (two the left) and anti-bonding (right): The energies of the two H atomic orbitals split into energy of the bonding molecular orbital and the energy of the anti-bonding molecular orbital. Here are ... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Now carbon monoxide’s MO diagram is: Hope it helps :) 59.1K views · View upvotes · Answer requested … Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. F22+, b2. The bond angle in NH3 is . 107 degrees. Identify the number of electron groups around a molecule with sp2 hybridization. 3. Consider the molecule below. Determine the molecular geometry at each of the 2 labeled carbons. C1 = trigonal planar, C2 = tetrahedral. Give the … Solved Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the ...
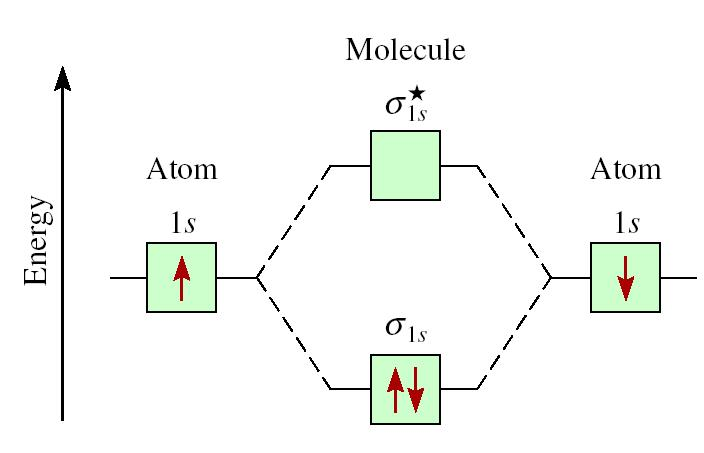
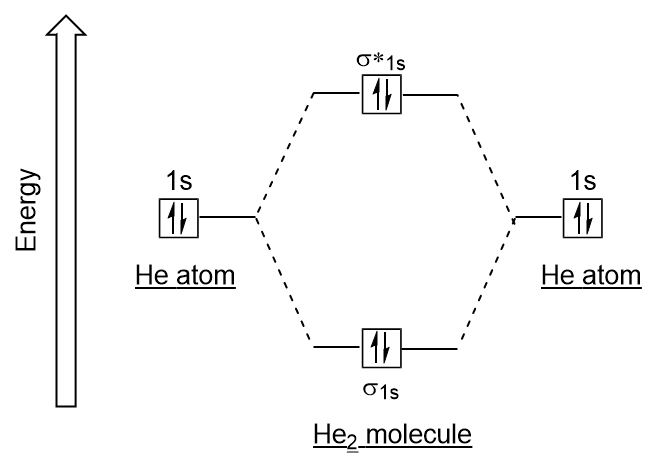
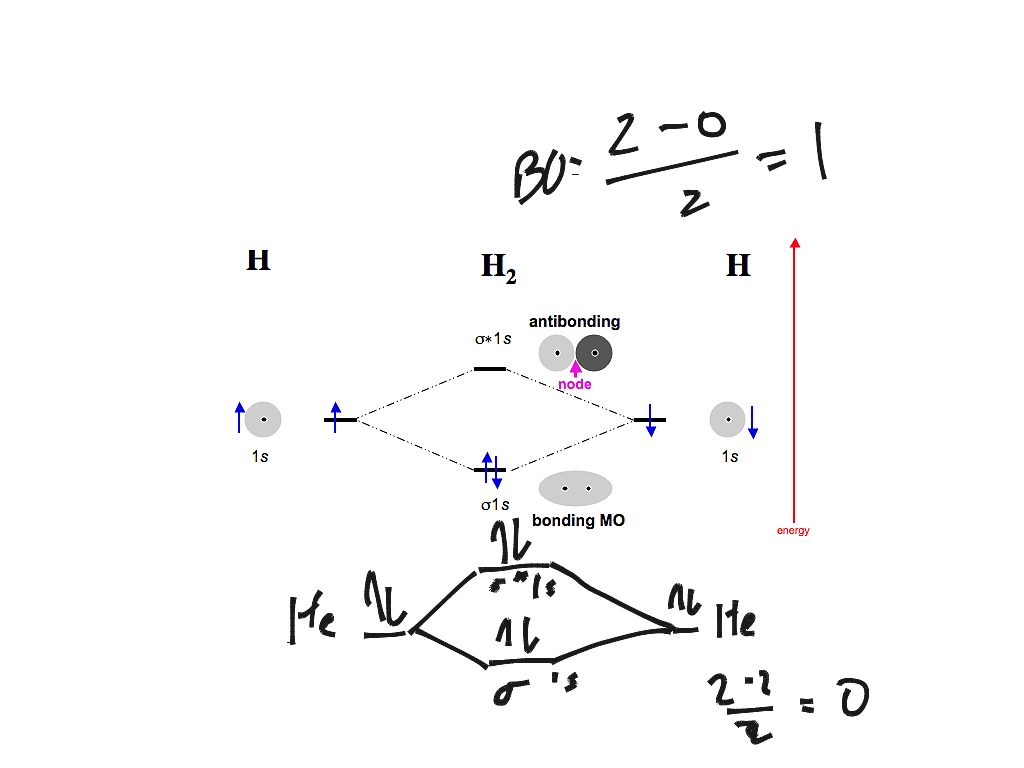
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ... -Be2+ has a weaker bond than H2.-The MO bond order for Be2+ is 1/2.-Be2+ is more likely to exist than Be2. Which of the following options correctly describe a molecular orbital (MO) energy-level diagram? Select all that apply. - The MO diagram typically includes valence-shell molecular orbitals only. - The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict … How many grams of H2 would be formed if 34 grams of carbon reacted with an unlimited amount of H2O? The reaction is: C + H2O → CO + H2 The equation is balanced. The starting substance is carbon, C. The ending substance is hydrogen, H2. Using the periodic table, find the molecular