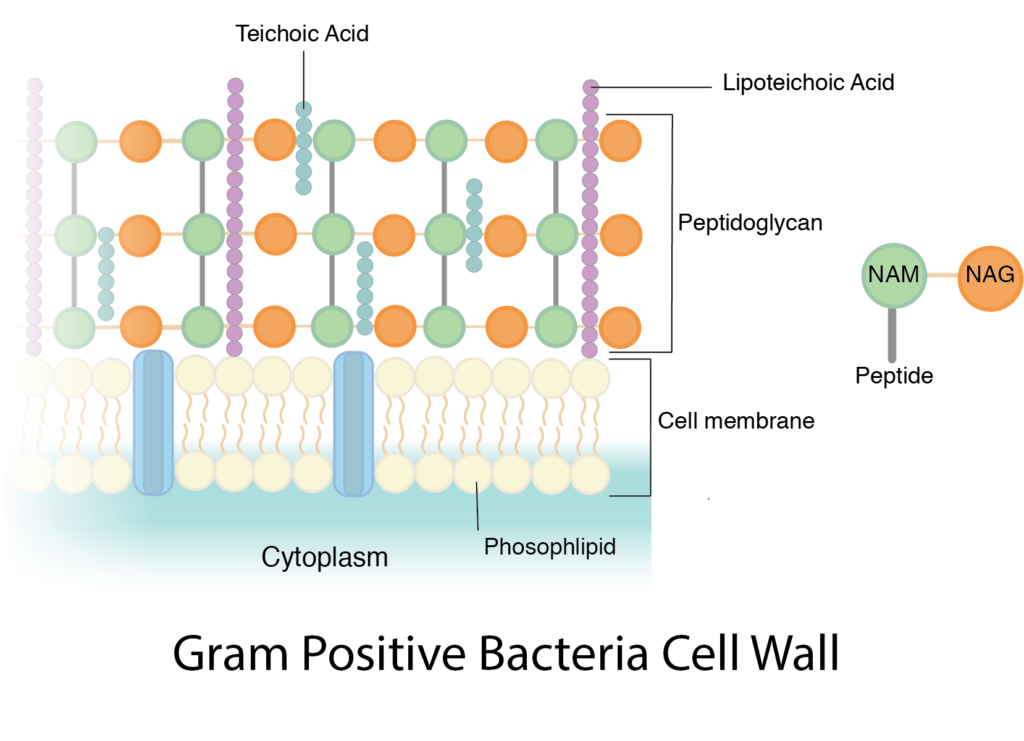
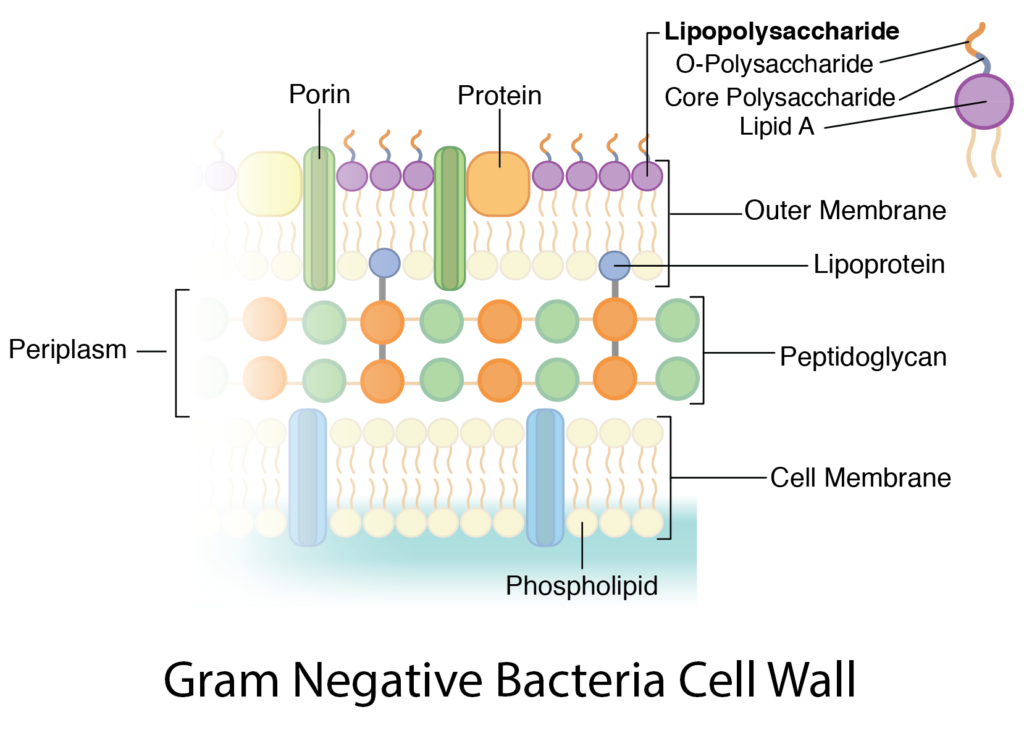
36 bacterial cell wall diagram
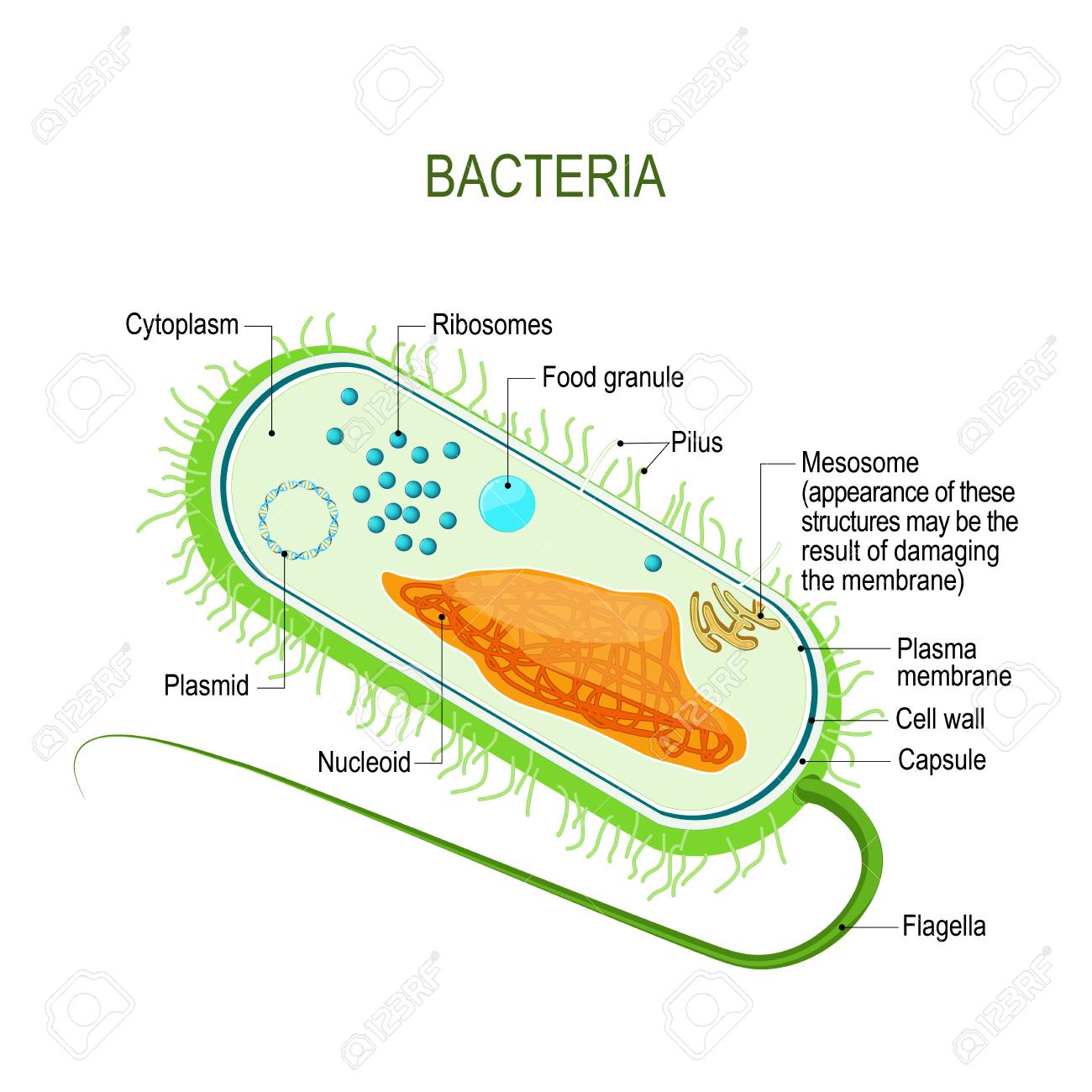
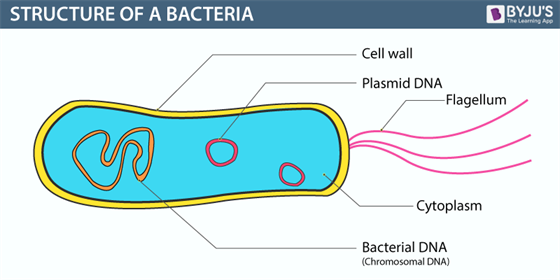
What are bacteria? | Live Science 14/10/2021 · Bacterial cells are generally surrounded by an outer cell wall and an inner cell membrane. Certain bacteria, like the mycoplasmas, do not have a cell wall at all. Some bacteria may even have a ... Bacterial Cell Structure and Function - Pharmapproach.com 28/02/2022 · Diagram of a bacterial cell showing structural parts. Bacterial Cell Structure and Function 1. Slime layers and capsules. The outermost surface of a bacterial cell consists of a layer of excreted polysaccharide material. This viscous material that essentially forms a covering layer or a sort of envelope around the cell wall material is called slime layer if it is loose and …
