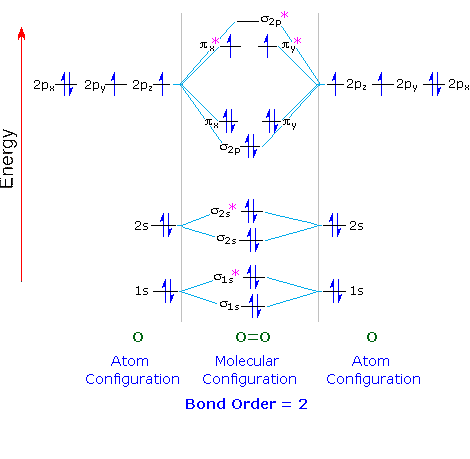
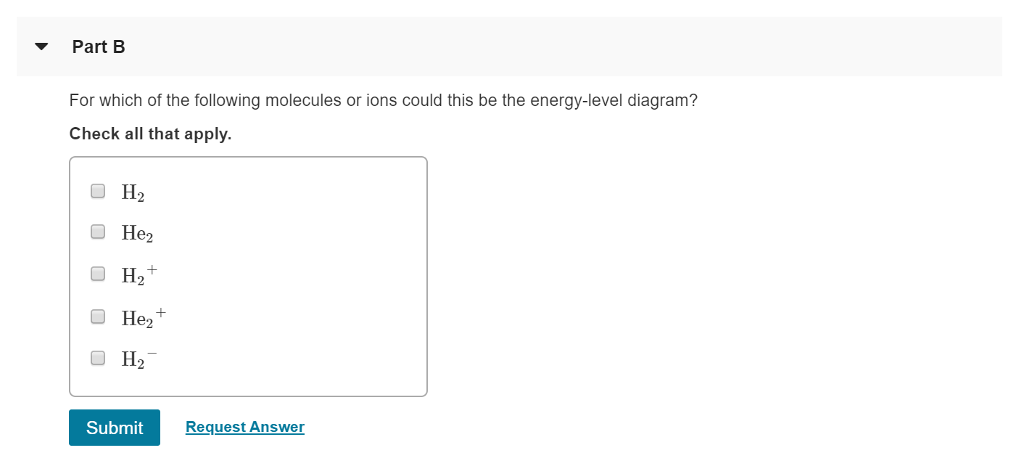
37 for which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram:
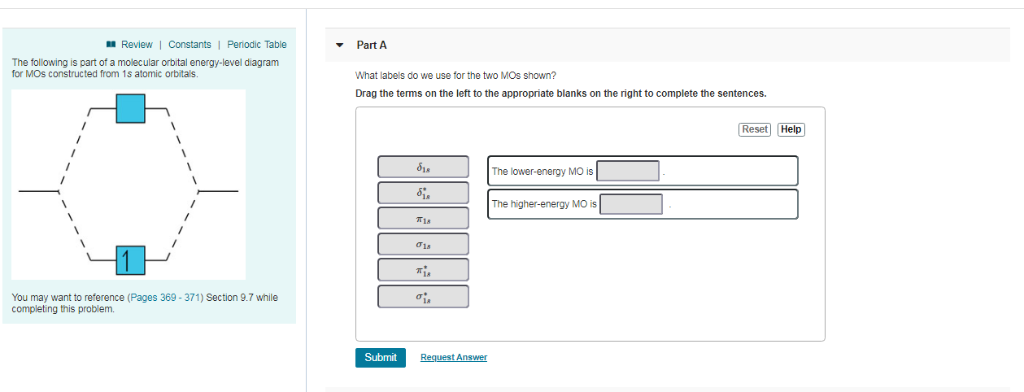
The ions are then detected electronically and the resulting information is stored and analyzed in a computer. A mass spectrometer operating in this fashion is outlined in the following diagram. The heart of the spectrometer is the ion source. Here molecules of the sample (black dots) are bombarded by electrons (light blue lines) issuing from a ... Get the detailed answer: The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for MOs constructed from 1s atomic orbitals.(a) What labels do w. Get the detailed answer: The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for MOs constructed from 1s atomic orbitals.(a) What labels do w ...
