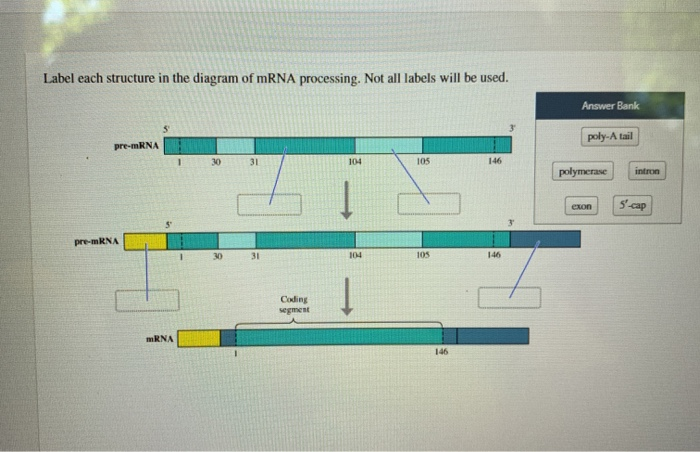
35 label each structure in the following diagram of mrna processing. not all labels will be used.
cloverleaf structure of 4 stems, each consisting of four to seven WatsonCrick type base pairs. Five reg- ions of the tRNA are not base paired, the CCA acceptor stem, the -loop (named for the presence ofD dihydrouridine), the anticodon loop which interacts with the mRNA, the "extra arm" and the TYC loop- Hence is the name Ribonucleic acid. RNA is also referred to as an enzyme as it helps in the process of chemical reactions in the body. Basic Structure of RNA. The basic structure of RNA is shown in the figure below-The ribonucleic acid has all the components same to that of the DNA with only 2 main differences within it.
• genes can be expressed (use to make proteins) or repressed (not used) • regions of DNA are divided into coding and non-coding segments • over 50% of human DNA is non-coding • genes can be spliced together • genes are organized in the large-scale structure of the DNA in the nucleus In bacteria, genome usually circular
Label each structure in the following diagram of mrna processing. not all labels will be used.
Answer Key 4. Problem Set 4 Answers. 1a. The template DNA strand, from which the mRNA is synthesized, is 5' CAAACTACCCTGGGTTGCCAT 3'. (RNA synthesis proceeds in a 5' à 3' direction, so the template strand and the mRNA will be complementary to each other) b. The coding DNA strand, which is complementary to the template strand, is 5 ... The genetic code present in the DNA and later transcribed into mRNA consists of 64 triplets of nucleotides. These triplets are called codons.With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. That produces some redundancy in The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made. During protein synthesis, an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA, reads its base sequence, and uses the genetic code to translate each three-base triplet, or codon, into its corresponding amino acid.
Label each structure in the following diagram of mrna processing. not all labels will be used.. A quick overview of the process. You will remember that messenger RNA contains a sequence of bases which, read three at a time, code for the amino acids used to make protein chains. Each of the sets of three bases is known as a codon. The table below repeats one from the previous page: Drag the correct labels onto the nucleotides in the RNA transcript. Not all labels will be used. Drag the correct labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and molecules involved in translation. The diagram below shows the arrangement of the translation components during initiation. Label each structure in the diagram of mRNA processing. Not all labels will be used. Why is a cap added to mRNA, but not to tRNA or rRNA? RNA polymerase II transcribes mRNA, whereas RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNA, and RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA. The domain that assists other enzymes in adding the cap is found in RNA polymerase II only. Biology. Biology questions and answers. Label each structure in the following diagram of mRNA processing. Not all labels will be used. Questions 11-14 Use asnwers A - E below pre-mRNA 1 30 31 104 105 146 + 1 12.. pre-mRNA 30 31 105 146 13.. Coding segment 14.. mRNA 146 exon 5-cap polymerase poly-A tail intron.
