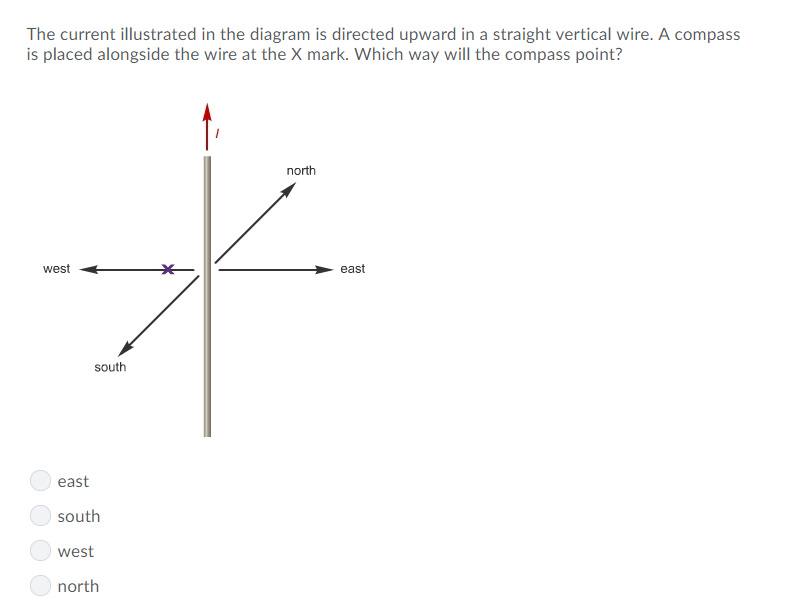
36 the current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire
An object with mass m and charge q is moving vertically downward with speed v when it is at the same vertical position as a horizontal current-carrying wire, as shown above. The current in the wire is directed out of the page. The magnitude of the magnetic field created by the wire at the location of the object is B. depends on its velocity and charge . In the case of a current-carrying wire, many charged particles are simultaneously in motion, so the magnetic force depends on the total current and the length of the wire . The size of the magnetic force on a straight wire of length carrying current in a uniform magnetic field with strength is.
The ratio F/l is the force per unit length between two parallel currents and separated by a distance r.The force is attractive if the currents are in the same direction and repulsive if they are in opposite directions. This force is responsible for the pinch effect in electric arcs and other plasmas. The force exists whether the currents are in wires or not.

The current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire
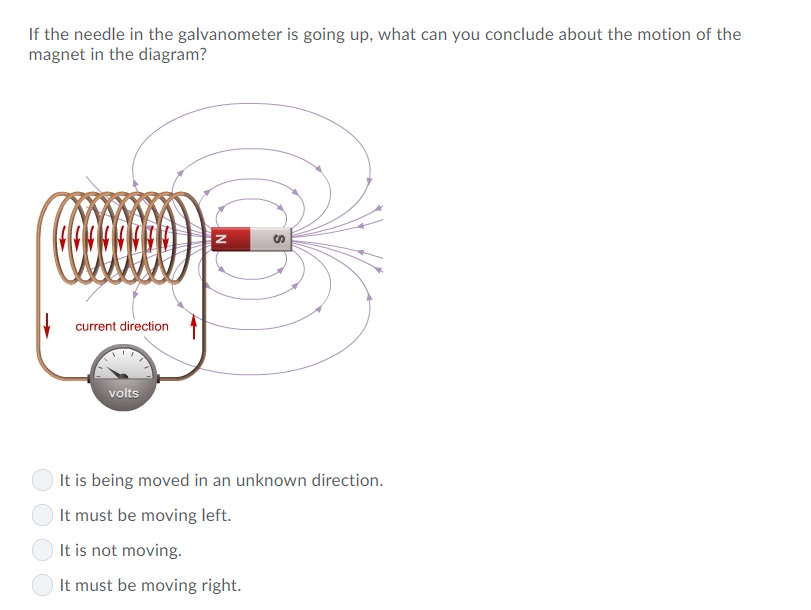
The current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire. A compass is placed alongside the wire at the X mark. Which way will - 2166040 Lenz's Law. The direction of the induced emf drives current around a wire loop to always oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes the emf. Lenz's law can also be considered in terms of conservation of energy. If pushing a magnet into a coil causes current, the energy in that current must have come from somewhere. The direction of the current in the conductor (wire) is shown by the central arrow. and they also have a direction indicated by the arrows on the lines. Similar to the situation with electric field lines, the greater the number of lines (or the closer they are together) in an area the stronger the magnetic field.
