38 actin and myosin diagram
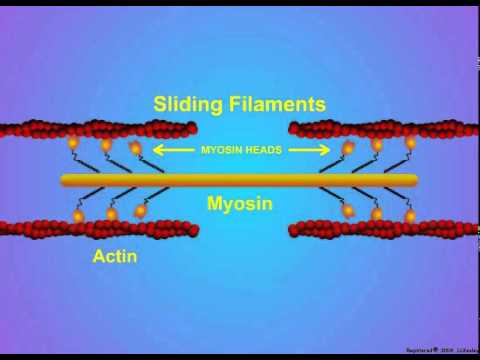
PDF The diagram shows part of a muscle myofibril - StudyWise (c) After death, cross bridges between actin and myosin remain firmly bound resulting in rigor mortis. Using information in the diagram, explain what causes the cross bridges to remain firmly bound. Respiration stops so no ATP is produced and ATP is needed for the separation of actin and myosin cross bridges 3. › biology › sliding-filament-theorySliding Filament Theory – Definition, Diagram and Important FAQs Myosin heads bind to an actin filament, bend to drag the actin filaments closer together, then release, reattach, and pull again, according to the sliding filament theory. ATP energy is required for the myosin head to be released from the actin filament; otherwise, the myosin heads would remain in the same position and the muscle would not ...
Actin, Myosin, and Cell Movement - SlideShare Actin, Myosin, and Cell Movement Actin filaments, usually in association with myosin, are responsible for many types of cell movements. Myosin is the prototype of a molecular motor—a protein that converts chemical energy in the form of ATP to mechanical energy, thus generating force and movement.

Actin and myosin diagram
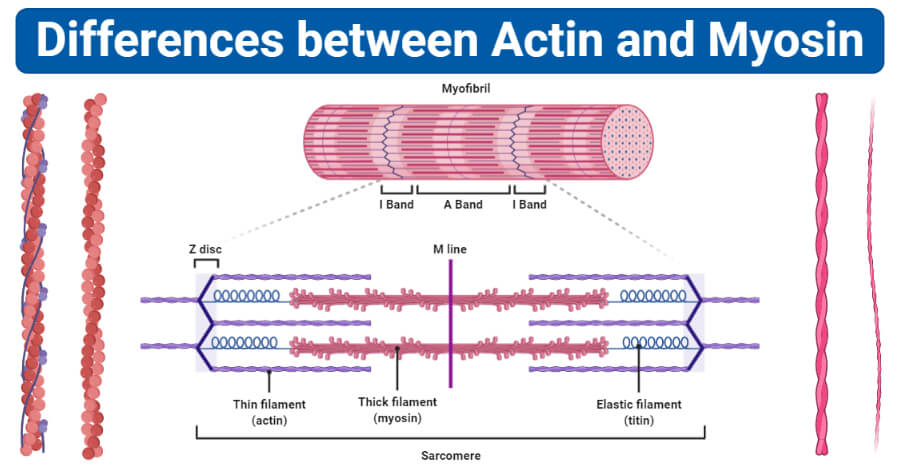
Actin and Myosin - Biology Dictionary Actin and myosin are both proteins that are found in all types of muscle tissue. Myosin forms thick filaments (15 nm in diameter) and actin forms thinner filaments (7nm in diameter). Actin and myosin filaments work together to generate force. Myosin Function & Structure | What is Myosin? - Video ... This diagram shows how actin filaments and myosin