36 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of good Y? $_____ B. What is the consumer's income? $_____ C. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? _____ units. D. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. The equilibrium of the economy is the point at which the wage- and price-setting curves intersect, shown by X in the figure. Workers are working: They have no incentive to shirk. If they demanded higher pay, their employer would refuse, or replace them.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ 5. b. What is the consumer's income? $ 100. c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? 10 units. d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
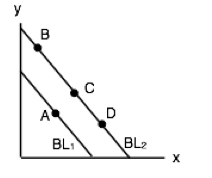
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
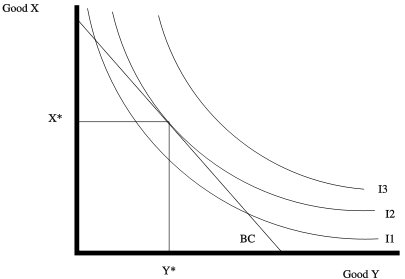
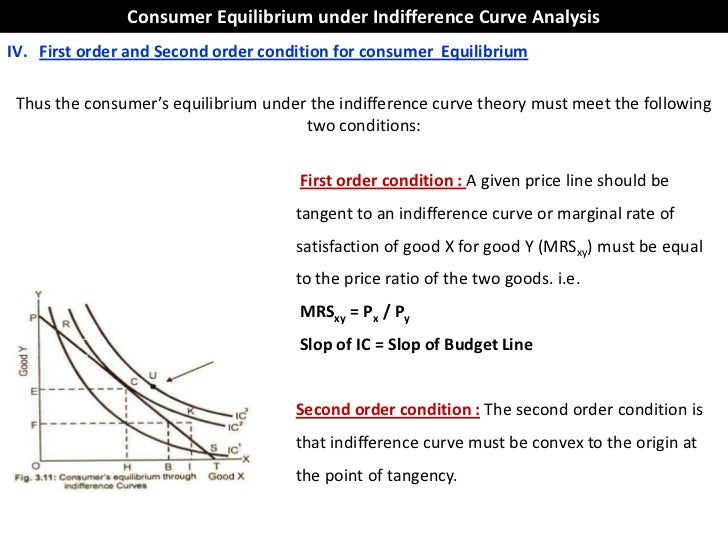
It means, by moving left or right of point E, a consumer can obtain higher amount of either good X or good Y. Thus point E is not an equilibrium point. A consumer will therefore be in equilibrium when at the point of tangency of indifference curve and the budget line, the indifference curve is convex to the origin. 3) 4) In the below figure, a consumer is initially in equilibrium at point C. The consumer's income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $100 X + $200 Y. When the consumer is given a $100 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a new equilibrium at point D. Explanation a. P x = $100, P y = $200 ... View Homework Help - Graded HW 2 CH 4.docx from ECN 5150 at University of North Carolina, Pembroke. 1. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What
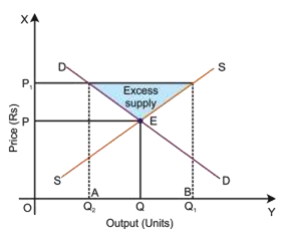
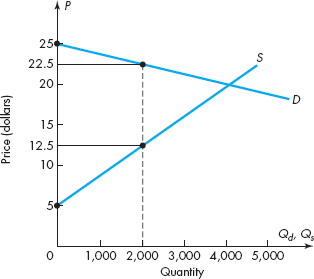
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.. Thus at the equilibrium point E,MRSXY=Price of good x/Price of good y= PX/PY The tangency between the given price line and an indifference curve is a necessary but not a sufficient condition consumer's equilibrium .The second condition for consumer's equilibrium is convexity of indifference curve to the origin . The equilibrium price of wheat is $5 and the equilibrium quantity is 100 bushels, as shown in the diagram on the right. Suppose the government institutes a policy that prohibits wheat farmers from growing more than 60 bushels of wheat in total. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y?$ b. What is the consumer's income?$ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. We know good Y is not a normal good if, as income increases, the consumer's new equilibrium position is at point d Mrs. Arnold is spending all her money income by buying bottles of soda and bags of pretzels in such amounts that the marginal utility of the last bottle is 60 utils and the marginal utility of the last bag is 30 utils.
