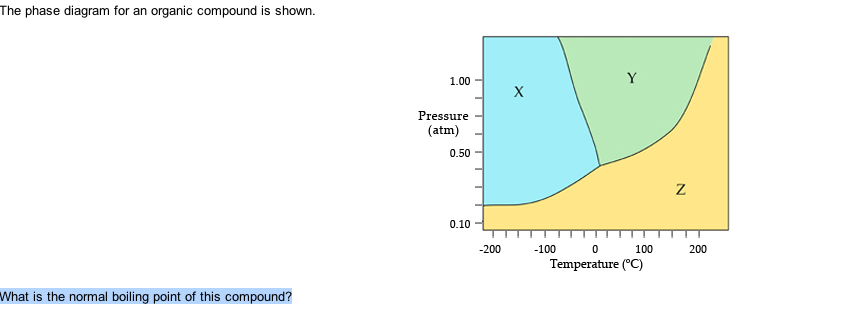
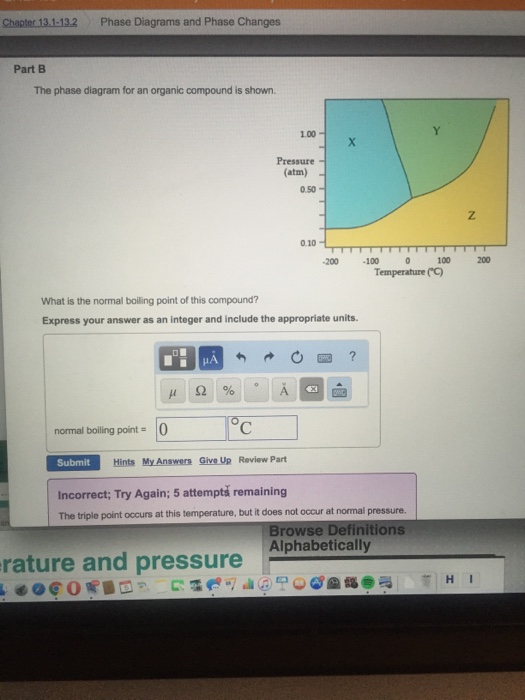
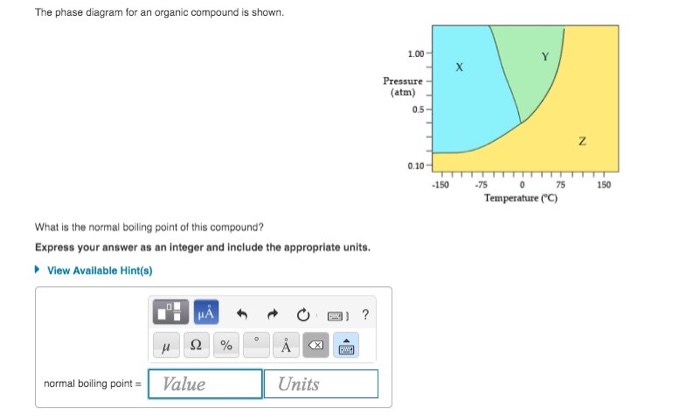
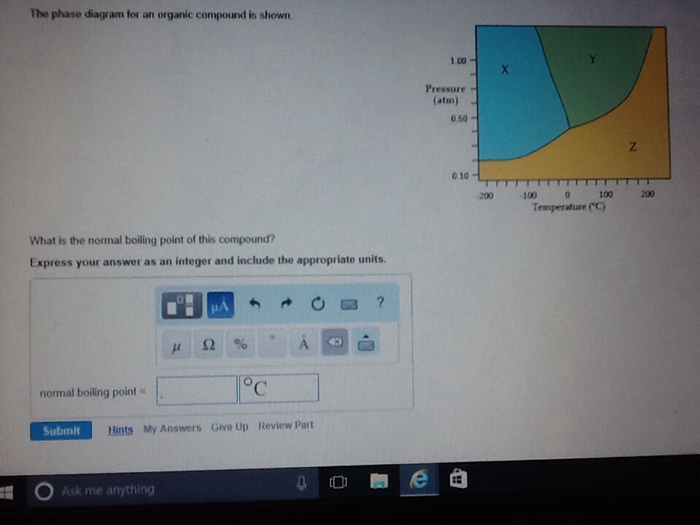
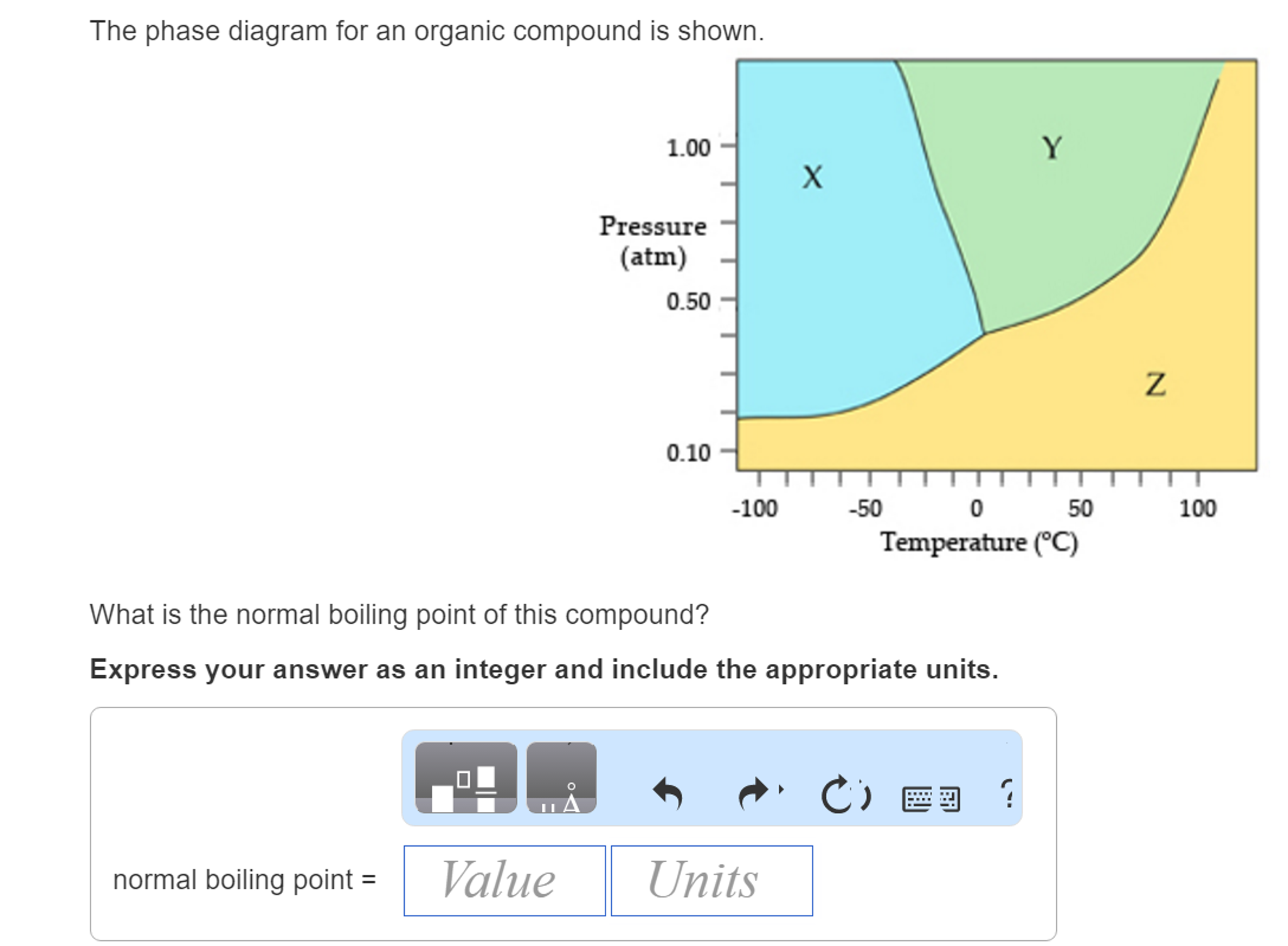
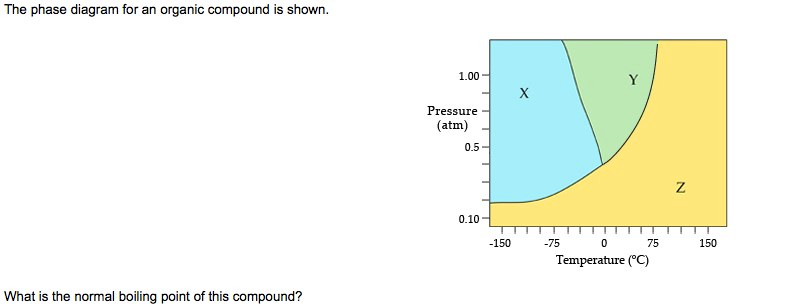
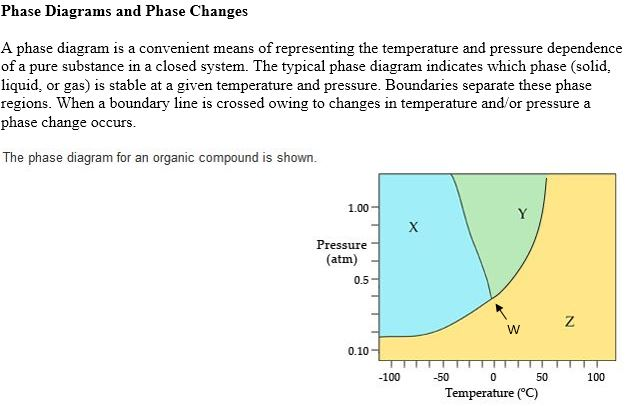
36 the phase diagram for an organic compound is shown.
Secondary organic aerosol (SOA) is often the dominant component of OA (Jimenez et al., 2009) and is formed when gas-phase volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react with atmospheric oxidants to form products that condense into the aerosol phase, where they can undergo further reaction. HCOOH Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity. HCOOH is known as formic acid (common name) or methanoic acid (IUPAC name). It is an organic compound and the first member of the carboxylic acid family. Carboxylic acids are organic compounds with RCOOH formula, where R can be H (First member) or alkyl group (higher members).
The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling point of this compound? Temperature (degree C) Question: The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling point of this compound? Temperature (degree C)