arrange themselves in the myofibril. Actin filaments create the thin filaments (gray), while myosin molecules arrange themselves into thick ... Major Differences Between Actin and Myosin - BYJUS Actin and myosin are two protein molecules present in muscles and are mainly involved in the contraction of the muscle in both humans and animals. Both actin and myosin function by controlling the voluntary muscular movements within the body, along with the regulatory proteins known as troponin, tropomyosin and meromyosin. Actin and myosin proteins build filaments, …
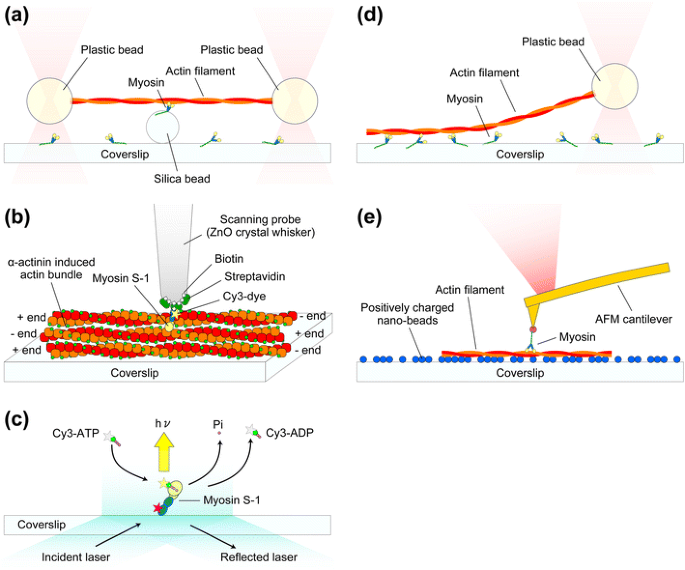
Actin and myosin diagram. UCSD Muscle Physiology Homepage - Myofilament Structure (B) Schematic drawing of the myosin S-1 portion based on the ribbon diagram presented in (A) and used to illustrate the cross-bridge cycle. Actin The other major component in force production. Actin, when polymerized into filaments, forms the "ladder" along which the myosin filaments "climb" to generate motion. Troponin Myosin and actin (video) | Muscles | Khan Academy So one, ATP binds to myosin head and as soon as that happens, that causes the myosin to release actin. So that's step one. So I start it off with this guy just touching the actin, the ATP comes, and it gets released. So in the next step-- so after that step, it's going to look something like this-- and I want to draw it in the same place. 3.4: Actin and myosin filaments Diagram | Quizlet No actin-myosin interaction at binding site Myofilaments overlap a little. Contracted state. Myosin head pulls actin toward sarcomere center (power stroke) Filaments slide past each other = sliding filament theory Sarcomeres, myofibrils, muscle