mass of H2. H2 =_____ g/mole The molecular orbital energy-level diagram shown in Figure 13 also applies (with changes of detail in the energies of the molecular orbitals) to the hypothetical species He 2. However, this species has four valence electrons, and its configuration would be 1σ 2 2σ 2.
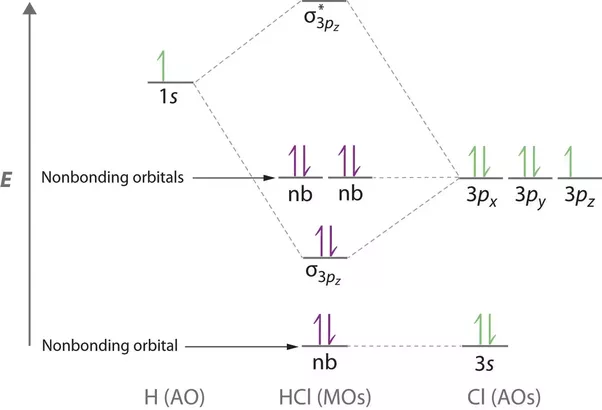
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular… MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital. The bond order = 1/2 x (Number of Bonding Electrons - Number of Antibonding Electrons) = . The Rules of Molecular Orbital Theory: First principle: The number of molecular orbitals produced is always equal to the number of atomic orbitals brought by the atoms that have combined. Second principle: Bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy that the parent orbitals, and the antibonding orbitals are higher in energy.
If you're following the pattern, you should draw the MO diagram for H2− 2 and see that we'd get: Bond Order = No. of Bonding e− −No. of Antibonding e− 2 = 2 − 2 2 = 0 The contribution of one electron in the antibonding orbital decreases the bond order, meaning that the bond in H2− 2 is even weaker than the bond in H− 2.
Question: Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Determine Whether He2 Or He2+ Is More Stable. These properties can be explained by the molecular orbital diagram of BN". The bond order of two suggests that the oxygen molecule is stable. Correct option (a) O-2. Diamagnetic Metals + properties give you a broad overview of these metals from multiple angels.
