37 potential energy diagram catalyst
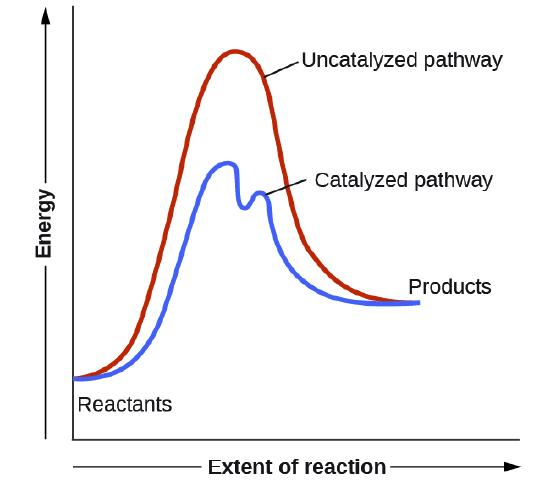
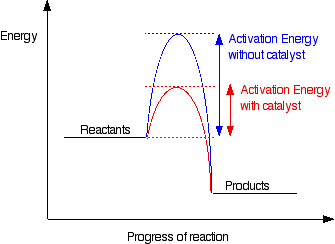
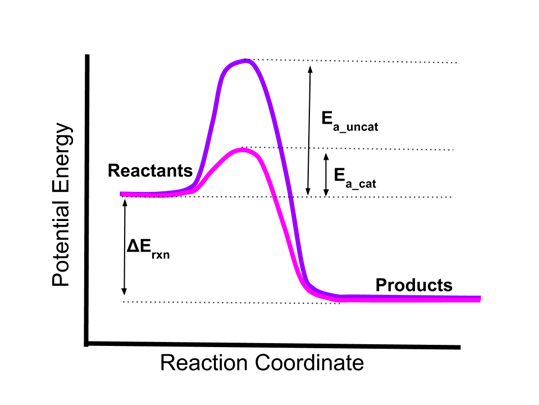
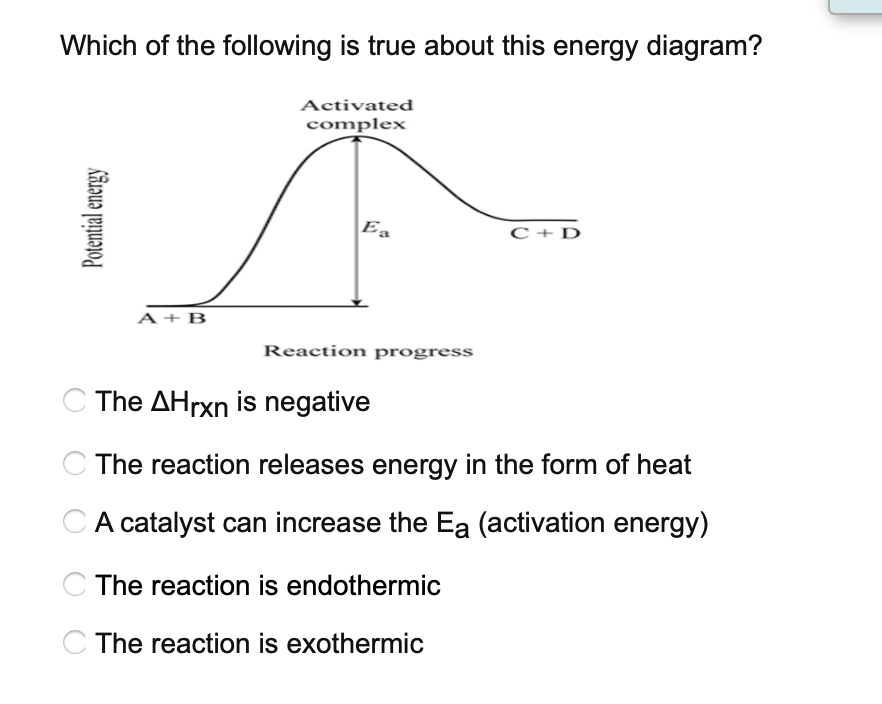
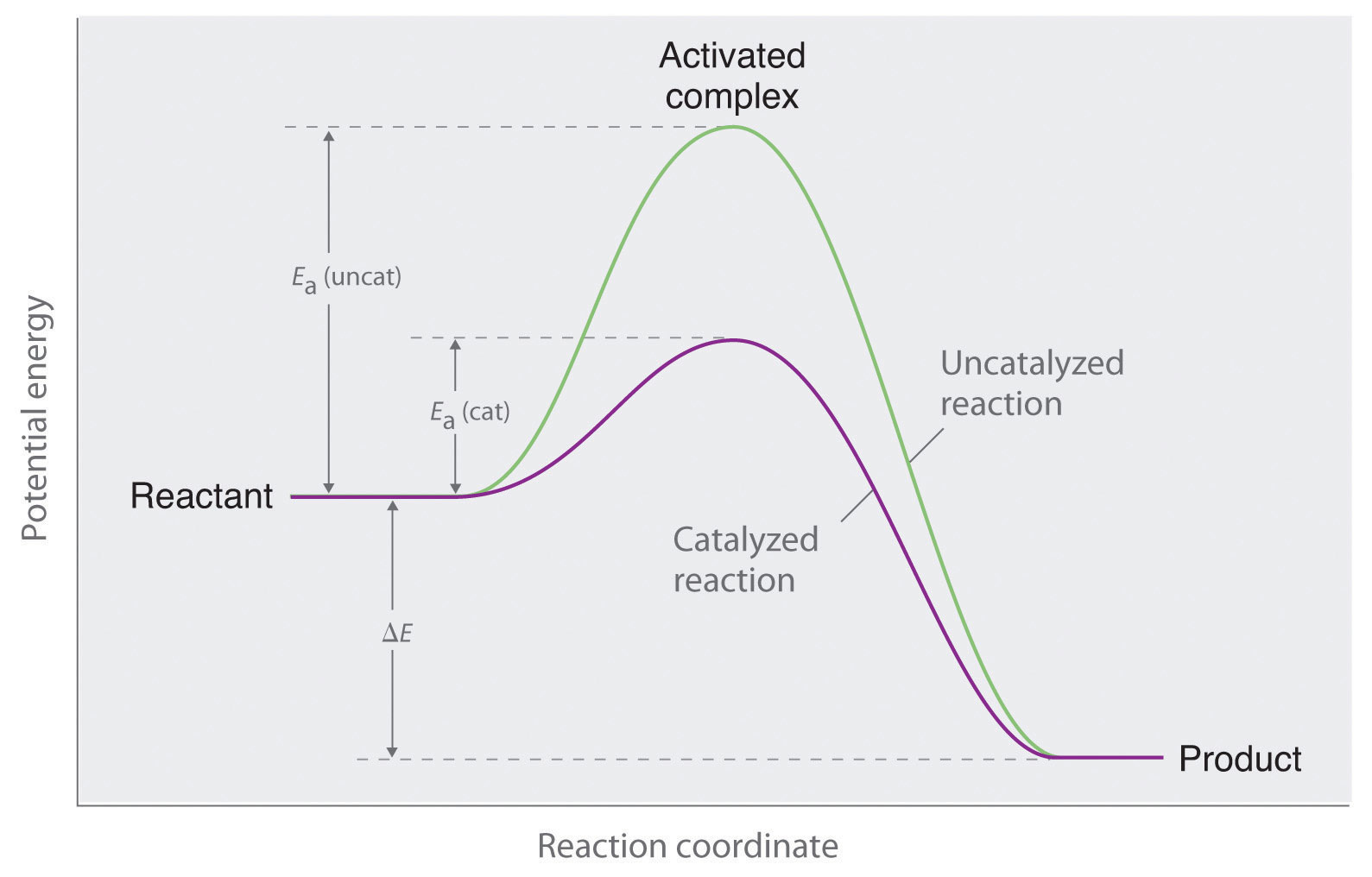
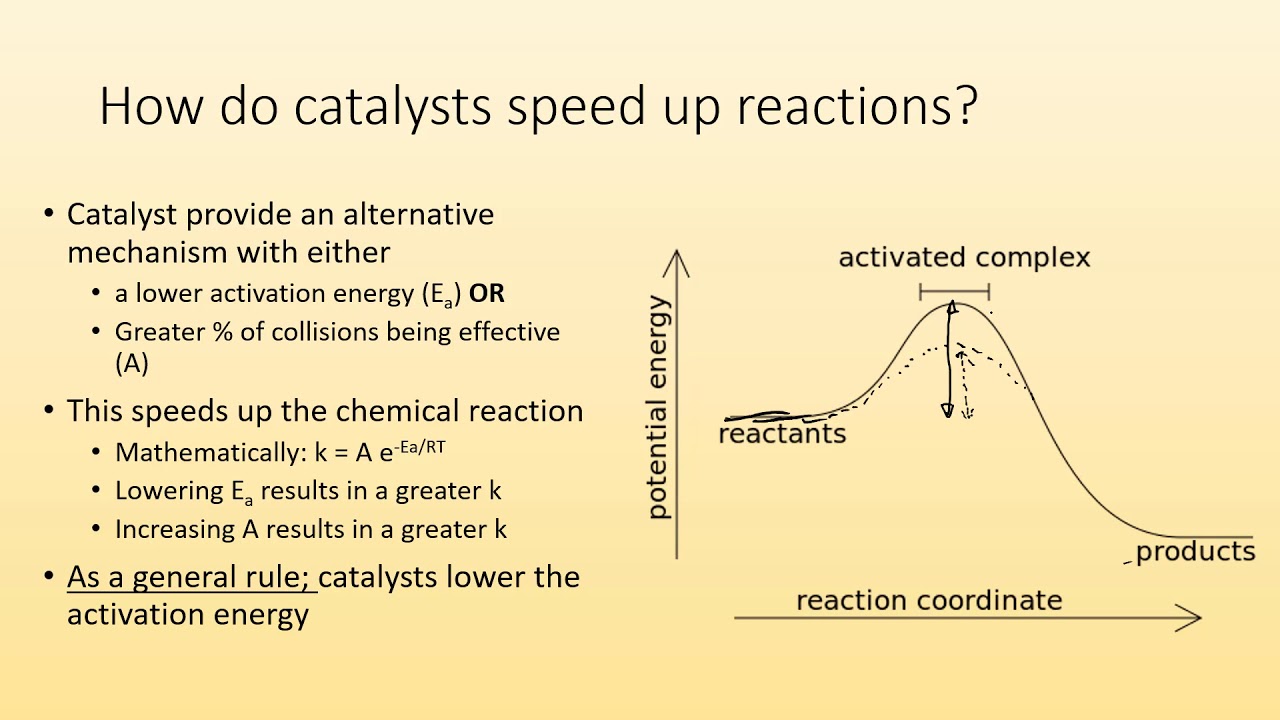
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. The catalyst provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy. PDF Garden City Public Schools / Homepage Does this potential energy diagram represent an exothermic or an endothermic reaction? [Explain whv.] According to the diagram, is the potential eneoy of the products greater than, less than, or equal to the potential energy of the reactants? Draw an alTOW on the diagram above to represent the activation energy for the forward reaction. Label the
physicscatalyst.com › class11Physics notes for class 11 - Physicscatalyst Master Class 11 Physics And Be Successful in exams. Here find Notes, assignments, concept maps and lots of study material for easy learning and understanding.