fiber all shorten. Actin vs Myosin- Definition, 14 Major Differences, Examples Each actin filament in a muscle fiber is composed of two strands of actin protein. Myosin Definition Myosin is a superfamily of motor proteins that, together with actin proteins, form the basis for the contraction of muscle fibers. Myosin is termed a motor protein as it is a type of enzyme that converts chemical energy into mechanical energy.
Special Issue: The Actin-Myosin Interaction in Muscle ... (b) Simplified diagram of a myosin II molecule; a long rod on the end of which are two myosin heads which bind and hydrolyse ATP and bind actin. Myosin molecules (b) aggregate to form myosin filaments (c); the rods are in the backbone and the heads are almost helically arranged on the filament surface. The head ends of the rods, myosin S2 ... muscle contraction stimulation 2 QP.docx - Questions on ... The diagram represents a longitudinal section through part of a myofibril from a skeletal muscle. H z o n e I b a n d A b a n d (a) The diagram shows the A band, ... (Ca 2+) help the myosin and actin filaments to slide over each other during the shortening of a muscle cell. ATP ... Actin Myosin Stock Illustrations - 361 Actin Myosin Stock ... Structure of muscle with isolated myosin and actin closeup outline diagram. Labeled educational arm bone muscular inner parts detailed description with Structure of myosin VI (green) - actin (brown) complex in the rigor (nucleotide-free) state. Sarcomere | Definition, Structure, & Sliding Filament Theory 10.08.2019 · H zone becomes smaller by increasing actin overlap and myosin filaments, due to this muscles shorten. Sarcomere Diagram. Sarcomere Anatomy: Anatomical is said to be the term of microanatomy. The sarcomere is the basic unit function with muscle fiber cells. This is a distinguishing unit in some types of muscle tissue. Due to the striated nature of both skeletal …