Difference Between Plant Cell and Bacterial Cell ... 22/09/2017 · Bacterial Cell: The bacterial cell wall is made up of murine. Cytoskeleton. Plant Cell: Plant cells consist of a cytoskeleton, which is made up of microtubules and microfilaments. Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cells do not contain a cytoskeleton. Genetic Material. Plant Cell: The genetic material of the plant cell is arranged into a membrane-bound structure called nucleus. …

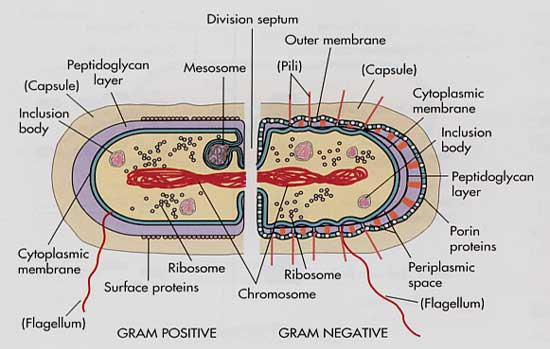
Bacterial cell wall diagram
Bacterial Transformation- definition, principle, steps ... 19/05/2021 · Bacterial Transformation Definition. Bacterial transformation is the transfer of free DNA released from a donor bacterium into the extracellular environment that results in assimilation and usually an expression of the newly acquired trait in a recipient bacterium.. This process doesn’t require a living donor cell and only requires free DNA in the environment. Bacteria (Prokaryote) Cell Coloring - The Biology Corner Color the cell wall purple. 2. On the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane. Its job is to regulate what comes in and out of the cell. Color the cell membrane pink. 3. The surface of some bacteria cells is covered in pilus, which help the cell stick to surfaces. Color the pilus light green. 4. Some bacteria can move within their environment by using structures called flagella, which ... › bacteria › bacterialBacterial Cell: Structure and Components | Microbiology Bacterial cells possess various structures external to the cell wall that basically contribute in protection attachment to objects, and cell movement. The Glycocalyx: Slime Layer and Capsule : The glycocalyx represents the gelatinous covering around many bacterial cells secreted at the time of their active growth.