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes. 2.1. mRNA vaccine structure. Construction of mRNA vaccines requires the insertion of the encoded antigen in a DNA template from where the mRNA is transcribed in vitro.Unlike DNA, mRNA only needs to reach the cytosol, where it will be transcribed into the antigen in vivo, using the cell machinery. This way, any desired sequence can be designed, produced in vitro, and delivered to any type of cell . Anticodon Definition Biology. Sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons are called anticodon. They are found in tRNAs and allow the tRNAs to take correct amino acid in a way with mRNA during protein production. During protein production, amino acid bounded together into a string, such as beads on the bracelet. The correct amino acid must be used in incorrect places because ... labeled 5′ and 3′ ends. Answer: transcription start promote. r 5´ UT 3´ UT translation start translation stop termination site ( ) ( ) 5´ 3´ mRNA DNA. 20. Draw a two-intron eukaryotic gene and its pre-mRNA and mRNA products. Be sure to include all the features of the prokaryotic gene included in your answer
The structure of mRNA is very similar to DNA in that it has a sugar-phosphate backbone to which the chemical bases are attached. However, there are some important differences: (1) mRNA is single-stranded and therefore does not form a double helix, (2) the sugar used to form the backbone is slightly different, The mRNA transcript is coated in RNA-stabilizing proteins to prevent it from degrading while it is processed and exported out of the nucleus. The three most important steps of pre-mRNA processing are the addition of stabilizing and signaling factors at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the molecule, and the removal of intervening sequences that do not specify the appropriate amino acids. Thus, catalysing all the three steps. (vii) Since, the mRNA does not require any processing to become active and also since transcription and translation take place in the same compartment, many times the translation can begin much before the mRNA is fully transcribed. As a result,transcription and translation can be coupled in bacteria. 23. 1. Strands and Directions of Synthesis. All strands are synthesized from the 5' ends > > > to the 3' ends for both DNA and RNA. Protein chains are synthesized from the amino ends > > > to the carboxy ends. Color mnemonic: the old end is the cold end (blue); the new end is the hot end (where new residues are added) (red).
In the nucleus, a pre-mRNA is produced through transcription of a region of DNA from a linear chromosome. This transcript must undergo processing (splicing and addition of 5' cap and poly-A tail) while it is still in the nucleus in order to become a mature mRNA. The mature mRNA is exported from the nucleus to the cytosol, where it is translated ...
The diagram below represents a part of the process of protein synthesis. 8.1 Name or provide labels for N, P, Q, and Z (4) 8.2 Write down the sequence of the FIRST THREE nitrogenous bases on the DNA strand that led to the formation Z. (2)
The structure of the DNA and RNA molecule is very important and is often examined. Make sure that you know the labels of each component. Remember to label the diagram first and then move onto the questions . Learner Note: Please ensure that you understand that the nucleus is an organelle located in a cell.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 1- Exon …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label each structure in the following diagram of mRNA processing. Not all labels will be used.
6. The diagram below shows a DNA molecule in the process of replication. Arrows show the direction of new DNA synthesis. a. Some of the enzymes and features are labeled, but some labels are incomplete or have been omitted. Fill in the boxes with the appropriate labels. b.
mRNA Processing • Cap -7-methyl guanosine (7mG) added to 5' end of mRNA -Protects against nucleases -Recognition for transport out of nucleus • Tail -Poly-A sequence added to 3' end of mRNA -3' terminal end cleaved at AAUAAA sequence before polyadenylation (most mRNA) -Protects from degradation
Chapter 9 - 10 Phase Diagrams • Indicate phases as function of T, Co, and P. • For this course:-binary systems: just 2 components.-independent variables: T and Co (P = 1 atm is almost always used). • Phase Diagram
Base-Pairing Underlies DNA Replication and DNA Repair. As discussed briefly in Chapter 1, DNA templating is the process in which the nucleotide sequence of a DNA strand (or selected portions of a DNA strand) is copied by complementary base-pairing (A with T, and G with C) into a complementary DNA sequence ().This process entails the recognition of each nucleotide in the DNA template strand by ...
Partially unzips/unwinds during the process of transcription: _____ 18. Complete the following table, which compares the three different kinds of RNA. mRNA tRNA rRNA Description The RNA copy of the DNA message The RNA that binds to the amino acid and binds to the mRNA; brings each new amino acid to the growing polypeptide The RNA that is a
Each group of three bases in mRNA constitutes a codon, and each codon specifies a particular amino acid (hence, it is a triplet code). The mRNA sequence is thus used as a template to assemble—in ...