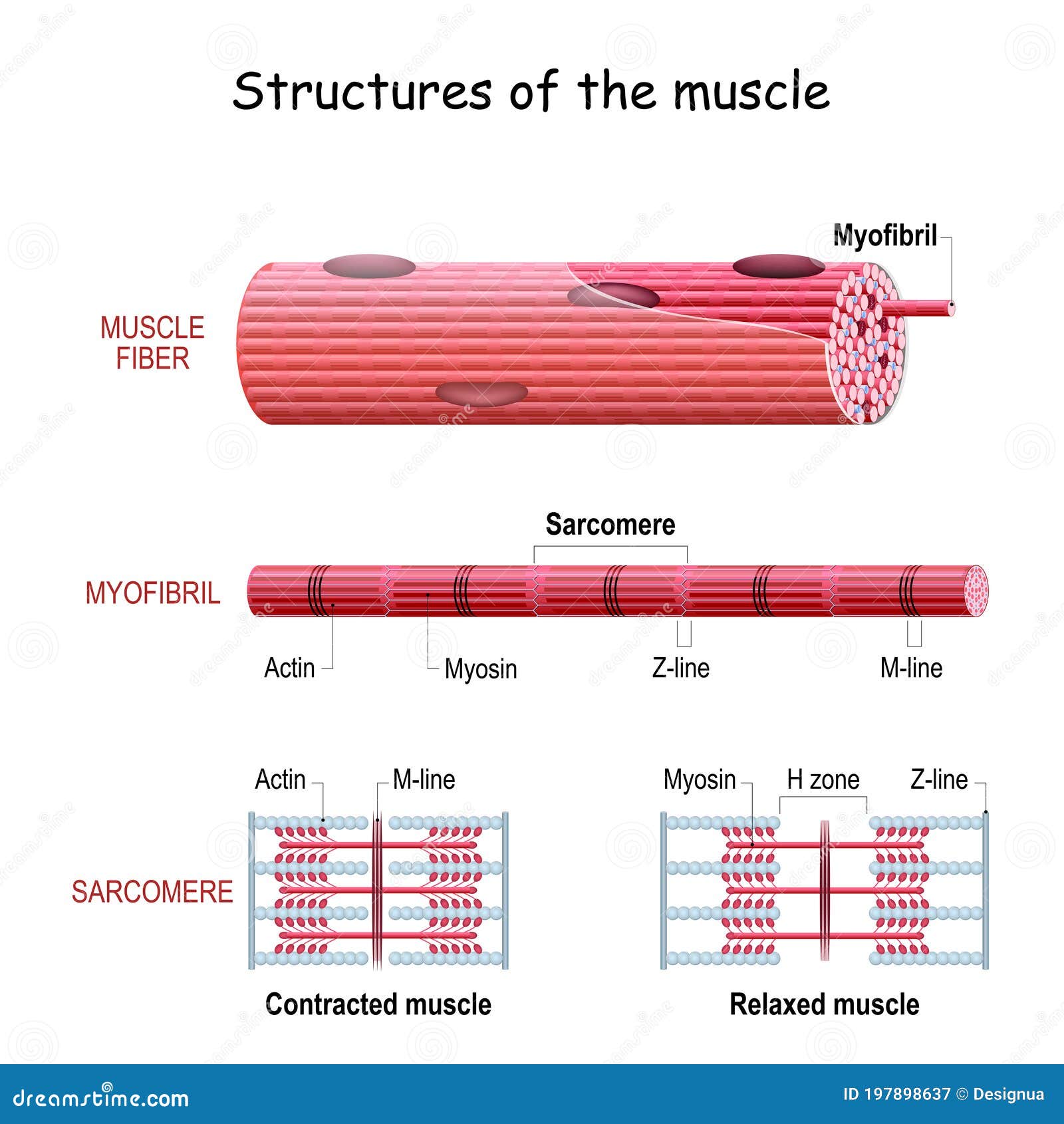
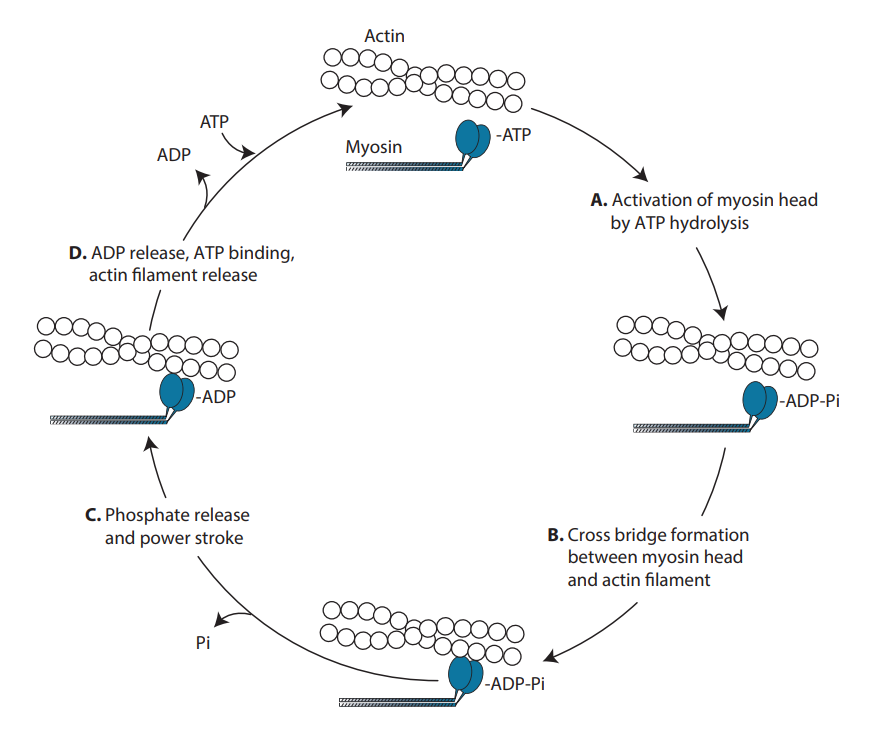
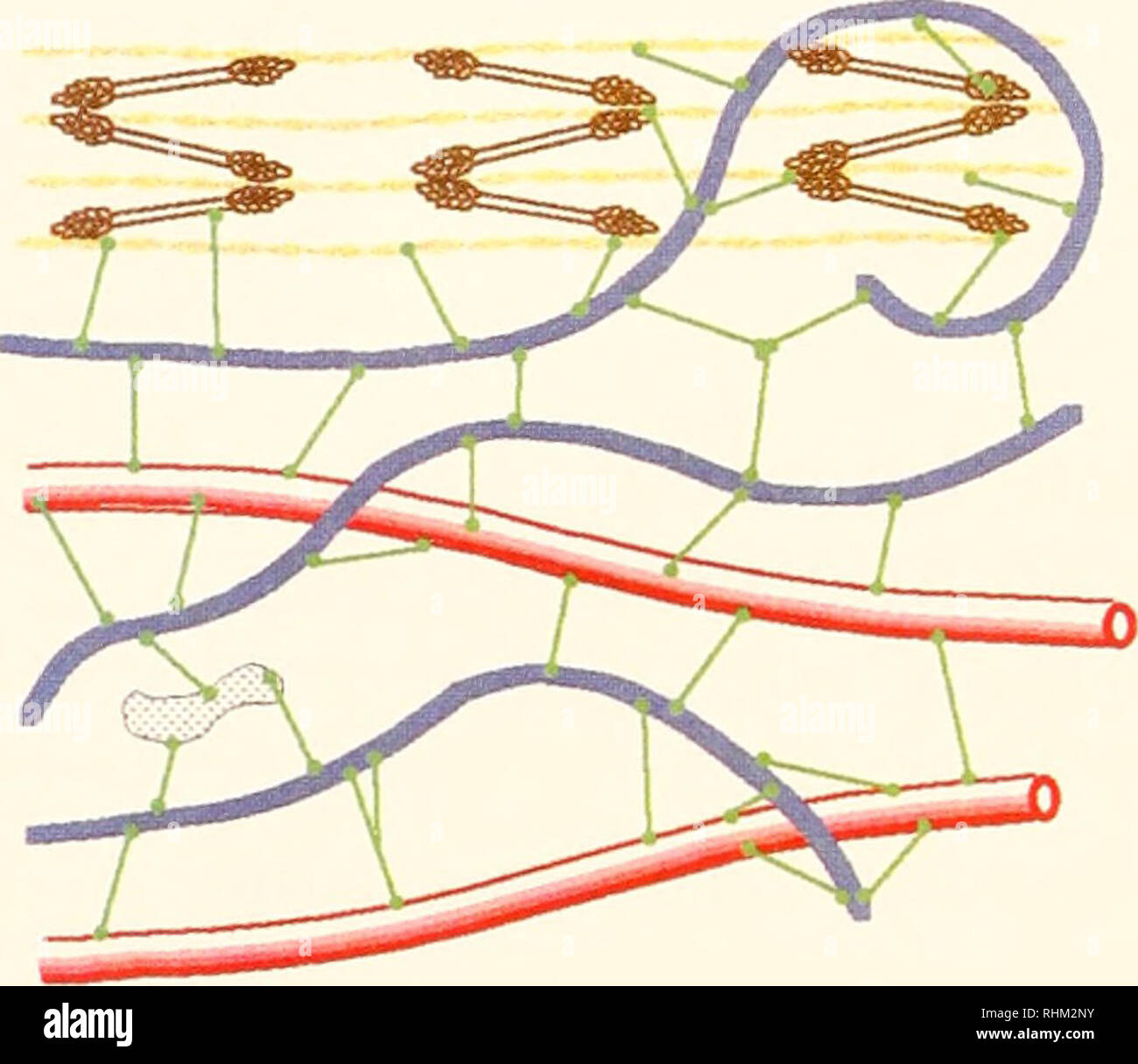
Sarcolemma - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Electron micrograph and schematic diagram of a sarcomere. The darkly staining regions that flank the sarcomere are the Z lines. Myosin-containing thick filaments are in the center of the sarcomere and interact with actin-containing thin filaments by way of myosin heads that protrude from the thick filaments. Thin-filament regulatory proteins, the troponin and tropomyosin, … Myosin isoforms and the mechanochemical cross-bridge cycle ... A minimal ATPase cycle for the actin and myosin cross-bridge cycle. Filled circles represent the actin monomers in a thin filament and the blue shape represents the motor domain of myosin. M is myosin, A is actin, T is ATP, D is ADP and Pi is inorganic phosphate. AMD, for example, represents a complex between actin, myosin and ADP. Learn About Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram | Chegg.com The myosin moves and reaches actin the contracts and releases actin. This cycle goes on repetition and is known as myosin-actin cycling. This cycle is responsible for forming cross bridge and also extending the thick filaments of myosin towards the thin filaments of actin. The contraction of myosin's S1 area is known as the power wave. Labeled Sarcomere Diagram Dodge Durango Wiring Diagram. Start studying UNIT 5: Label the parts of the Sarcomere. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere, including Z lines, actin filaments, myosin filaments with heads, and the resultant light and dark bands.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of (a) An actin filament (b ... Draw a neat labelled diagram of (a) An actin filament (b) Myosin. 0. Myofibrils are made up of 1. Myosin and actin 2. Myosin and troponin 3.
Actin, Myosin, and Cell Movement - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf The myosin and actin filaments overlap in peripheral regions of the A band, whereas a middle region (called the H zone) contains only myosin. The actin filaments are attached at their plus ends to the Z disc, which includes the crosslinking protein α-actinin. The myosin filaments are anchored at the M line in the middle of the sarcomere.
Discovery of ultrafast myosin, its amino acid sequence ... 22.02.2022 · In order for a myosin-bound vesicle to remain associated with actin filaments and to move continuously along the actin filaments, at least one of the myosin MDs on the vesicle must always be strongly bound to the actin filaments. Therefore, the reciprocal of the duty ratio is the lowest number of MDs on a vesicle required for continuous movements of the myosin-bound …
Describe the structure of myosin and actin filaments, with ... 6. In sarcomere, myosin tails are arranged to point towards the centre of the sarcomere and the heads point to the sides of the myofilament band. ii. Actin filament: It is a complex type of contractile protein. It is made up of three components: 1. F actin: It forms the backbone of actin filament. F actin is made up of two helical strands.