The current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire. PHY2049: Chapter 30 21 Induced currents ÎA circular loop in the plane of the paper lies in a 3.0 T magnetic field pointing into the paper. The loop's diameter changes from 100 cm to 60 cm in 0.5 s What is the magnitude of the average induced emf? What is the direction of the induced current? If the coil resistance is 0.05Ω, what is the average induced current? Problem 4: 31-9 A loop of wire in the shape of a rectangle of width w and length L and a long, straight wire carrying a current I lie on a tabletop as shown below. (a) Determine the magnetic flux through the loop due to the current I. (b) Suppose that the current is changing with time according to I =a+bt =10.0 Charged Particle Moving Near Wire ÎWire carries current of 400 A upwards Proton moving at v = 5 ×106 m/s downwards, 4 mm from wire Find magnitude and direction of force on proton ÎSolution Direction of force is to left, awayfrom wire Magnitude of force at r = 0.004 m v I 0 2 I F evB ev r μ π ⎛ ⎞ ==⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ ()() 19 6 2 10 4007 1 ... 28 The diagram below represents straight wave fronts passing from deep water into shallow water, with a change in speed and direction. Which phenomenon is illustrated in the diagram? (1) reflection (3) diffraction (2) refraction (4) interference 29 Which diagram best represents the path taken by a ray of monochromatic light as it passes from ...
Model the vortex as a long, straight wire carrying a current. In each of parts (a) through (c) of Figure P30.2, find the direction of the current in the wire that would produce a magnetic field directed as shown. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point 25.0 cm from a long, thin conductor carrying a current of 2.00 A. current flows in the counterclockwise direction. The current then sets up an induced magnetic field and produces a positive flux to counteract the change. The situation described here corresponds to that illustrated in Figure 10.1.7(c). Alternatively, the direction of the induced current can also be determined from the point of view of magnetic ... A straight, vertical wire carries a current of 1.27 A downward in a region between the poles of a large superconducting electromagnet, where the magnetic field has a magnitude of B = 0.592 T and is horizontal. PART A: What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a section of the wire with a length of 1.00 cm that is in this uniform magnetic ... A straight vertical wire carries a current of 1.45 A downward in a region between the poles of a large electromagnet where the field strength is 0.550 T and is horizontal. What are the magnitude of the magnetic force on a 1.80 cm section of this wire if the magnetic-field direction is 20.0 o south of west ?
Consider a straight current-carrying wire which is held vertically in the upward direction from A to B. The wire is held as in the given figure to find the direction of the magnetic field lines that is produced when the current flows through the wire. ... The force on the wire due to the magnet is directed: a) from N to S. b) from S to N. c ... The magnetic field of a straight, current-carrying wire is A. Parallel to the wire. B. Inside the wire. C. Perpendicular to the wire. D. Around the wire. E. Zero. Slide 32-16 ... A long, straight wire extends into and out of the screen. The current in the wire is A. Into the screen. B. Out of the screen. C. There is no current Lakhmir Singh solutions for Class 10 Physics (Science) chapter 2 (Magnetic Effects of Electric Current) include all questions with solution and detail explanation. This will clear students doubts about any question and improve application skills while preparing for board exams. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clear your confusions, if any. 24. A long, straight wire carries 20 A. A 5.0-cm by 10-cm rectangular wire loop carrying 500 mA is located 2.0 cm from the wire, as shown in Fig. 30-53. Find the net magnetic force on the loop. Solution At any given distance from the long, straight wire, the force on a current element in the top segment cancels
22. A vertical straight wire carrying an upward 12-A current exerts an attractive force per unit length of 8.8E-4 N/m on a second parallel wire 7.0 cm away. What current (magnitude and direction) flows in the second wire? OK, use the formula F/l = (m 0 /2 p)(I 1 I 2 /r)and solve for I(2) and then just plug in the values!!
Use Ampere's Law to derive that inside a wire with a uniform current distribution, B(r) is proportional to r. Recall the case of the electric field E(r) inside a wire with a uniform charge distribution: E(r) is also proportional to r. Outside a long, straight wire, both E and B as proportional to 1/r.
The current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire. A compass is placed alongside the wire at the X mark. Which way will the compass point? - north - south - west - east The right answer is South. But why? Thank you.
A long straight wire carries a current of 20 A, as shown in the figure. A rectangular coil with 2 sides parallel to the straight wire has sides 5 cm and 10 cm with the near side at a distance 2 cm from the wire. The coil carries a current of 5 A. (a) Find the force on each segment of the rectangular coil due to the current in the long straight ...
Force on a straight wire Force on electric wires due to Earth's Magnetic Field Power line of 1000 meters runs along the Earth's equator where the B-field = 0.5 Gauss points South to North. The current in the wire is 500 Amps going East to West. F total IL B v v v ( ) = × F =(500A)(1000m)(0.5×10−4T) =25N up v Weight of the wire ~ 20,000 ...