Potential energy diagram catalyst
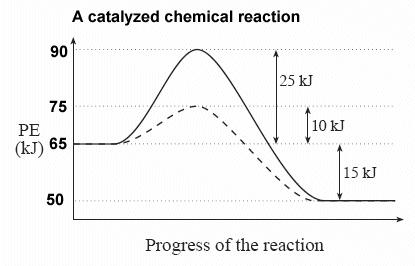
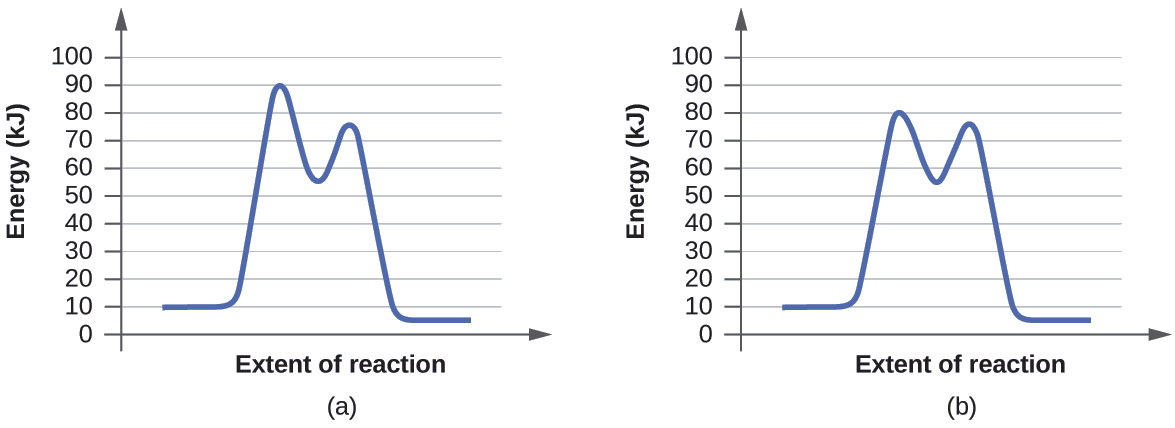
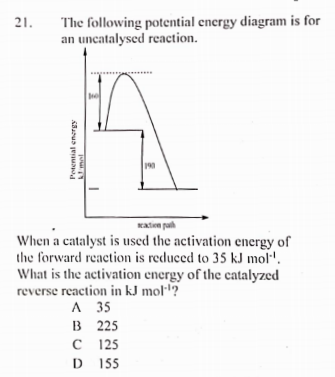
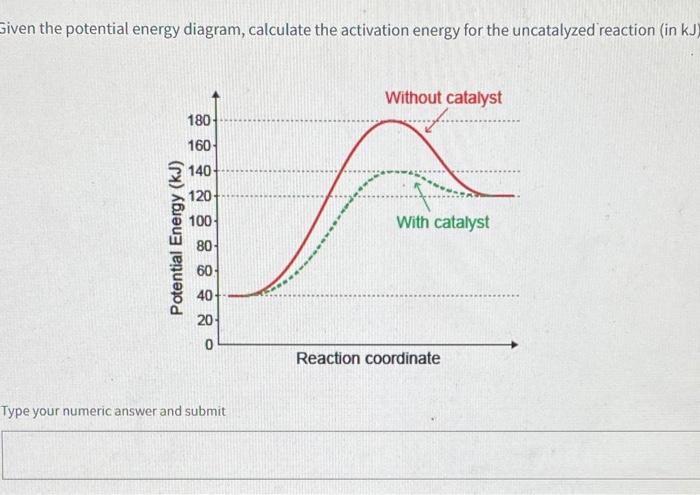
Solved H3.25-Level 1 Given the potential energy diagram ... Without catalyst 1801 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 With catalyst 0. 20 Reaction coordinate ; Question: H3.25-Level 1 Given the potential energy diagram, calculate the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction (kJ). Without catalyst 1801 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 With catalyst 0. 20 Reaction coordinate Explain with the help of a potential energy diagram that ... Potential energy barriers for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions The potential energy diagram compares