LCAO MO Energy Diagram for H2 Energy H-H ∆E1 ∆E2 • ∆E2> ∆E1, so the antibonding orbital is always more anti-bonding than the bonding orbital is bonding H2molecule: two 1s atomic orbitals combine to make one bonding and one antibonding molecular orbital. Ha Hb
Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals.
The bonding and anti-bonding orbitals are usually depicted by the molecular orbital diagram. Below mentioned is the molecular orbital diagram of the dihydrogen ion H2+. The atomic valence electrons (which are represented by the left and right boxes) at first fills the lower-energy molecular orbitals, and then it fills the higher ones.
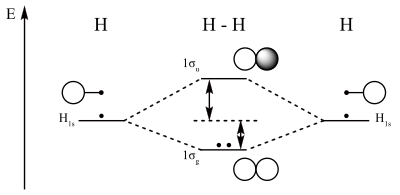
the molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the h 2 molecule is shown in figure on either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms a and b, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.the …
H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram MO diagram of dihydrogen Bond breaking in MO diagram The smallest molecule, hydrogen gas exists as dihydrogen (H-H) with a single covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms. As each hydrogen atom has a single 1s atomic orbital for its electron, the bond forms by overlap of these two atomic orbitals.
Mo Diagram H2. molecular orbital diagram a molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory marcus va 100 primary volts 120 240 secondary volts 12 24. Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2- And Then Identify The Bond Order.
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here.
04.09.2021 · Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic \(\ce{Be2+}\), showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and Hund’s rule. We predict the distribution of electrons in these molecular orbitals by filling the orbitals in …

Vaccine. Dr. J. Michael Hamilton preparing the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) vaccinia vaccine used to try to prevent cancer. He is diluting the concentrated vaccinia virus into a dose level appropriate for administration to a patient. This vaccinia marks any cancer cells expressing the CEA.
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the H2(2+) molecule. The bond order of H2(2+) is calculated and the meaning of this n...
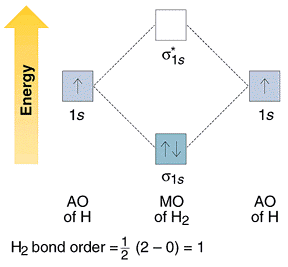
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H

Enteric Diseases Laboratory Branch (EDLB) Public Health scientist, who was using a whole genome DNA sequencer, in order to determine the “DNA fingerprint†of a specific bacterium. Photographer James Gathany
Molecular orbital diagram of h2 Answer General guidance Concepts and reason The bonding and anti - bonding interaction of the molecules can be explained with the help of a molecular orbital diagram. It also gives a detailed description of bonding in molecules. Bond order represents the number of bonds present in between two bonded atoms.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.The Hydrogen Molecule Ion H2+Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules - Chem
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule: Following the MO treatment of H2+, assume the (normalized) ground electronic state wavefunction is given by: gs ψψ αβ ... Qualitative MO theory orbital diagram for homonuclear diatomics composed of 1st or 2nd row elements:
starting with the lowest energy molecular orbital. The two electrons associated with a pair of hydrogen atoms are placed in the lowest energy, or bonding, molecular orbital, as shown in the figure below. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2molecule is As a result, the H2molecule is more stable than a pair of isolated atoms.
In H2, we have 2 hydrogen atoms, each with a 1s orbital. These orbitals are pointing at each other along the z axis, so they will make sigma orbitals. We can make molecular orbitals by combining these 2 atomic orbital to obtain 2 molecular orbitals. One orbital comes from addition, {H11s + H21s}, and the other comes from subtraction, {H11s - H21s}.