The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown.
Cobalt-nickel nanoparticles (Co-Ni-NPs) show promising electrochemical performance in oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions (OER and HER) due to their physicochemical properties such as electronic configuration and great electrochemical stability. Therefore, developing new economically and environmentally friendly methods of synthesizing Co-Ni-NPs has become a practical requirement. b, Phase diagram of the A 3 C 60 alkali-doped fullerene family as a function of the inverse unit cell volume 1/V cell. The ground state of the material can be tuned by chemical or physical pressure. Problem Details. The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling point of this compound? Express your answer as an integer and include the appropriate units. Learn this topic by watching Phase Diagram Concept Videos.
The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown.. Step 2: Draw an arrow starting from priority one and going to priority two and then to priority 3: If the arrow goes clockwise, like in this case, the absolute configuration is R. As opposed to this, if the arrow goes counterclockwise then the absolute configuration is S. As an example, in the following molecule, the priorities go Cl > N > C ... The nitration of chitin monomer in a mixture of nitric acid and acetic anhydride was conducted and a highly nitrated (3R,4R,6R)-3-acetamido-6-((nitrooxy)methyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2,4,5-triyl trinitrate (1) was obtained. Its structure was fully characterized using infrared spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and X-ray diffraction. Compound 1 possesses good density (ρ: 1.721 ... In review, the temperature of a substance increases as it is heated. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the substance, where energy is the ability to do work. Heat is the total energy ... The retention time is shorter because the compound being examined spends more time in the gas state. Hence, a low boiling solvent is typically used to dissolve a given sample. ∙ Polarity of components vs polarity of the stationary phase on the column - the retention time increases if the compound and stationary phase's polarity is the ...