the potential energy barriers for the catalysed and uncatalysed reactions. The barrier for uncatalysed reaction (E a) is larger than that for the same reaction in the presence of a catalyst E a. 12.7 Catalysis | Chemistry - Lumen Learning This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. The catalyst provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy.
Potential energy diagram catalyst. › eere › fuelcellsTypes of Fuel Cells | Department of Energy Phosphoric acid fuel cells (PAFCs) use liquid phosphoric acid as an electrolyte—the acid is contained in a Teflon-bonded silicon carbide matrix—and porous carbon electrodes containing a platinum catalyst. The electro-chemical reactions that take place in the cell are shown in the diagram to the right. 11. What does a catalyst do for a reaction... | Clutch Prep Problem Details. 11. What does a catalyst do for a reaction? Sketch out potential energy diagram with two reaction pathways: one for a reaction without a catalyst and one for the same reaction with a catalyst. Learn this topic by watching Catalyst Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems Catalyst Practice Problems. › science › articleSelective bimetallic sites supported on graphene as a ... The free energy variation determines that it is easier to form *OCH 3 than to form *CH 2 OH. Thus, among paths 1–3, Path 3 is the optimized reaction path. According to Fig. 7, the free energy variation of the reaction (*OCHO → *HCOOH) is about 1.89 eV on Fe_Ni/DG, and it cannot be the optimized reaction pathway on Fe_Ni/DG. For Cu_Fe/DG and ... 1 Potential energy diagram of a heterogeneous catalytic ... Download scientific diagram | 1 Potential energy diagram of a heterogeneous catalytic reaction (A + B → P) with gaseous reactants (A, B), product (P), and solid metal catalyst from publication ...