Let's look at the molecular orbital diagram of no plus. We know that nitrogen has five valence electrons. Oxygen has six fails. Electrons minus the positive charge is equal to 10 valence electrons. That means it's a next balance show or outermost energy level, so we know that nitrogenous five and oxygen has six. However, we have a positive charge.

For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram:
When iodine molecules are dissolved in aqueous solutions containing iodide ions, they react to form triiodide ions (I 3-). I 2 + I- I 3 - The reaction above between I- ions and S 2 O 8 2- ions has a high activation energy and S 2 O 8 2- ions are only reduced slowly to SO 4 2- ions. The reaction is catalysed by Fe 2+ ions. This problem has been solved! B For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: Check all that apply. Check all that apply. H2 He2 H2+ He2+ H2−. Part C What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? 0 1/2 1 3/2 2 5/2 3. N b = 2 , Na =0. Bond order = 1. Positive value of bond order indicates that H 2 molecule is stable.. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +.. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.. As no unpaired electron is present ...
For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram:. Express your answers numerically as percents, but do not add percent symbols (%). Enter your three answers separated by commas in the order a, b, c. 14.9, 10.6, 12.0 %. Which of the following statements about energy flow are true? Select the four statements that are true. -Animals that produce their own body heat and maintain a high body ... Chemistry questions and answers. The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for MOs constructed from 1s atomic orbitals. For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: Check all that apply. H_2 He_3 H^+_2 He^+_2 What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? 0 1/2 1. Use the following diagram for the next 2 questions 3. If molecule X causes depolarization at Y, what could X be? A. sodium ions B. calcium ions C. acetylcholine D. acetylcholinesterase 4. In an excitatory neuron, the molecules labelled X function to A. open sodium ion gates. B. speed up the transmission of impulses. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons.
Jan 3, 2021 — 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H2+ ion, (b) the He2+ ion, and (c) ... We can use energy-level diagrams such as the one in Figure 9.19 "Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for H" to describe the bonding in other pairs of atoms and ions where n = 1, such as the H 2 + ion, the He 2 + ion, and the He 2 molecule. Again, we fill the lowest-energy molecular orbitals first while being sure not to violate the Pauli ... The lattice energy of a salt is related to the energy required to separate the ions. For which of the following pairs of ions is the energy that is required to separate the ions largest? (Assume that the distance between the ions in each pair is equal to the sum of the ionic radii.) A. NaCl B. CaBr C. MgO D. CaO The lattice energy of a salt is related to the energy required to separate the ions. For which of the following pairs of ions is the energy that is required to separate the ions largest? (Assume that the distance between the ions in each pair is equal to the sum of the ionic radii.)
B For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: Check all that apply. Check all that apply. H2 He2 H2+ He2+ H2âˆ'. Generalized energy-level diagram for atomic orbitals in an atom with two or more electrons (not to scale). Electrons in successive atoms on the periodic table tend to fill low-energy orbitals first. Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5 p orbitals fill immediately after the 4 d , and immediately before the 6 s . The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for MOs constructed from 1s atomic orbitals. (a) What labels do we use for the two MOs shown? (b) For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: ParB For which of the following molecules ions could [ this be the energy-level diagram? Check all that apply: Hez Hez` Submit Request Answer Fart€ What is ...
B For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: Check all that apply. Check all that apply. H2 He2 H2+ He2+ H2âˆ' Part C What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? What is the bond order of the molecule or...