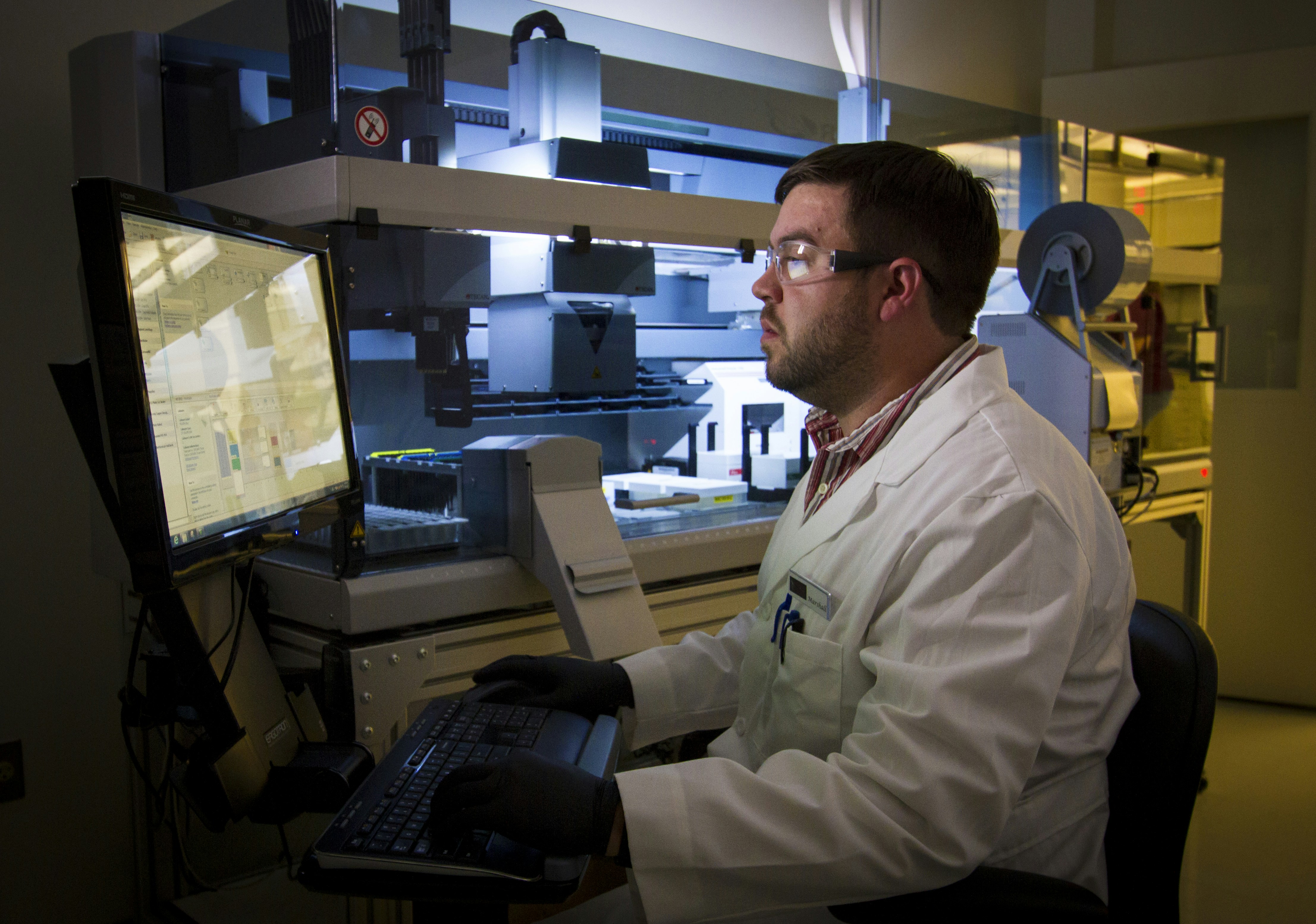
A technician performing an RNA-sequencing experiment on the Life Technologies 5500XL sequencer at the Advanced Technology Research Facility (ATRF), Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute.
Answer (1 of 4): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...