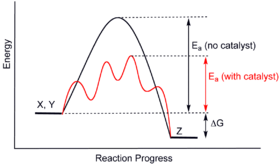
› chapters › 62151Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis as a Promising ... Feb 15, 2018 · This level of catalyst loading is too high to meet the long-term cost targets for energy markets [23, 25, 26]. Furthermore, while using current electrolysis technology, the translation of catalyst development from lab scale to the megawatt scale remains challenging in terms of catalyst cost and stability [ 25 ]. Which of the following phase diagrams represents how a ... A regular exothermic potential energy diagram is shown, with a dotted line representing how the potential energy diagram changes with the use of a catalyst. The dotted line shows a new potential energy diagram with a taller activation energy hill than that in the original potential energy diagram. Consider the Potential Energy vs. Reaction... | Clutch Prep Consider the Potential Energy vs. Reaction Coordinate diagram shown to the right. For each of the following questions, circle the best answer. If a catalyst is added, i) ΔG° for the reaction increases. ii) ΔG° for the reaction decreases. iii) ΔG° for the reaction equals 0. iv) ΔG° for the reaction in unchanged. Potential Energy Diagrams - Chemistry - Catalyst ... This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the f...
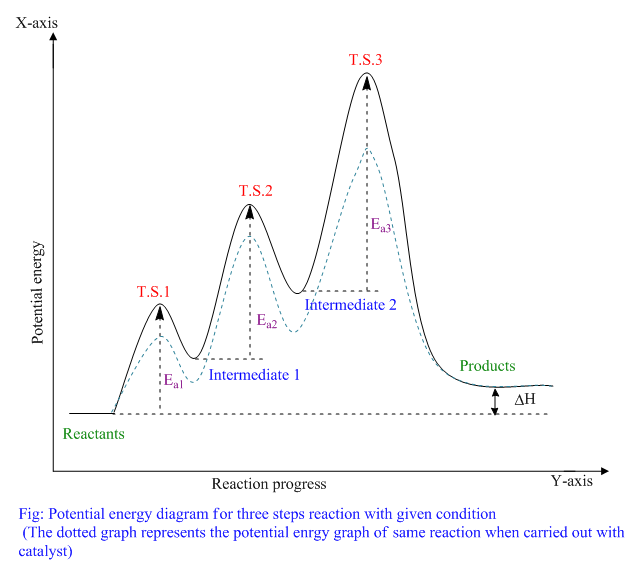
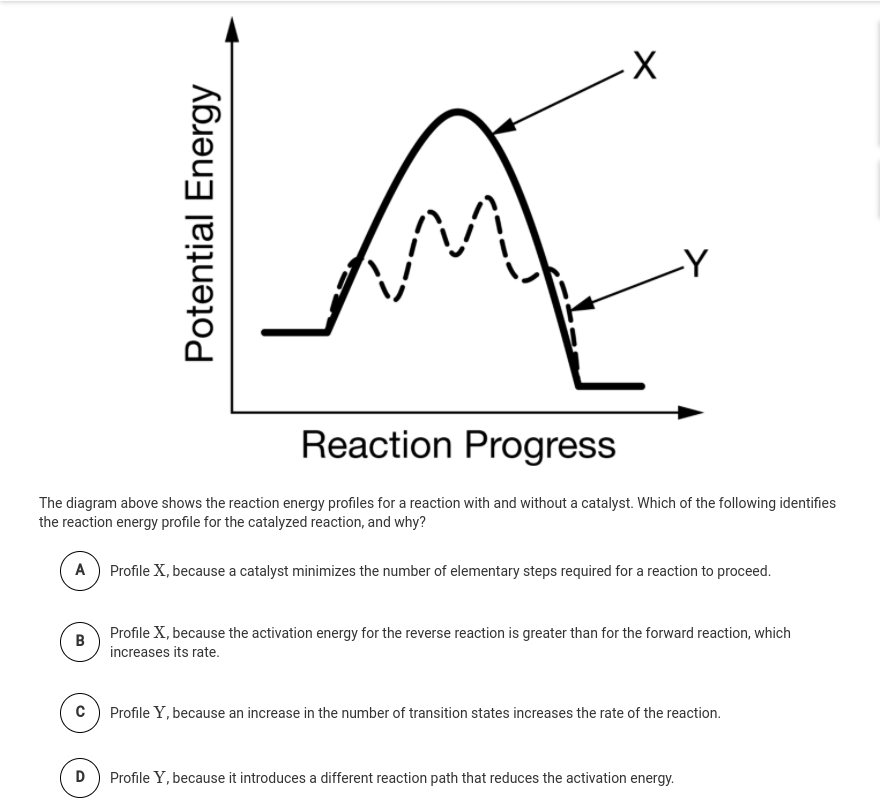
Catalysis - Chemistry This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. The catalyst provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy. As shown, the catalyzed pathway involves a two-step mechanism (note the presence of two transition states) and an intermediate species (represented by the valley between the two ... Potential energy diagrams - Controlling the rate - Higher ... The activated complex (high energy intermediate state where bonds are breaking and forming) can be shown on potential energy diagrams. It is the 'energy barrier' that must be overcome when changing... Potential Energy Diagrams | Chemical Bonds Quiz - Quizizz Q. Interval C in this potential energy diagram could be changed by adding a _____? answer choices . Cookies. More energy. Catalyst. Changing the temperature. Tags: Question 16 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Q. Which numbered interval on the diagram