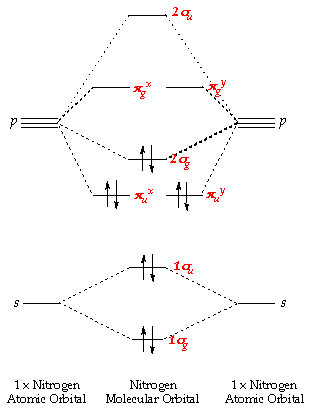
3 4. What is the effect of 2s‐2p mixing on the energy level diagram? The 2px provides bonding (constructive) interactions in the s2s and s2s* m.o.'s LOWERING their energies. The 2s participates in the s2p and s2p* m.o.'s with antibonding (destructive) interactions and thus RAISES the energies of the s2p and s2p* m.o.'s.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
The diagram for O2, F2, and Ne2 molecules has the orbital at a lower energy than the two 2p orbitals. 132.) Which of the following statements concerning the molecular orbital energy level diagrams for first and second period homonuclear diatomic molecules is false?
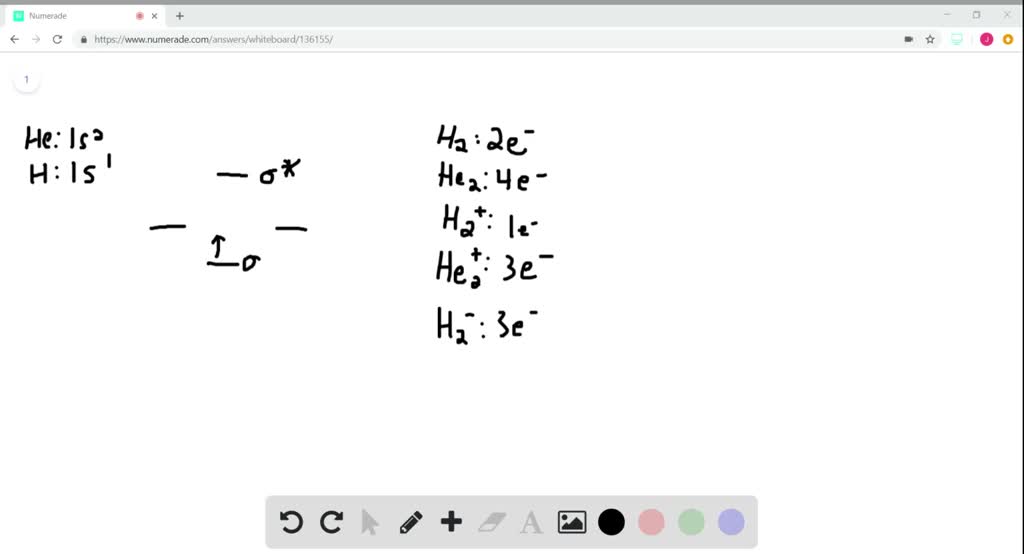
The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagramfor MOs constructed from 1s atomic orbitals. (a) What labels do we use for the two MOs shown? (b) Forwhich of the following molecules or ions could this be theenergy-level diagram:H2, He2, H2+, He2+, or H2-?(c) What is the bond order of the molecule or ion?
Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: s ...
The following energy-level diagram could correspond to which coordination compound? hexacyanoferrate(III) Which of the following ions could exist in either the high-spin or low-spin state in an octahedral complex? ... (Each circle represents 1.0 ×10-3 mol of atoms, and the volume of the box is 1.0 L. Solvent water molecules are omitted for ...
