36 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q 2: A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. B. resources are underallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. C. productive efficiency is achieved, but resources are underallocated to this product. 10. On a project schedule network diagram, leads and lags are used to define the relationships between activities. These leads and lags indicate either acceleration or delay, respectively, of the successor activity. If a team member on your project indicates FF+3 on the network diagram, what does that notation indicate? a.
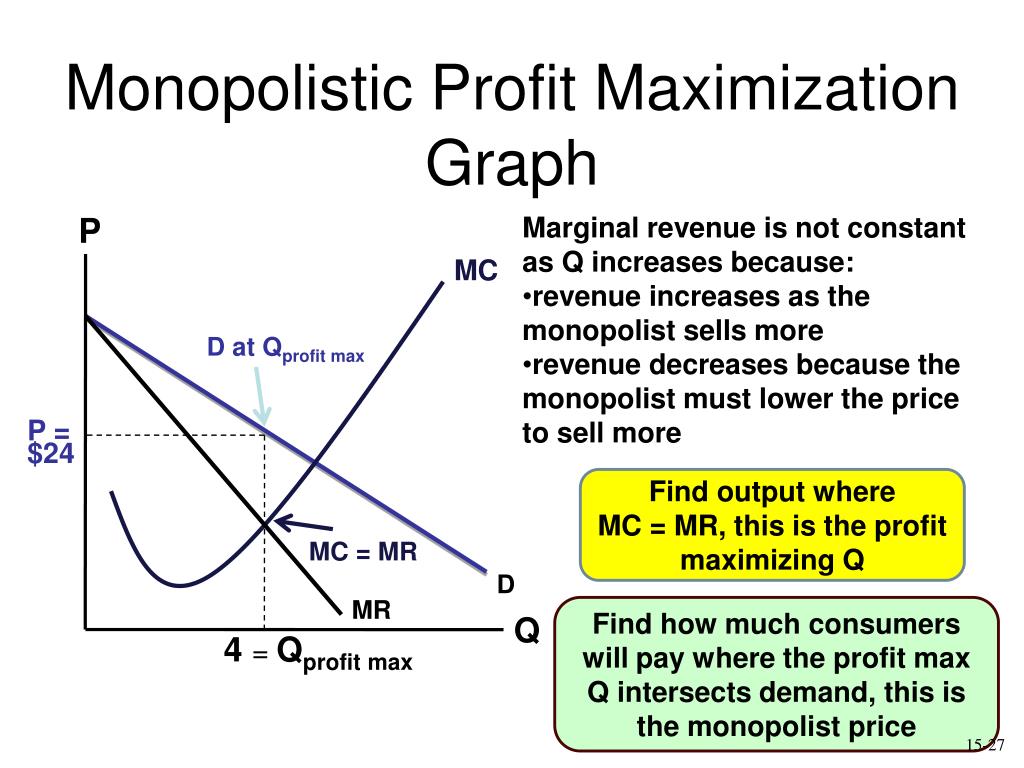
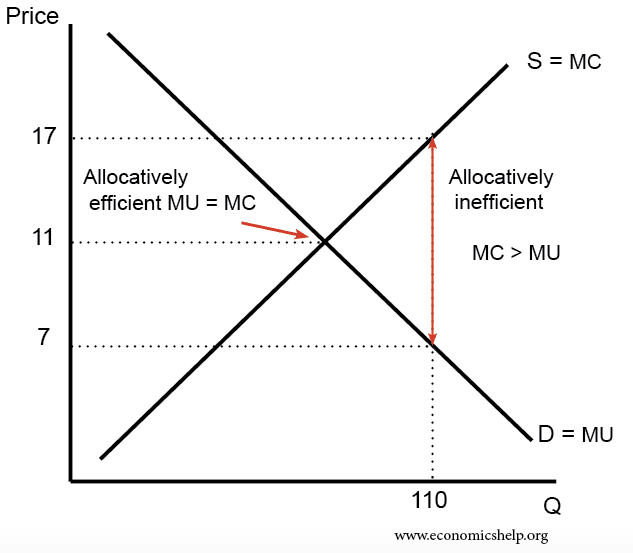
(MR=MC) When produced less than Output of equilibrium quantity (Q*), as the red part showed, MR is greater than MC. The firm produce extra output because the revenue of gaining is more than the cost to pay. So, total profit will increase. However, if the output level is greater than Q*, MR

Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
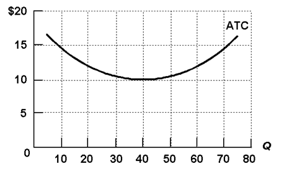
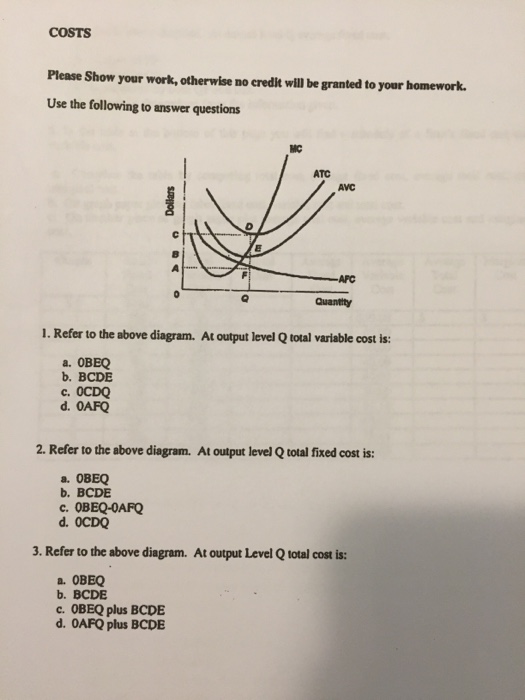
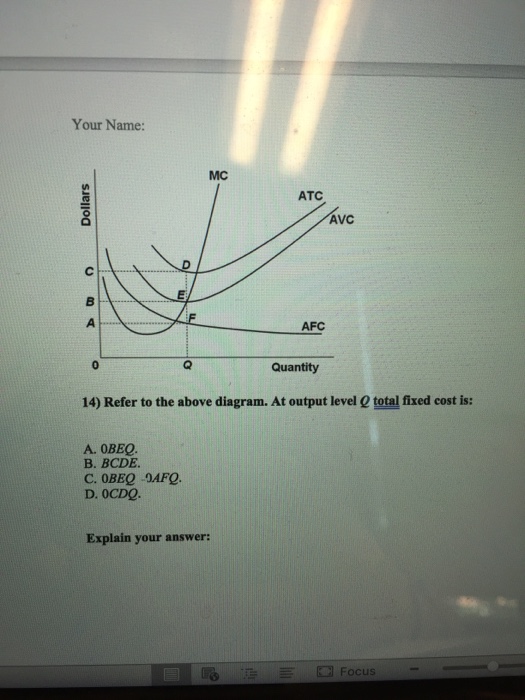
Page: 157-158 Subtopic: Marginal cost Type: Graphic Q38.Refer to the short-run production and cost data above. The curves of Figures A and B suggest that: A) marginal product and marginal cost reach their maximum points at the same output. B) marginal cost reaches a minimum where marginal product is at its maximum. C) marginal cost and marginal product reach their minimum points at the same ... Refer to the above diagram at output level q total. TVC = Q x AVC = OBEQ. A is correct. fixed cost: A) is equal to EF. B) is equal to QE. C) is measured by both QF and ED. D) cannot be determined from the information given. This is the correct answer, C, since the height of the AFC or the height between ATC and AVC at Q is a measure of AFC. 23. Aggregate supply refers to the total output of goods and services in the economy. Aggregate supply is determined by the level of inputs available to produce goods and services, and how efficiently these inputs are used. The main inputs into production are labour and capital.
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. b. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. c. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. d. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not. 6. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B. price P3 and producing output Q3. C. price P2 and producing output Q2. D. price P1 and producing output Q1. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. both productive and allocative efficiency is achieved. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. b. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. c. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. d. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not.
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. Refer to the diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: is measured by both QF and ED. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and has average variable costs of $150. The firm's total fixed costs are: $5,000. Refer to the diagram above. By producing at output level Q: ... Refer to the diagram above. At output level Q1: A. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. 14. Refer to the diagram above. At output level Q2: A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. The outputs from both comparators are connected to the two inputs of the flip-flop which in turn produces either a “HIGH” or “LOW” level output at Q based on the states of its inputs. The output from the flip-flop is used to control a high current output switching stage to drive the connected load producing either a “HIGH” or “LOW ...