would change when a catalyst is added? answer choices . B & C. C & D . E & C. A & D . Tags: Question 17 ... Dublin Schools - Lesson : Catalysts Potential Energy Diagram The graph shows a reaction rate with and without the use of a catalyst. Summary A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction. A catalyst provides an alternate pathway for the reaction that has a lower activation energy.
The Potential Energy Diagram - Fundamental Concepts in ... This chapter starts by considering the simplest possible potential energy diagrams: those that describe the elementary step of adsorption of a single atom or molecule on a surface. The dissociation of H 2 over a Cu surface is an example of an elementary surface reaction. Other types of elementary surface reactions are also illustrated in the ...
Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning Explain the function of a catalyst in terms of reaction mechanisms and potential energy diagrams List examples of catalysis in natural and industrial processes Among the factors affecting chemical reaction rates discussed earlier in this chapter was the presence of a catalyst , a substance that can increase the reaction rate without being ...
Answer the following in brief. How a catalyst increases ... Potential energy barriers for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. ii. The potential energy diagram compares the potential energy barriers for the catalysed and uncatalysed reactions. The barrier for uncatalysed reaction (E a) is larger than that for the same reaction in the presence of a catalyst E a. iii.
How would a catalyst affect the potential energy diagram ... A catalyst, or enzyme, works with a substrate to decrease the amount of initial energy required to perform a specific chemical opperation, speeding the reaction up. Enzymes also work to increase ...
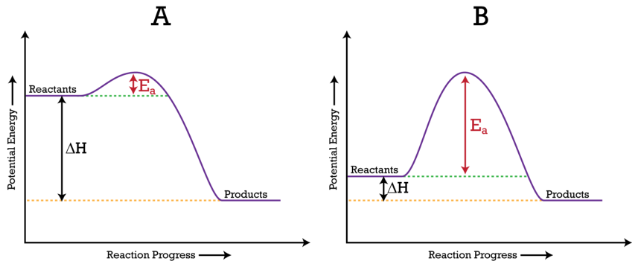
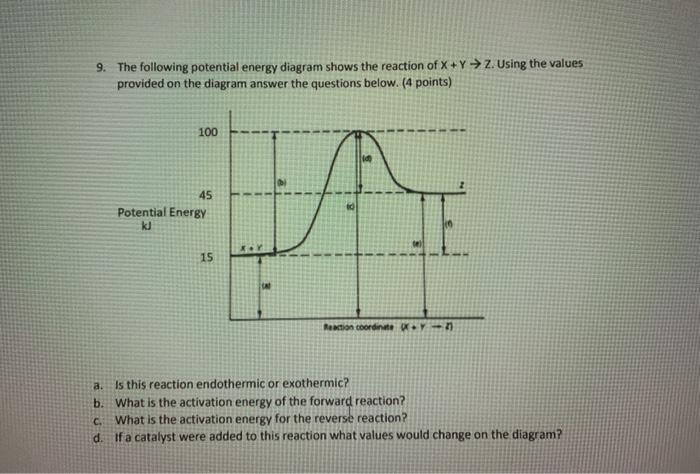
PDF The Leon M. Goldstein High School for the Sciences Potential Energy Diagram pathway without with catalyst Course Ca culate the heat o reaction. What effect does a catalyst have in a potential energy diagram? Does the. potential energy of-the products or reactants change with the addition of a catalyst? Find the activation energy for the catalyzed and un-catalyzed reaction.