The diagram or the structure of the Neuron is useful for both Class 11 and 12 board exams as it has been repetitively asked in the board examinations. It is also one among the few topics having the highest weightage of marks. Learn More: Difference between Sensory and Motor Neuron. Diagram Of Neuron with Labels
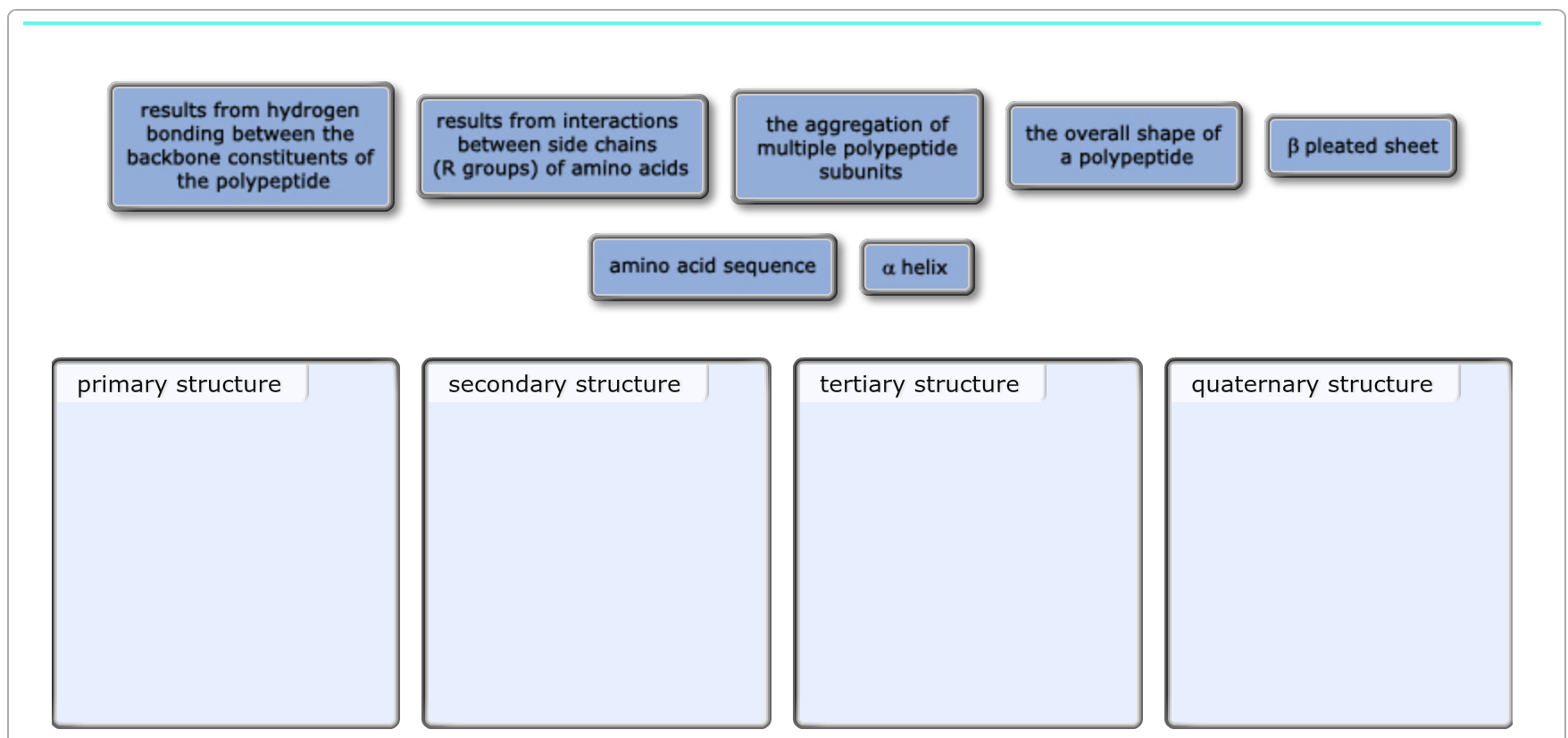
The secondary structure of a typical tRNA, in this case tRNAAla, is shown in Figure 1, below. The structure consists of hydrogen bonded stemsand associated loops, which often contain nucleotides with modified bases (e.g. inosine[I], ribothymidine [T], pseudouridine[Ψ], methylguanosine[D]). Figure 1. Schematic of tRNA (tRNAAlanine) secondary structure. Figure modified from Becker, et al., The World of the Cell. The tertiary structure of all tRNAs is similar to that of tRNAPhe, at left, a canonical "L-shaped" molecule. As can be seen, the "cloverleaf" secondary structure shown in Figure 1 results in a complex three dimensional folding of the molecule. The amino acid attachment site at the 3' end and the anticodon loopare observed at the two ends of the "L." The hydrogen bonded stems stabilize the tertiary structure. The Acceptor and Anticodon stemsare indicated. Modified bases in the Anticodon, T, and Dloops are indicated by thick wireframe. The anticodon bases project from the antico...