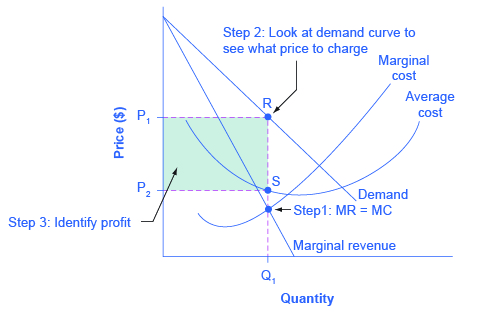
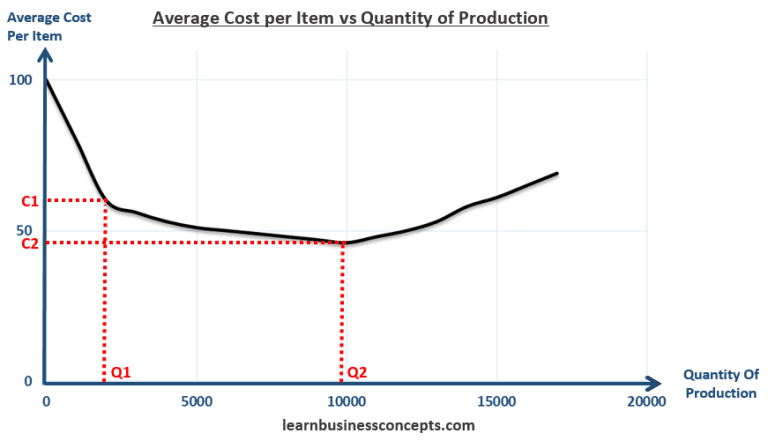
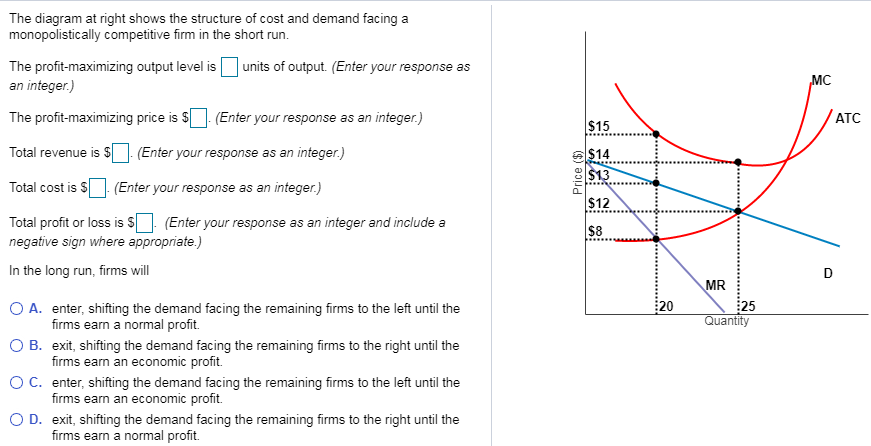
Step 1. Draw a graph of a supply curve for pizza. Pick a quantity (like Q 0). If you draw a vertical line up from Q 0 to the supply curve, you will see the price the firm chooses. An example is shown in Figure 7. Figure 7. Supply Curve. The supply curve can be used to show the minimum price a firm will accept to produce a given quantity of ... MC ATC Price MR Q, O Quantity Q, Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not. Aug 10, 2021 · Incorporating Q Factor. Below's another circuit you would like to know about. The circuit basically makes use of the “Q factor” of the tank network achieved from the coil and the capacitor for generating a relatively high voltage. This stepped up potential attributes the circuit with a rather longer range of transmission. Refer to Figure 15-4. If the monopoly firm is currently producing Q3 units of output, then a decrease in output will necessarily cause profit to ~ decrease. ~ increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q2. ~ remain unchanged. ~ increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q1.
If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. 3. earn an economic profit. 4. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. 10. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: 1. neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. 2.
Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: O A. unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. O B. unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. O C. obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. O D. obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently.
Economics. Economics questions and answers. MC 3 ATC 0 MR Q, Qa2 Quantity Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q O productive efficiency is achieved. but allocative efficiency ls not. D neither productive nor allocetive etficiency s achieved O aflocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not O both productive ...
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost. is measured by both QF and ED. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q. ... Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct.
Refer to the diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: A) attainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently. B) unattainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. C) unattainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. D) attainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources.
Aggregate supply refers to the total output of goods and services in the economy. Aggregate supply is determined by the level of inputs available to produce goods and services, and how efficiently these inputs are used. The main inputs into production are labour and capital.
Refer to the above diagram at output level q total. TVC = Q x AVC = OBEQ. A is correct. fixed cost: A) is equal to EF. B) is equal to QE. C) is measured by both QF and ED. D) cannot be determined from the information given. This is the correct answer, C, since the height of the AFC or the height between ATC and AVC at Q is a measure of AFC. 23.