Potential Energy Diagrams Flashcards - Quizlet potential energy diagram. One change in a reaction, other than adding a catalyst, that can increase the rate of the given reaction. is a change in temperature. One of the basic concepts of kinetics is that in order for a reaction to occur. reactant particles must collide.
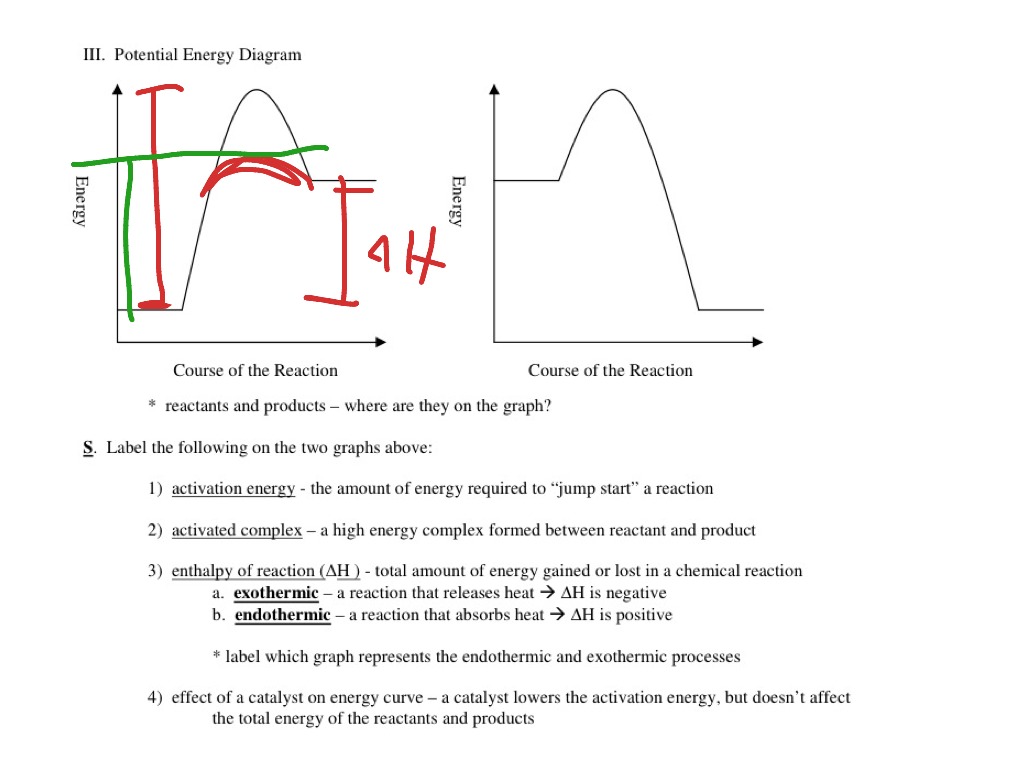
PDF Potential Energy Diagrams Activation energy is the energy required to "jump start" the reaction. Its the energy added to initiate reaction. The energy requirements can be reduced with the addition of a catalyst. Catalyst -substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed. Ex. Enzymes are a biological catalyst speeding up biochemical processes.
eere-exchange.energy.gov › defaultFinancial Opportunities: Funding Opportunity Exchange - Energy Geothermal energy is a renewable and diverse energy solution for the United States, providing reliable and flexible electricity generation and delivering unique technology solutions to America’s heating and cooling demands. Geothermal resources can be found nationwide, are “always on,” and represent vast domestic energy potential.
Solved 3. What does a catalyst do for a reaction? Sketch ... Sketch out a potential energy diagram with reaction pathways: one for a reaction without a catalyst and one for the same reaction with a catalyst. two . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer.
catalysis - Potential Energy Diagrams and the Effect of ... Why does a potential energy diagram showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy not move left on the reaction pathway scale (compared to uncatalysed reaction) if a catalyst speeds up reac...