A long straight wire lies on a table and carries a current I. A small circular loop of wire is pushed across the top of the table from position 1 to 2. Determine the direction of the induced current (clockwise OR counter-clockwise) as the loop moves past (A) position 1 and (B) position 2. Explain in complete detail. Table top
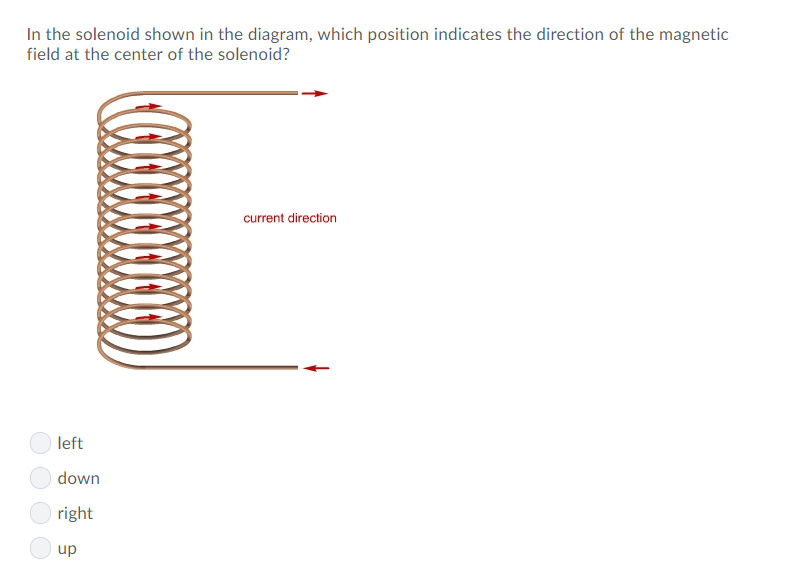
In the solenoid shown in the diagram, which position indicates the direction of the magnetic field at the center of the solenoid? current direction left down right up The current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire. A compass is placed alongside the wire at the X mark.
As an example, consider a curved wire carrying a current I in a uniform magnetic field B G, as shown in Figure 8.3.4. Figure 8.3.4 A curved wire carrying a current I. Using Eq. (8.3.3), the magnetic force on the wire is given by ( ) b B a Fs=Id∫ ×B=I×B GGG GG A (8.3.4) where is the length vector directed from a to b. However, if the wire ...
A square loop of wire is carrying current in the counterclockwise direction. There is a horizontal uniform magnetic field pointing to the right. CheckPoint 1b In which direction will the loop rotate? (assume the z axis is out of the page) A) Around the x axis B) Around the y axis
The direction of the current in the conductor (wire) is shown by the central arrow. and they also have a direction indicated by the arrows on the lines. Similar to the situation with electric field lines, the greater the number of lines (or the closer they are together) in an area the stronger the magnetic field.
Lenz's Law. The direction of the induced emf drives current around a wire loop to always oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes the emf. Lenz's law can also be considered in terms of conservation of energy. If pushing a magnet into a coil causes current, the energy in that current must have come from somewhere.
The current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire. A compass is placed alongside the wire at the X mark. Which way will - 2166040



















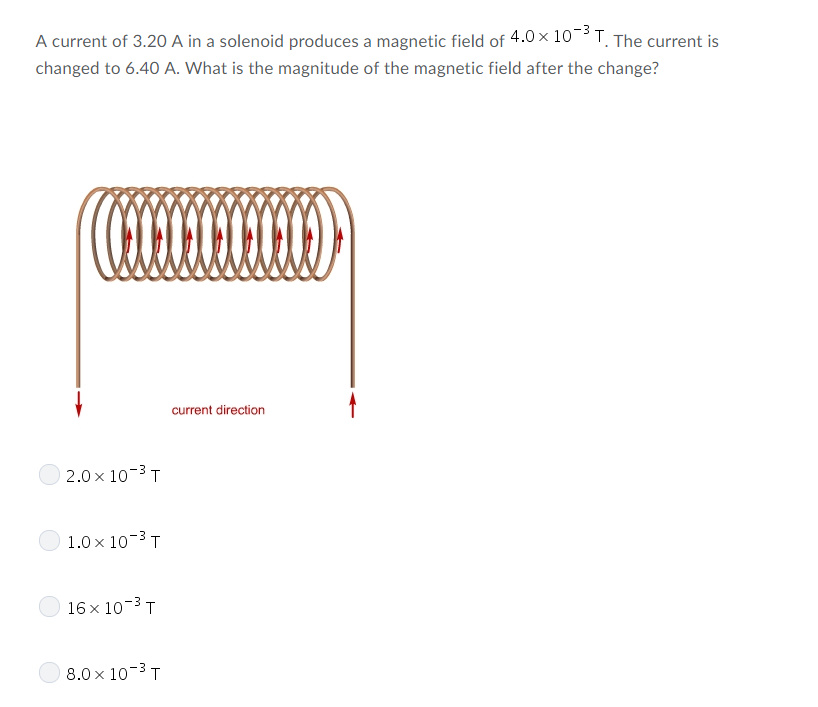







0 Response to "36 the current illustrated in the diagram is directed upward in a straight vertical wire"
Post a Comment