Mastering A&P Chapter 3 - Cells: The Living Units Diagram ... During cytokinesis, a ring of actin and myosin filaments contract to form a cleavage furrow and the cell divides in two. The cell cycle is divided into two main parts: interphase and cell division. Interphase is the period in which the cell is performing normal functions and not actively engaged in cell division. Most of your body's cells spend a lot of their time in interphase. Before a cell ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Phosphoinositide-dependentPhosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 - Wikipedia 18607 Ensembl ENSG00000140992 ENSMUSG00000024122 UniProt O15530 Q9Z2A0 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001261816 NM_002613 NM_031268 NM_001080773 NM_001286662 NM_011062 RefSeq (protein) NP_001248745 NP_002604 NP_112558 NP_001074242 NP_001273591 NP_035192 Location (UCSC) Chr 16: 2.54 – 2.6 Mb Chr 17: 24.29 – 24.37 Mb PubMed search Wikidata View/Edit Human View/Edit Mouse In the field of biochemistry ...
Difference Between Actin and Myosin | Definition ... Actin and myosin proteins form filaments arranged in the myofibrils in a longitudinal manner. The main difference between actin and myosin is that actin forms a thin filament whereas myosin forms a thick filament. The sliding over of the two filaments over one another in a series of repetitive events leads to the contraction of the muscles.
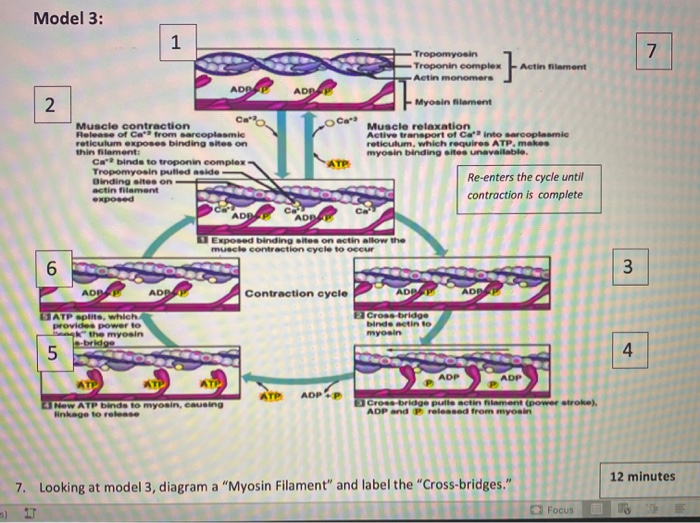
Biology Unit 5 Chapter 11 - Muscle Contraction - Quizlet Myosin head now attaches to the binding site on the actin molecule; Head of myosin changes angle, moving the actin filament along. ADP molecule is released; ATP molecule fixes to the myosin head, causing it to detach from binding site; Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP by ATPase provides the energy for the myosin head to resume its normal position. This ...
Actin/Myosin V. Myosin - Actin Interaction. The interaction of a myosin II S1 subfragment with an actin filament has been modeled. As can be observed, actin binding is mediated by residues in the upper and lower subdomain cleft. Residues 335-372 in an actin monomer of the filament show the most extensive contact with these loops.
Actin and Actin-Binding Proteins Most actin-binding proteins are widely distributed in eukaryotes, and so they arose in an ancient common ancestor. Giardia is an exception as it lacks genes encoding many actin-binding proteins, including myosin, cofilin, formins, and the Arp2/3 complex (Paredez et al. 2011). It might have branched before the actin system was fully developed or ...