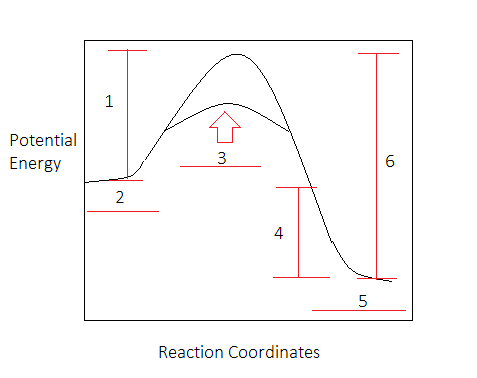
kentchemistry.com › links › KineticsPotential Energy Diagrams - Kentchemistry.com A potential energy diagram plots the change in potential energy that occurs during a chemical reaction. This first video takes you through all the basic parts of the PE diagram. Sometimes a teacher finds it necessary to ask questions about PE diagrams that involve actual Potential Energy values.
Potential Energy Diagrams Chemistry Catalyst Endothermic ... potential energy diagrams chemistry catalyst, endothermic & exothermic reactions. this chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. it also shows the this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into endothermic and exothermic reactions as well as the corresponding in this …
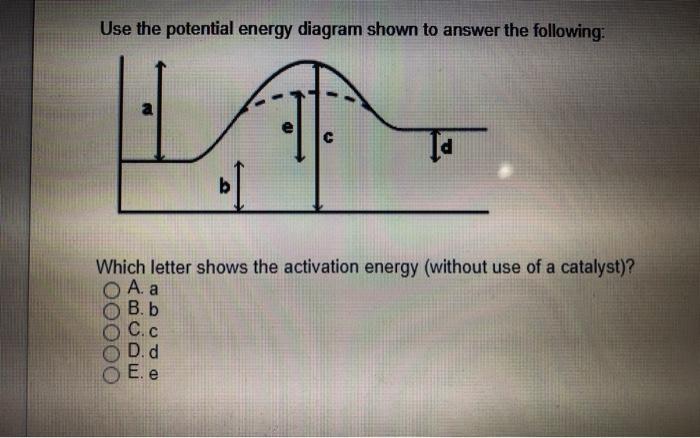
PDF Potential Energy Diagram Worksheet ANSWERS Potential Energy Diagram Worksheet ANSWERS 1. Which of the letters a-f in the diagram represents the potential ... A catalyst changes the reaction mechanism, in the process lowering the activation energy. 5. Name 4 things that will speed up or slow down a chemical reaction.
› science › articleIn situ studies of energy-related electrochemical reactions ... Jan 01, 2022 · Hydrogen is absorbed onto the catalyst surface to form H*, which is in turn converted to a proton by releasing an electron. Thus, it is widely acknowledged that the hydrogen binding energy (HBE) can serve as an active descriptor for HOR activity [72, 73, 74]. However, the role of OH – in the base solution remains unclear. The two possible ...
Potential energy diagram with/without catalyst in a ... Potential energy diagram with/without catalyst in a hypothetical exothermic chemical reaction coordinate of Boltzmann distribution. The presence of the catalyst opens a different reaction pathway...
Potential Energy Diagram - Catalyst Added - YouTube Sketch the potential energy diagram for an exothermic reaction with a catalyst added.
PDF Chemical kinetics Name: Date - The Leon M. Goldstein High ... 1. In the potential energy diagram, which letter represents the potential energy of the activated complex? A. A B. B C. C D. D 2. The addition of a catalyst to a reaction will cause a change in the A. potential energy of the reactants B. potential energy of the products C. heat of reaction D. activation energy 3.
12.7 Catalysis | Chemistry - Lumen Learning This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. The catalyst provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy.
Explain with the help of a potential energy diagram that ... Potential energy barriers for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions The potential energy diagram compares the potential energy barriers for the catalysed and uncatalysed reactions. The barrier for uncatalysed reaction (E a) is larger than that for the same reaction in the presence of a catalyst E a.
Solved H3.25-Level 1 Given the potential energy diagram ... Without catalyst 1801 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 With catalyst 0. 20 Reaction coordinate ; Question: H3.25-Level 1 Given the potential energy diagram, calculate the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction (kJ). Without catalyst 1801 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 With catalyst 0. 20 Reaction coordinate












0 Response to "37 potential energy diagram catalyst"
Post a Comment