Page: 157-158 Subtopic: Marginal cost Type: Graphic Q38.Refer to the short-run production and cost data above. The curves of Figures A and B suggest that: A) marginal product and marginal cost reach their maximum points at the same output. B) marginal cost reaches a minimum where marginal product is at its maximum. C) marginal cost and marginal product reach their minimum points at the same ...

Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,
Page: 157-158 Subtopic: Marginal cost Type: Graphic Q38.Refer to the short-run production and cost data above. The curves of Figures A and B suggest that: A) marginal product and marginal cost reach their maximum points at the same output. B) marginal cost reaches a minimum where marginal product is at its maximum. C) marginal cost and marginal product reach their minimum points at the same ... Refer to the above diagram at output level q total. TVC = Q x AVC = OBEQ. A is correct. fixed cost: A) is equal to EF. B) is equal to QE. C) is measured by both QF and ED. D) cannot be determined from the information given. This is the correct answer, C, since the height of the AFC or the height between ATC and AVC at Q is a measure of AFC. 23. Aggregate supply refers to the total output of goods and services in the economy. Aggregate supply is determined by the level of inputs available to produce goods and services, and how efficiently these inputs are used. The main inputs into production are labour and capital.
Refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. b. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. c. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. d. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not. 6. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B. price P3 and producing output Q3. C. price P2 and producing output Q2. D. price P1 and producing output Q1. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. C. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. D. both productive and allocative efficiency is achieved. Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q: a. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. b. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. c. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. d. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not.
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q. A. productive efficiency is achieved but allocative efficiency ls not. B. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. Refer to the diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: is measured by both QF and ED. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and has average variable costs of $150. The firm's total fixed costs are: $5,000. Refer to the diagram above. By producing at output level Q: ... Refer to the diagram above. At output level Q1: A. neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved. 14. Refer to the diagram above. At output level Q2: A. resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. The outputs from both comparators are connected to the two inputs of the flip-flop which in turn produces either a “HIGH” or “LOW” level output at Q based on the states of its inputs. The output from the flip-flop is used to control a high current output switching stage to drive the connected load producing either a “HIGH” or “LOW ...
Step 1. Draw a graph of a supply curve for pizza. Pick a quantity (like Q 0). If you draw a vertical line up from Q 0 to the supply curve, you will see the price the firm chooses. An example is shown in Figure 7. Figure 7. Supply Curve. The supply curve can be used to show the minimum price a firm will accept to produce a given quantity of ... MC ATC Price MR Q, O Quantity Q, Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved. allocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not. productive efficiency is achieved, but allocative efficiency is not. Aug 10, 2021 · Incorporating Q Factor. Below's another circuit you would like to know about. The circuit basically makes use of the “Q factor” of the tank network achieved from the coil and the capacitor for generating a relatively high voltage. This stepped up potential attributes the circuit with a rather longer range of transmission. Refer to Figure 15-4. If the monopoly firm is currently producing Q3 units of output, then a decrease in output will necessarily cause profit to ~ decrease. ~ increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q2. ~ remain unchanged. ~ increase as long as the new level of output is at least Q1.
If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. 3. earn an economic profit. 4. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. 10. Refer to the above diagram. By producing output level Q: 1. neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. 2.
Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: O A. unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. O B. unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. O C. obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. O D. obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently.
Economics. Economics questions and answers. MC 3 ATC 0 MR Q, Qa2 Quantity Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q O productive efficiency is achieved. but allocative efficiency ls not. D neither productive nor allocetive etficiency s achieved O aflocative efficiency is achieved, but productive efficiency is not O both productive ...
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost. is measured by both QF and ED. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q. ... Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct.
Refer to the diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: A) attainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently. B) unattainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. C) unattainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. D) attainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources.
Aggregate supply refers to the total output of goods and services in the economy. Aggregate supply is determined by the level of inputs available to produce goods and services, and how efficiently these inputs are used. The main inputs into production are labour and capital.
Refer to the above diagram at output level q total. TVC = Q x AVC = OBEQ. A is correct. fixed cost: A) is equal to EF. B) is equal to QE. C) is measured by both QF and ED. D) cannot be determined from the information given. This is the correct answer, C, since the height of the AFC or the height between ATC and AVC at Q is a measure of AFC. 23.
Page: 157-158 Subtopic: Marginal cost Type: Graphic Q38.Refer to the short-run production and cost data above. The curves of Figures A and B suggest that: A) marginal product and marginal cost reach their maximum points at the same output. B) marginal cost reaches a minimum where marginal product is at its maximum. C) marginal cost and marginal product reach their minimum points at the same ...













.png)

0 Response to "36 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q,"
Post a Comment