(a) Use an energy level diagram to explain typical vibration absorbance observed IR spectroscopy. (b) Indicate region(s) in the energy diagram where the harmonic oscillator model fails. What are the sources of these deviations from the harmonic oscillator model (c) Indicate where rotational vibrations occurs on this diagram. (a)
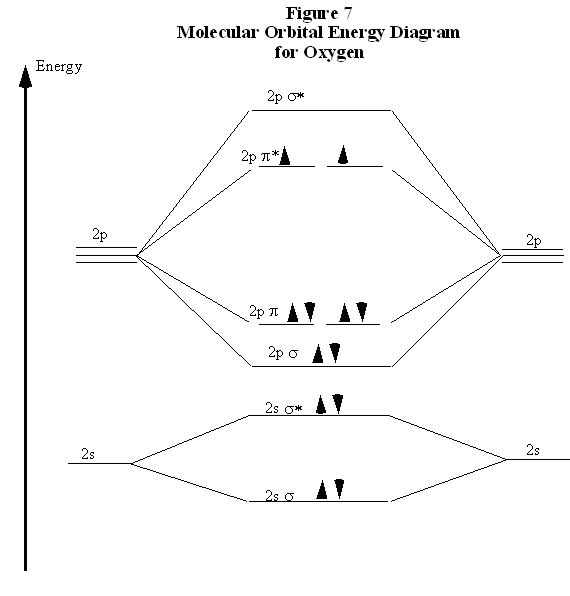
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds ...
Upon electrification, hydrogen produces a line spectrum with the following lines in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. If the light emitted corresponds to the transitions from the third (n=3), fourth (n=4), fifth(n=5)or sixth (n=6) energy level down to the second (n=2).
A) A triple bond is composed of two sigma bonds and one pi bond. B) sigma bonds result from the head-to-head overlap of atomic orbitals. C) Free rotation may occur about a double bond. D) pi bonds have electron density on the internuclear axis. E) More than one of these statements are correct.
The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for MOs constructed from 1s atomic orbitals. For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: Check all that apply. H_2 He_2 H^+_2 He^+_2 H^-_2 What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? 0 1/2 1 3/2 2 5/2
MOLECULES Simplest would be HHe. Differs from H2 in two ways: (1) A.O. energies for H, He different. He - greater nuclear charge, electrons more tightly bound. (2) Now three electrons to feed into m.o.'s. Energy level diagram is now: 1sH 1sHe ψb ψa average energy of a.o.'s H HHe He
bonding in molecules of which of the lowing? A) C02 ( 03 H20 (D) CH4 (E) H-ð-H 2. The lattice energy of a salt is related to the energy required to separate the ions. For which of the following pairs of ions is the energy that is required to separate the ions largest? (Assume that the distance between the ions in each pair is equal
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for MOs constructed from 1 s atomic orbitals. a) What labels do we use for the two MO s shown? b)For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: H2, He2, H2+,He2+, or H2-?
which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: H2, He2, H2 +, He2 +, or H2-? (c) What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? If an d electron is added to the system, into which of the MOs will it be added? [Section 9.7] 9.11 For each of these contour representations of molecular orbit-
The following is part of a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for MOs constructed from 1s atomic orbitals. (a) What labels do we use for the two MOs shown?(b) For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram:H 2, He 2, H 2 +, He 2 +, or H 2-? (c) What is the bond order of the molecule or ion?(d) If an electron is added to the system, into which of the MOs ...
N b = 2 , Na =0. Bond order = 1. Positive value of bond order indicates that H 2 molecule is stable.. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +.. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.. As no unpaired electron is present ...
This problem has been solved! B For which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram: Check all that apply. Check all that apply. H2 He2 H2+ He2+ H2−. Part C What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? What is the bond order of the molecule or ion? 0 1/2 1 3/2 2 5/2 3.
When iodine molecules are dissolved in aqueous solutions containing iodide ions, they react to form triiodide ions (I 3-). I 2 + I- I 3 - The reaction above between I- ions and S 2 O 8 2- ions has a high activation energy and S 2 O 8 2- ions are only reduced slowly to SO 4 2- ions. The reaction is catalysed by Fe 2+ ions.