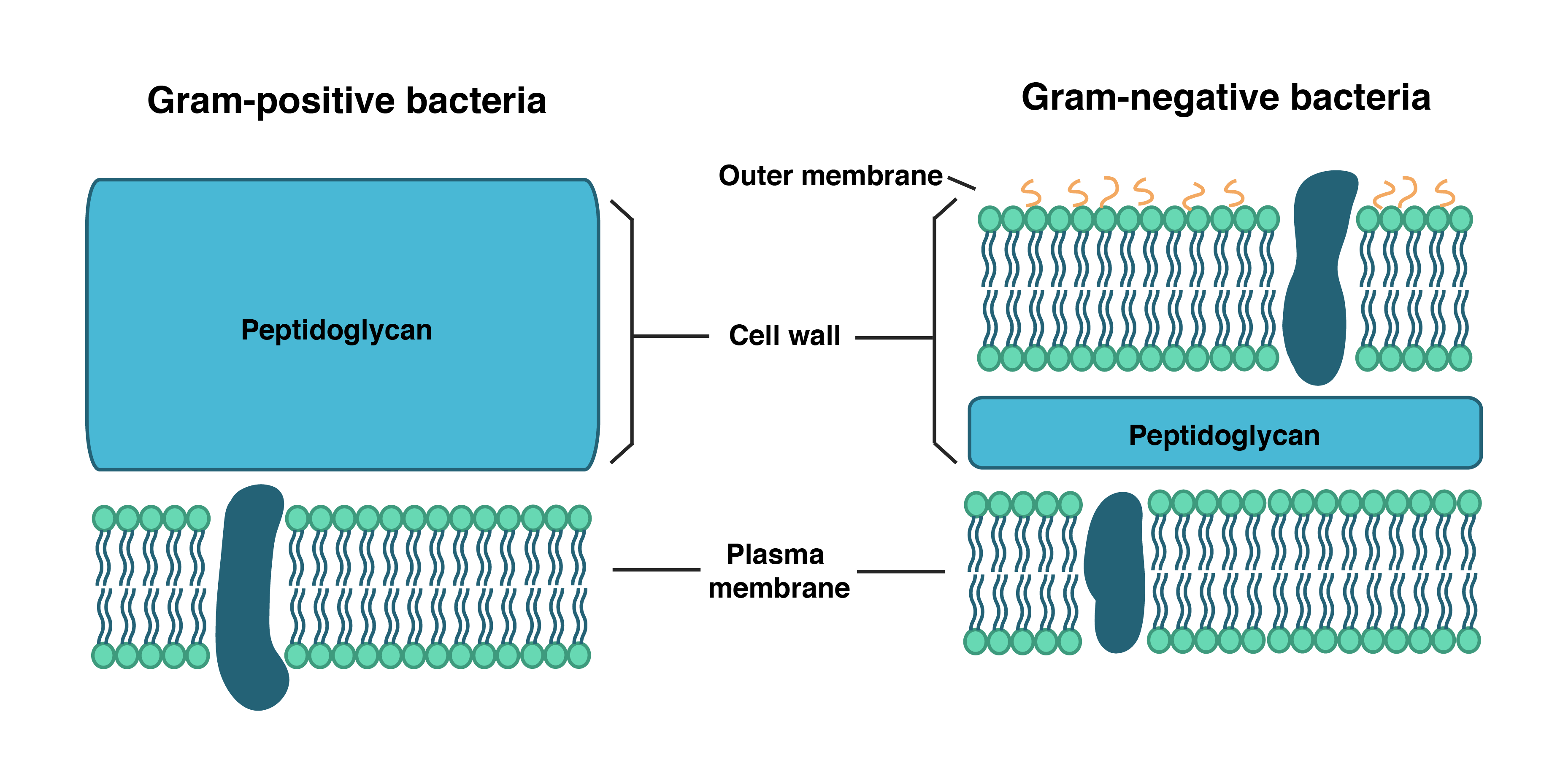
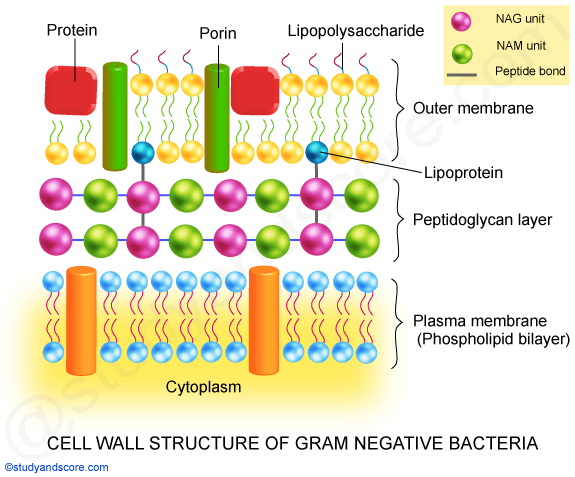
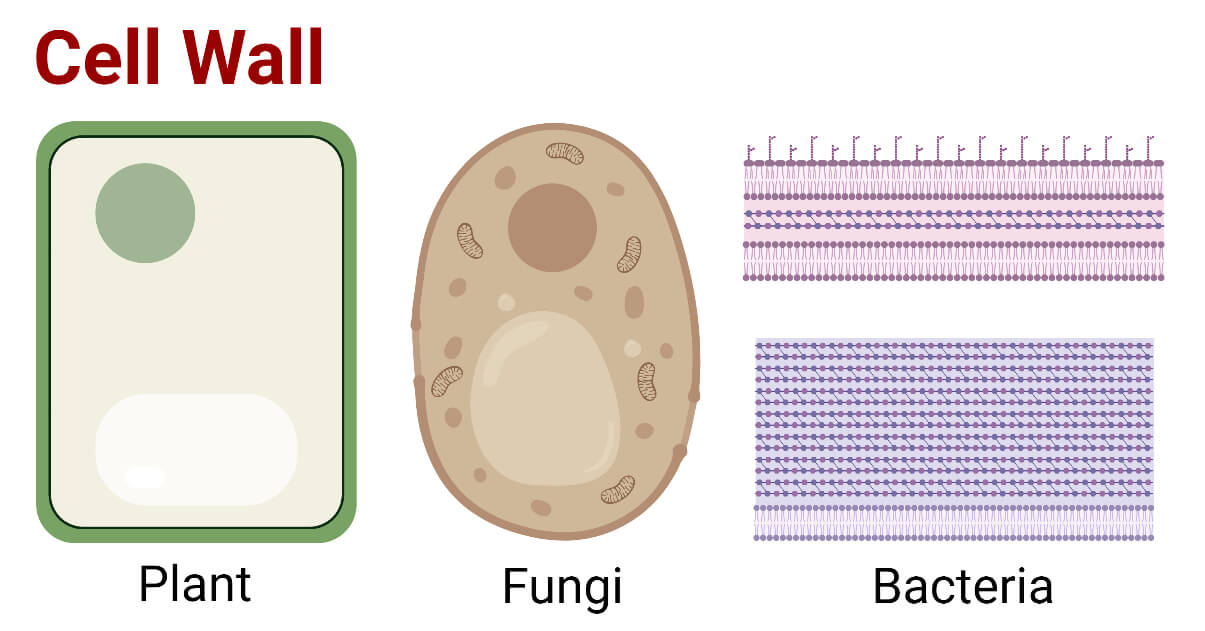
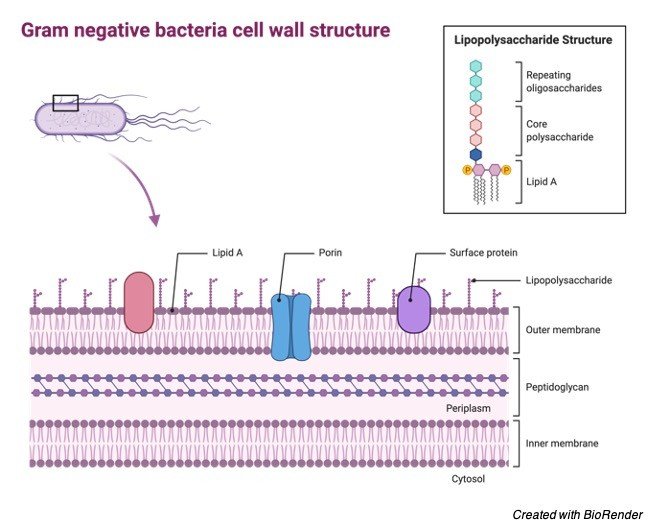
Bacterial cell wall diagram. Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Bacteria Cell Structure 13/11/2015 · Cell wall composition varies widely amongst bacteria and is one of the most important factors in bacterial species analysis and differentiation. For example, a relatively thick, meshlike structure that makes it possible to distinguish two basic types of bacteria. A technique devised by Danish physician Hans Christian Gram in 1884, uses a staining and washing … › cells › bactcellBacterial Cell - CELLS alive They have an outer cell wall that gives them shape. Just under the rigid cell wall is the more fluid cell membrane. The cytoplasm enclosed within the cell membrane does not exhibit much structure when viewed by electron microscopy. Use the following animation to explore bacterial structure. Cell Wall - Definition, Cell Wall Function, Cell Wall Layers The cell wall is the outer covering of a cell, present adjacent to the cell membrane, which is also called the plasma membrane. As mentioned earlier, the cell wall is present in all plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea. An animal cell is irregular in their shape and this is mainly due to the lack of cell wall in their cells. The compositions of the cell wall usually vary along ... Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe Animal cell- Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells and can be found in various shapes and sizes. It lacks a cell wall. Plant cell- The plant is also a multicellular organism but it has a cell wall (unlike animal cell and is made of cellulose) with other cell components like plastid, larger vacuole. Plastids are involved in storage ...