Answer (1 of 4): The bond order will be 3. Bond order is calculated as: (Bonding e - antibonding e) / 2 In normal O2, there are 6 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, making the bond order 2. By removing the 2 highest electrons, which reside in …

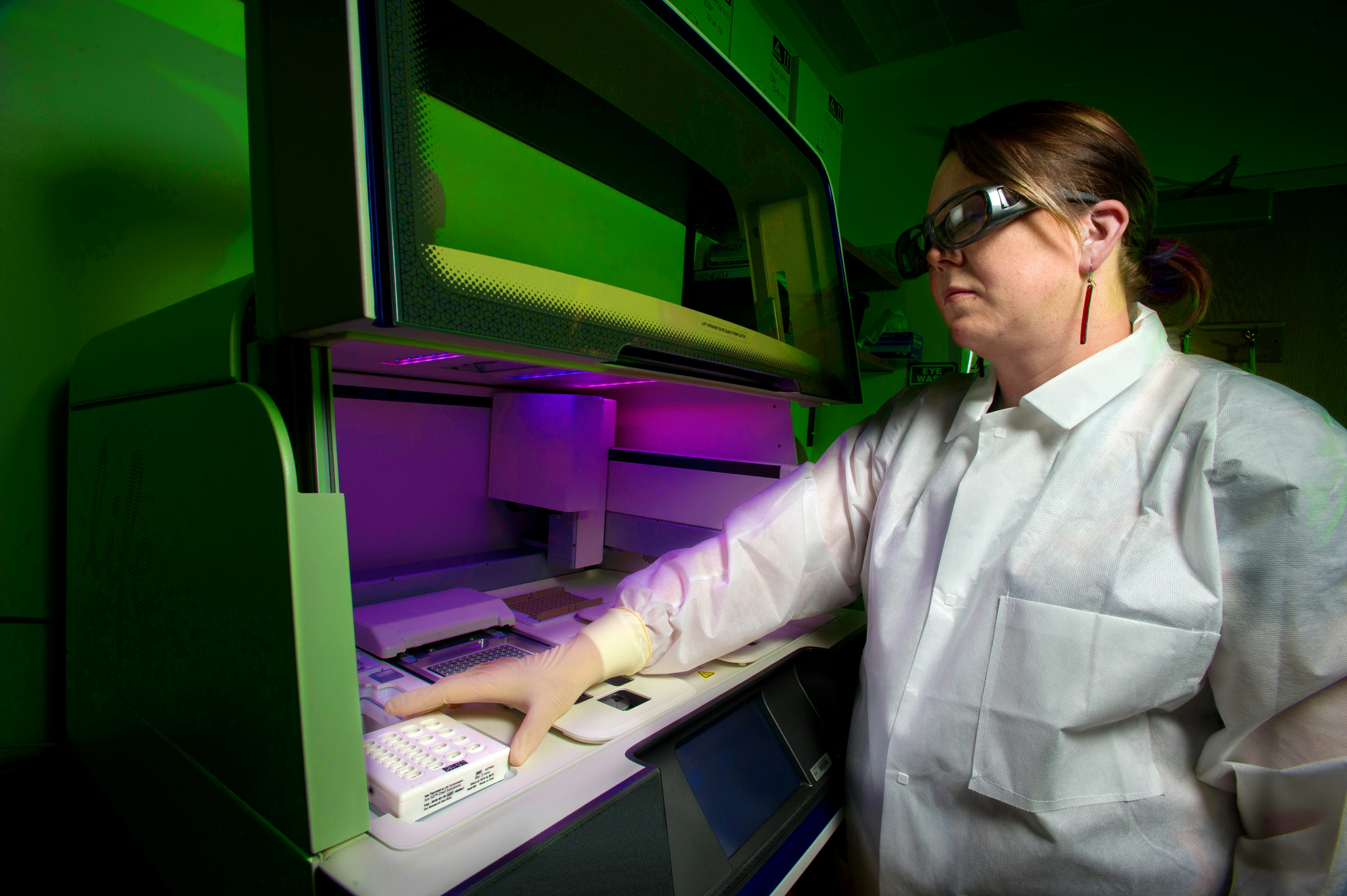
A female lab technician loading a semiconductor DNA sequencing chip used to identify specific cancer mutations in an individual. Photo taken at the Advanced Technology Research Facility (ATRF) at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute.
Vials of Blood. Vials of blood taken in the course of patient care at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland. Test tubes. Blood test. Creator: Daniel Sone

H2(-)MoleculeMODiagram.png)











0 Response to "34 molecular orbital diagram for h2"
Post a Comment