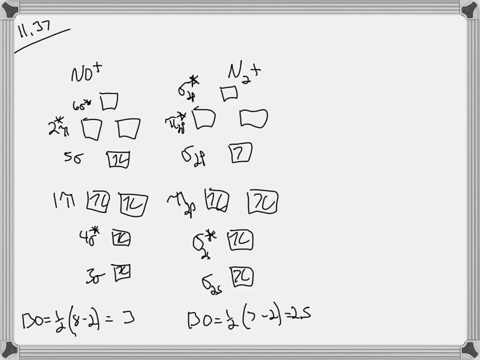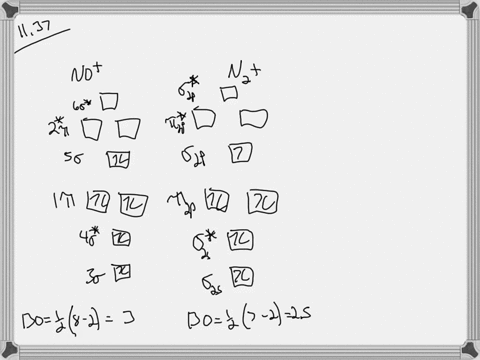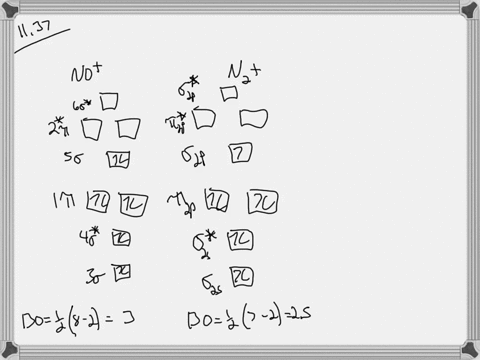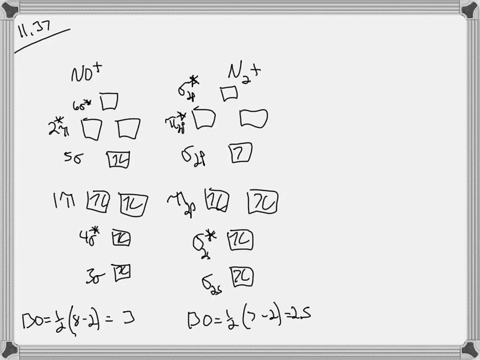






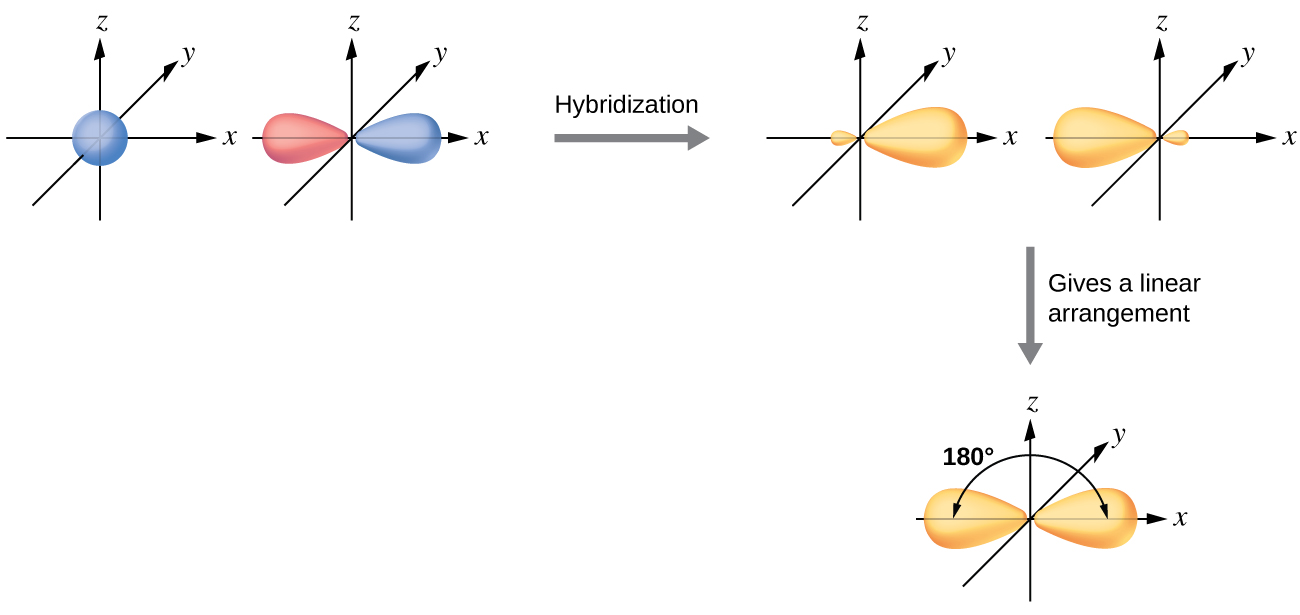