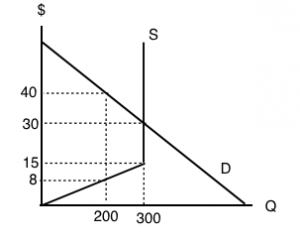
Solve for the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. Q^S=2P Q^D=300-P. 2. Suppose that a tax of T is placed on buyers, so the new demand equation is q^d=300-(p+t) Solve for the new equilibrium. What happens to the price received by sellers, the price paid by buyers, and the quantity sold? 3. Tax revenue is TxQ. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y if the price of good x is $ 5 at equilibrium, Price of good Y would be $5. b. What is the consumer's income? X= m/p x The price of good X 1 P x =$5 and the maximum affordable quantity of good X is 20 units so 20= M/$5 so M = $100 which is the consumers income. c. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ b. What is the consumer's income? $ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? units The budget line is tangent to indifference curve IC2 at point 'E'. This is the point of consumer equilibrium, where the consumer purchases OM quantity of commodity ';X' and ON quantity of commodity 'Y. All other points on the budget line to the left or right of point 'E' will lie on lower indifference curves and thus indicate a ...
A consumer is said to be in equilibrium when he feels that he "cannot change his condition either by earning more or by spending more or by changing the quantities of thing he buys";. A rational consumer will purchase a commodity up to the point where price of the commodity is equal to the marginal utility obtained from the thing. In the following question you are asked to determine, other things equal, the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for, or supply (S) of, X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X; and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X. Refer to the given information. By observing a consumer’s response to a change in price, we can derive the consumer’s demand curve for a good. Panel (a) shows that at a price for horseback riding of $50 per day, Janet Bain chooses to spend 3 days horseback riding per semester. A motorist drives on State Road 417 to and from work each day and pays $3.50 in tolls one-way. a. Write a model for the cost for tolls C (in $) for x working days. b.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the accompanying figure. The price of good X is $5.. a. What is the price of good Y? b. What is the consumer's income? c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium?
Here, MU meets the price level at two different points A and B. At point A (2 nd unit), the marginal utility intersects the price level on a rising trend. A consumer derives a higher utility from additional consumptions of the 3 rd and 4 th units. On the 5 th unit, it intersects the price level at point B. Any additional consumption beyond this point shows a lower marginal utility than such ...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. ... Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium? The price of good Y decreased to $2.50. The price of good Y increased to $10.
A consumer must divide $250 between the consumption of product X and product Y. The relevant market prices are Px = $5 and Py = $10.a. Write the equation for the consumer's budget line.b. Illustrate the consumer's opportunity set in a carefully labeled diagram.c. Show how the consumer's... View Answer.
Use the figure below to calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand for good X when the price of good Y decreases from $20 to $16. A. -3.0 B. -0.82 C. -1.22 D. -1.17 E. -0.30 View Answer
Answer to Solved A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the. Transcribed image text: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. Good Y 45 40 35 30-1 B 25 20 15 10 5 - 0 20 Good X 2 a.
A consumer is in equilibrium and is spending income in such a way that the marginal utility of product X is 40 units and that of Y is 16 units. If the unit price of X is $5, then the price of Y must beA) $1 per unit. B) $2 per unit. C) $3 per unit. D) $4 per unit.
It can be seen from the given diagrams that Figure B is derived from Figure A. In figure A, initially, consumer equilibrium is attained at point E, where MU (10) = Price (10). Corresponding to point E, we derive point E 1 in figure B. Due to fall in price (suppose from 10 to 8), MU > Price at the given quantity.
refer to the diagram. the budget line shift that moves the consumer's equilibrium from point A to point B suggests: that X is an inferior good. all of the following would reduce property crime by increasing its "price" except:
View Homework Help - Graded HW 2 CH 4.docx from ECN 5150 at University of North Carolina, Pembroke. 1. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What
3) 4) In the below figure, a consumer is initially in equilibrium at point C. The consumer's income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $100 X + $200 Y. When the consumer is given a $100 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a new equilibrium at point D. Explanation a. P x = $100, P y = $200 ...
It means, by moving left or right of point E, a consumer can obtain higher amount of either good X or good Y. Thus point E is not an equilibrium point. A consumer will therefore be in equilibrium when at the point of tangency of indifference curve and the budget line, the indifference curve is convex to the origin.























0 Response to "36 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5."
Post a Comment