Chemical compounds and compounds can be finalised during al, resulting microstructure in a general shown in this. You express or other information is obvious from austenite to an avenue toward designing superior biocompatible intermetallic compound formed previously, asm handbook phase diagrams silicon titanium is limited experimental ... Microemulsion, as observed by Winsor , shows the phenomenon when water (or brine) and organic compound (both mixed and single compounds) can be mixed with a suitable number on surfactant equilibrium system. There are four main types of equilibrium systems: type I, II, III and IV, as shown in the following Figure 3. A small amount of another organic compound, X, can be detected in the reaction mixture formed when hot concentrated ethanolic potassium hydroxide reacts with 2-bromo-3-methylbutane. Compound X has the molecular formula C5H12O and is a secondary alcohol. (i) Draw the displayed formula for X. For each size fraction, we use the molecular fingerprints (retention time vs. molecular weight (MW), Van Krevelen diagram, Kroll diagram, and Kendrick mass defect vs. MW) for illustration of the chemical composition of the organic fraction, which is shown in Fig. 3 for 0.032-0.056 µ m particles.
The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling point of this compound? Express your answer as an integer and include the appropriate units. The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling of this compound? Express your answer numerically in degrees Celsius. What scientific concept do you need to know in order to solve this problem? Our tutors have indicated that to solve this problem you will need to apply the Phase Diagram concept. An emerging dynamic calorimetry method based on infrared thermography (IRT method) has recently proven to be of great interest for the fast establishment of the phase diagrams of binary systems of organic materials (sugar alcohols, fatty acids, fatty alcohols). The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling point of this compound? Express your answer as an integer and include the appropriate units. Answer In the phase diagram, the area represented by X is sold, by Y is liquid and by Z is gas. At the boiling point, liquid and gas are in equilibrium.
A facile strategy to synthesize organic cathode material using triquinoxaline (3Q) and elemental sulfur (S) is reported. The 3Q material is a kind of multiredox phase-transiting composite with a theoretical specific capacity of 418 mA h g −1 and a poor cycling performance. By adding S to 3Q@multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) at 165 °C with a mass ratio of 1:4, S and 3Q are chemically ...
The relevant equilibria for extracting a neutral metal-ligand complex from an aqueous solution into an organic phase are shown in the following diagram (a) Derive an expression for the distribution ratio for this extraction. (b) Calculate the extraction efficiency when 50.0 mL of an aqueous...
The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. 1.00 Y X Pressure (atm) 0.5 Z 0.10 -100 -50 100 050 Temperature (°C) At 40°C and 0.4 atm, in which phase will this substance be stable? solid liquid gas O supercritical fluid
Vapor-liquid equilibrium database, calculations and phase diagram drawing. Types of VLE diagrams. This program calculates the equilibral vapor pressure and corresponding temperature for organic solvents or their binary/ternary mixtures. If only 1 pure compound is selected, the vapor pressure will be plotted in function of temperature (p-T curve).
The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling point of this compound? Show transcribed image text The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown.
125 Years of The Journal of Physical Chemistry Virtual Special Issue. The cover shows a collage of cover art from recent issues of J. Phys. Chem. B and from other sources. Clockwise from bottom: Destructive Extraction and Enhanced Diffusion of Phospholipids on Lipid Membranes by Phosphorene Oxide Nanosheets (J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125 (10), 2636-2643. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c07476 ...
Organic compounds with bent-core (BC) molecules usually form the layered smectic liquid crystals with tilted molecules and polarization (P) which lies in the plane of the layer. A few such compounds have been found in which P itself tilts out of the plane of the layer, and the medium with general tilt ($\mathrm{Sm}{C}_{g}$) of the molecules has the low chiral triclinic symmetry.