The information to produce a protein is encoded in the cell's DNA. When a protein is produced, a copy of the DNA is made (called mRNA) and this copy is transported to a ribosome. Ribosomes read the information in the mRNA and use that information to assemble amino acids into a protein. If the protein is going to be used within the cytoplasm ...
The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made. During protein synthesis, an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA, reads its base sequence, and uses the genetic code to translate each three-base triplet, or codon, into its corresponding amino acid.
The genetic code present in the DNA and later transcribed into mRNA consists of 64 triplets of nucleotides. These triplets are called codons.With three exceptions, each codon encodes for one of the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of proteins. That produces some redundancy in
Answer Key 4. Problem Set 4 Answers. 1a. The template DNA strand, from which the mRNA is synthesized, is 5' CAAACTACCCTGGGTTGCCAT 3'. (RNA synthesis proceeds in a 5' à 3' direction, so the template strand and the mRNA will be complementary to each other) b. The coding DNA strand, which is complementary to the template strand, is 5 ...











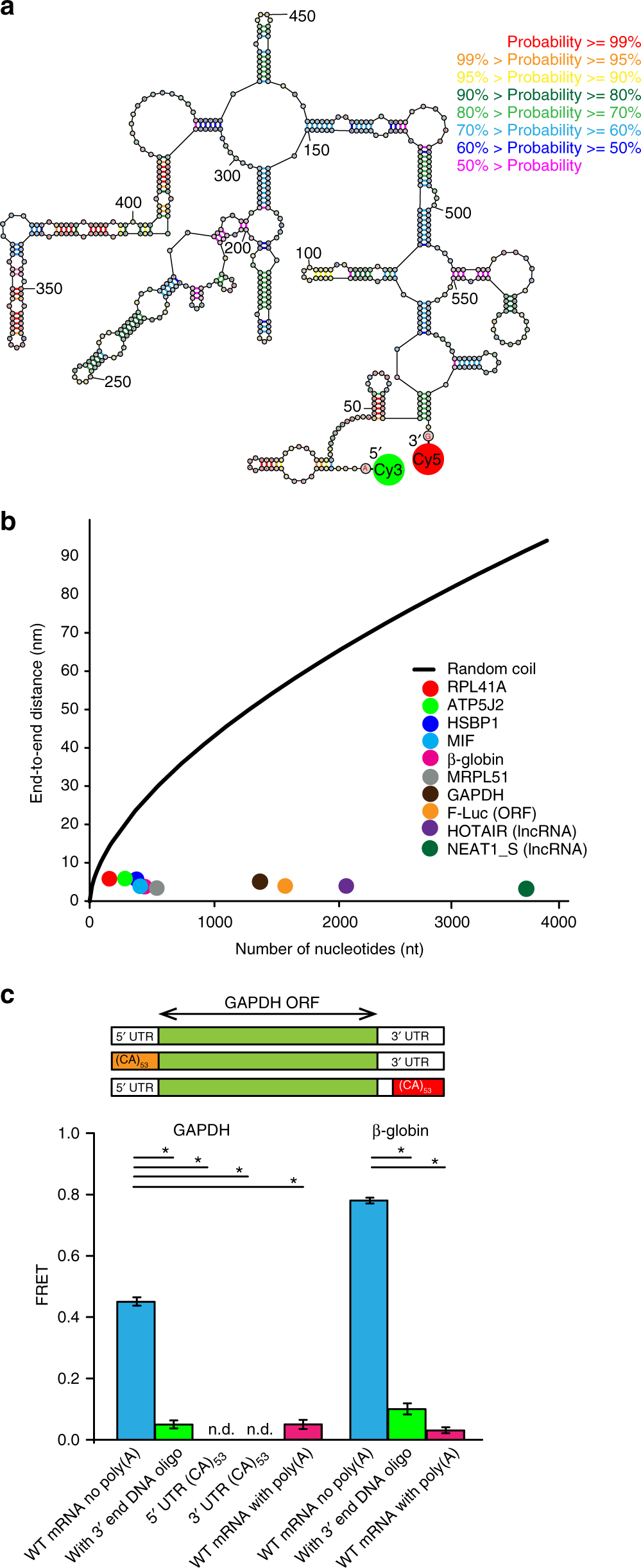






0 Response to "35 label each structure in the following diagram of mrna processing. not all labels will be used."
Post a Comment