› cms › lib0103 b) myosin heads attach to the actin filaments 5 c) ATP is ... energy needed to attach the Myosin head to the Actin, forming a cross-bridge. Ca2+ binds to Troponin, changing its shape, which moves the Tropomyosin from the active site of the Actin. This is repeated all along the myofibril. The Myosin detaches from the Actin and the cross-bridge is broken when another ATP molecule binds to the Myosin head.
study.com › learn › lessonAxial Skeleton Bones Function | What is the Axial Skeleton ... Oct 22, 2021 · Below is a diagram of the axial skeleton. The skull is located at the top while the laryngeal skeleton is found in the throat. ... Actin and Myosin Bonding 6:11 What Is the Muscular System ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Myosin_light-chain_kinaseMyosin light-chain kinase - Wikipedia Myosin light chain pulls the actin stress fiber attached to the cadherin, resisting the force of the adjacent cell's cadherin. However, when the inward pulling force of the actin stress fiber becomes greater than the outward pulling force of the cell adhesion molecules due to an overactive MYLK, tissues can become slightly pulled apart and ...
Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin Antibody (14-9760-82) Actin filaments interact with myosin to assist in muscle contraction as well as aiding in cell motility and cytokinesis. Smooth muscle actin is found on smooth muscle vessel walls, gut wall, myometrium, myoepithelial cells in breast and salivary glands. Defects in the smooth muscle actin gene cause aortic aneurysm familial thoracic type 6. Actin isoforms differ slightly in their N …
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle ... - Online Biology Notes 1. Blocking of myosin head: Actin and myosin overlaps each other forming cross bridge. The cross bridge is active only when myosin head attached like hook to the actin filament. When muscle is at rest, the overlapping of actin filament to the myosin head is blocked by tropomyosin. The actin myofilament is said to be in OFF position. 2.
IB DP Biology Topic 11: Animal physiology: 11.2 Movement ... 11.2 S 2 Drawing labelled diagrams of the structure of a sarcomere. Include Z lines, actin filaments, myosin filaments with heads, and the resultant light and dark bands. Draw a diagram of the structure of a sarcomere. Label a sarcomere diagram, including Z lines, actin filaments, myosin filaments with heads and the resultant light and dark bands.
Actin Myosin Interaction - SmartDraw Actin Myosin Interaction. Create healthcare diagrams like this example called Actin Myosin Interaction in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own.
PDF Structure and Function of Actin & Myosin Structure and Function of Actin & Myosin Outline: Actin Structure and Regulation Myosin Structure and Regulation Functions of Actin and Myosin in Cells Paper: Control of microtubule dynamics by the antagonistic activities of XMAP215 and XKCM1 in Xenopus egg extracts. Stationary cell - stress fibers.
Actin & Myosin - SlideShare 4. Myosin Myosin is a muscle protein constisting of head, neck and tail domains The head domain binds the filamentous actin, and uses ATP hydrolysis to generate force and to "walk" along the filament towards the barbed (+) . The neck domain acts as a linker and as a lever arm for transducing force generated by the catalytic motor domain.
Muscle Contraction & Sliding Filament Theory - TeachPE.com The diagram above shows a partially contracted muscle where there is more overlapping of the myosin and actin with lots of potential for cross bridges to form. The I - bands and H - zone is shortened. Fully Contracted Muscle The diagram above shows a fully contracted muscle with lots of overlap between the actin and myosin.
Major Differences Between Actin and Myosin - BYJUS Actin and myosin are two protein molecules present in muscles and are mainly involved in the contraction of the muscle in both humans and animals. Both actin and myosin function by controlling the voluntary muscular movements within the body, along with the regulatory proteins known as troponin, tropomyosin and meromyosin. Actin and myosin proteins build filaments, …
Myosin Function & Structure | What is Myosin? - Video ... This diagram shows how actin filaments and myosin arrange themselves in the myofibril. Actin filaments create the thin filaments (gray), while myosin molecules arrange themselves into thick ...
Actin and Myosin - Biology Dictionary Actin and myosin are both proteins that are found in all types of muscle tissue. Myosin forms thick filaments (15 nm in diameter) and actin forms thinner filaments (7nm in diameter). Actin and myosin filaments work together to generate force.

























0 Response to "38 actin and myosin diagram"
Post a Comment