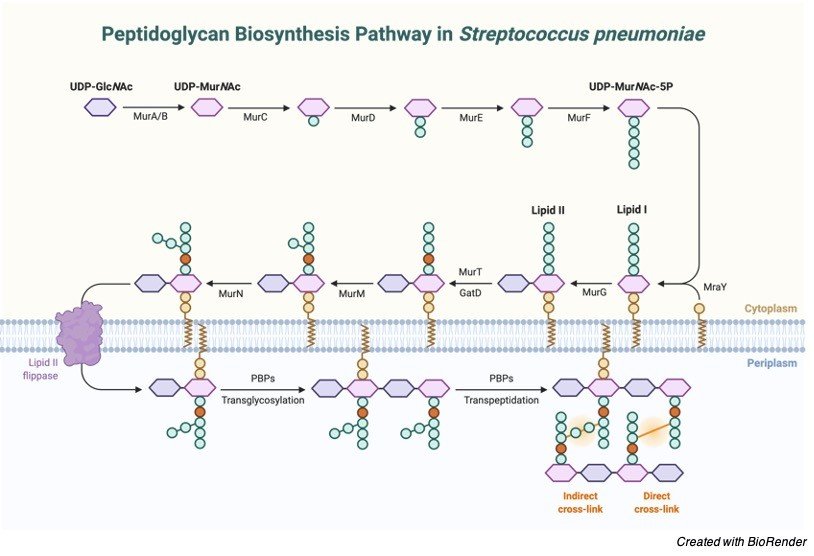
Prokaryotic Cells: Structure, Function, and Definition 30/10/2019 · Cell Wall: The cell wall is an outer covering that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is a gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules. Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane: The cell membrane surrounds the cell's cytoplasm and regulates the flow … Cell wall synthesis inhibitors- Definition, Examples ... May 24, 2021 · Generally, the bacterial cell consists of a cell wall, cell membrane, and nucleus. The cell wall is the outer covering of the bacteria-containing peptidoglycan layer which is made up of cross-linked polymers. Peptidoglycan is mainly responsible for all the mechanisms including resistivity, virulence factors including- the shape of the bacteria. › bacteria › bacterialBacterial Cell: Structure and Components | Microbiology Bacterial cells possess various structures external to the cell wall that basically contribute in protection attachment to objects, and cell movement. The Glycocalyx: Slime Layer and Capsule : The glycocalyx represents the gelatinous covering around many bacterial cells secreted at the time of their active growth. Bacteria (Prokaryote) Cell Coloring - The Biology Corner Color the cell wall purple. 2. On the inside of the cell wall is the cell membrane. Its job is to regulate what comes in and out of the cell. Color the cell membrane pink. 3. The surface of some bacteria cells is covered in pilus, which help the cell stick to surfaces. Color the pilus light green. 4. Some bacteria can move within their environment by using structures called flagella, which ...
Bacterial Transformation- definition, principle, steps ... 19/05/2021 · Bacterial Transformation Definition. Bacterial transformation is the transfer of free DNA released from a donor bacterium into the extracellular environment that results in assimilation and usually an expression of the newly acquired trait in a recipient bacterium.. This process doesn’t require a living donor cell and only requires free DNA in the environment.

















0 Response to "36 bacterial cell wall diagram"
Post a Comment