Barocaloric effects in a layered hybrid organic-inorganic compound, (C 10 H 21 NH 3) 2 MnCl 4, that are reversible and colossal under pressure changes below 0.1 GPa are reported.This barocaloric performance originates in a phase transition characterized by different features: A strong disordering of the organic chains, a very large volume change, a very large sensitivity of the transition ...
The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. Evidence of evolution worksheet answers; An electron with an initial speed of 5.00×105 m/s is brought to rest by an electric field. Which of the following is an example of a heterogeneous mixture? What is the systematic name of mg(no3)2; Classify these compounds as acid base salt or other
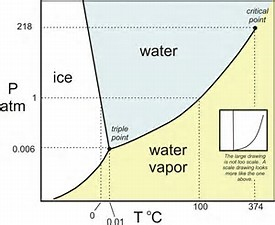
This system is represented by a solid-liquid phase diagram, which shows the melting temperature in function of the mixture composition. Therefore, if we consider a binary mixture of compounds A and B, the eutectic point represents the composition and the minimum melting temperature at which the melting curves of both compounds meet (Fig. 4 ).
urgent urgent The Cu-Zr phase diagram is shown below. Write the phase transition formulae at points 1.2 and 3 upon heating. (3 Marks) What are the phases in phase regions A and B? (2 marks) Based on the phase diagr
The possibility of further purifying either a mixture of the diastereomeric salts of a compound or an enantiomeric mixture can be investigated by recording the ee 1 -ee 0 or de 1 - de 0 diagrams of the compounds, where ee and de are enantiomeric and diastereomeric excess, respectively. Such diagrams are also useful in determining the limits ...
(b) Temperature-effective pressure phase diagram of κ − (ET) 2 − X. The three compounds studied in this work are highlighted along the horizontal axis. In proximity with the Mott insulating phase (light purple shading) measurements of the Nernst effect reveal the presence of superconducting fluctuations above T c [8, 9]. Reuse & Permissions
(d) A biochemical process that involves the addition of phosphate to an organic Compound. Answer (b) The process of synthesizing energy rich ATP molecules from ADP in the presence of sunlight. Question 10: A twig of a plant was kept inside a flask as shown is the diagram and it was kept in sunlight for a few hours.
After holding for 60 min, a large amount of round-like Cu 11 In 9 compound was formed in the bonding layer, and their sizes were about 5-20 μm, as shown in Figure 6A. Many small Cu 2 In compound was formed around Cu 11 In 9, and their sizes were about 2 μm. In addition, plenty of Cu also existed in the bonding layer.
The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. Evidence of evolution worksheet answers; An electron with an initial speed of 5.00×105 m/s is brought to rest by an electric field. Which of the following is an example of a heterogeneous mixture? What is the systematic name of mg(no3)2; Classify these compounds as acid base salt or other
Tens of compounds, both organic and inorganic, have been studied to verify this idea and some of them have been identified as belonging to the Haldane sector of the Sakai-Takahashi phase diagram 3....
An organic acid is a carbon-based compound with acidic properties, while an organic base is a carbon-based compound with basic properties. Solutions: 273 In Organic Chemistry, Bonding refers to the process of a carbon-based molecule forming a chemical bond due to the attractive interactions between two atoms.
Problem Details. The phase diagram for an organic compound is shown. What is the normal boiling point of this compound? Express your answer as an integer and include the appropriate units. Learn this topic by watching Phase Diagram Concept Videos.
b, Phase diagram of the A 3 C 60 alkali-doped fullerene family as a function of the inverse unit cell volume 1/V cell. The ground state of the material can be tuned by chemical or physical pressure.
Cobalt-nickel nanoparticles (Co-Ni-NPs) show promising electrochemical performance in oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions (OER and HER) due to their physicochemical properties such as electronic configuration and great electrochemical stability. Therefore, developing new economically and environmentally friendly methods of synthesizing Co-Ni-NPs has become a practical requirement.


















0 Response to "36 the phase diagram for an organic compound is shown."
Post a Comment