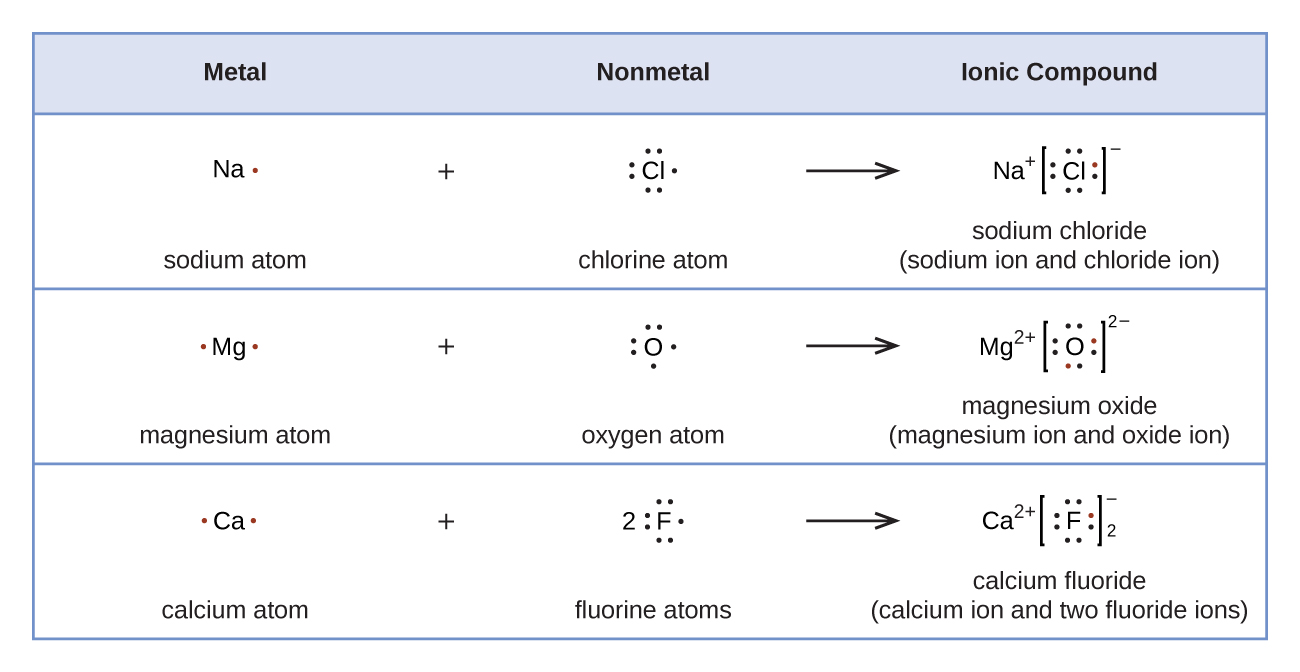
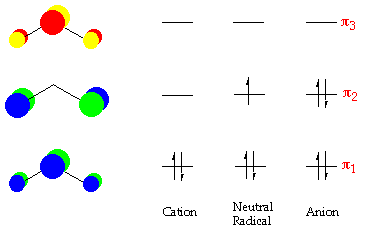

0 Response to "37 for which of the following molecules or ions could this be the energy-level diagram:"
Post a Comment